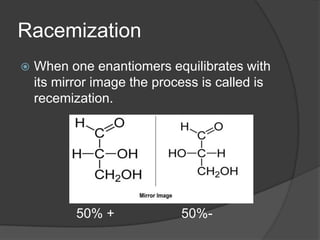
Enantiomers are mirror images of each other that cannot be superimposed. They exist as two different forms with opposite optical rotation. The R/S system is used to name the enantiomers based on the chiral center. Chiral compounds have an asymmetric carbon atom connected to four different groups. Enantiomers interact differently with plane-polarized light, causing optical rotation that can be measured with a polarimeter. A racemic mixture contains equal amounts of both enantiomers, resulting in no net optical rotation. Resolution separates enantiomers from a racemic mixture.