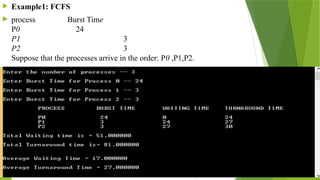
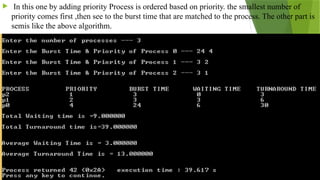
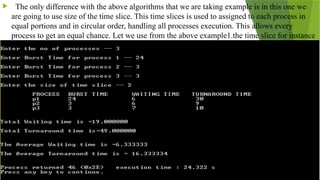
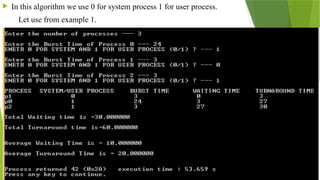
The document outlines various CPU scheduling algorithms, including FCFS, SJF, priority, round robin, and multi-level queue scheduling. Each algorithm is explained with its implementation steps, goals, and how to calculate waiting and turnaround times for processes. Additionally, the document presents examples to illustrate these concepts in practice.