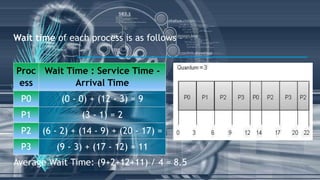
This document discusses CPU scheduling algorithms. It describes priority and round robin scheduling. Priority scheduling allocates processes priorities and executes the highest priority process first. Round robin scheduling gives each process a fixed time quantum to execute before switching to the next process, ensuring fair allocation of CPU time. The document compares the advantages and disadvantages of priority and round robin scheduling, such as indefinite blocking of lower priority processes with priority scheduling.