The document discusses process management and the First Come First Serve (FCFS) CPU scheduling algorithm. It covers:
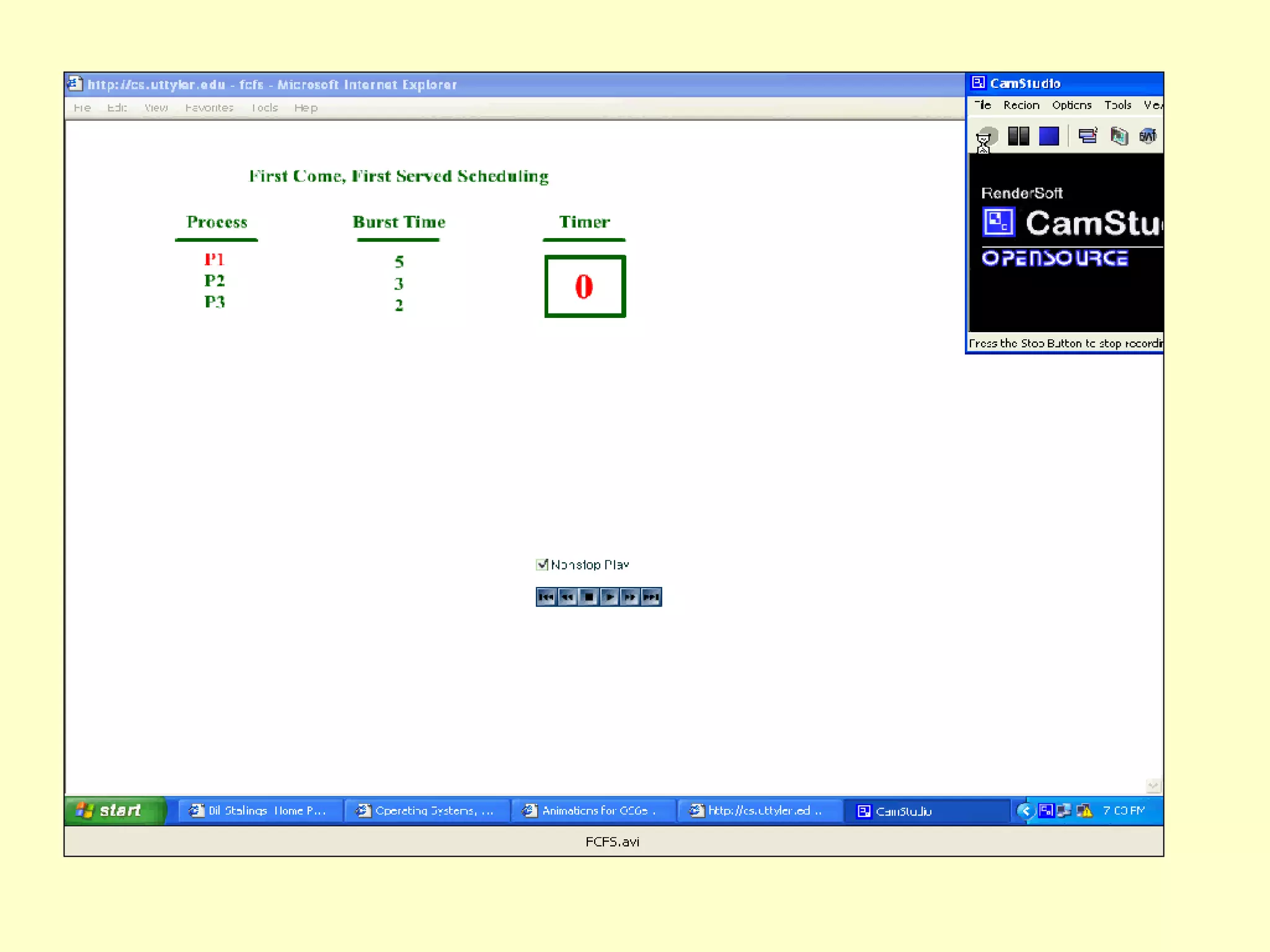
1) FCFS is the simplest scheduling algorithm that allocates the CPU to the process that requests it first. It is implemented using a FIFO queue where new processes are added to the tail.
2) FCFS can result in long waiting times for processes. An example is provided where the average waiting time is 17ms.
3) FCFS is non-preemptive and not suitable for time-sharing systems as it does not allow regular intervals of CPU allocation between users.