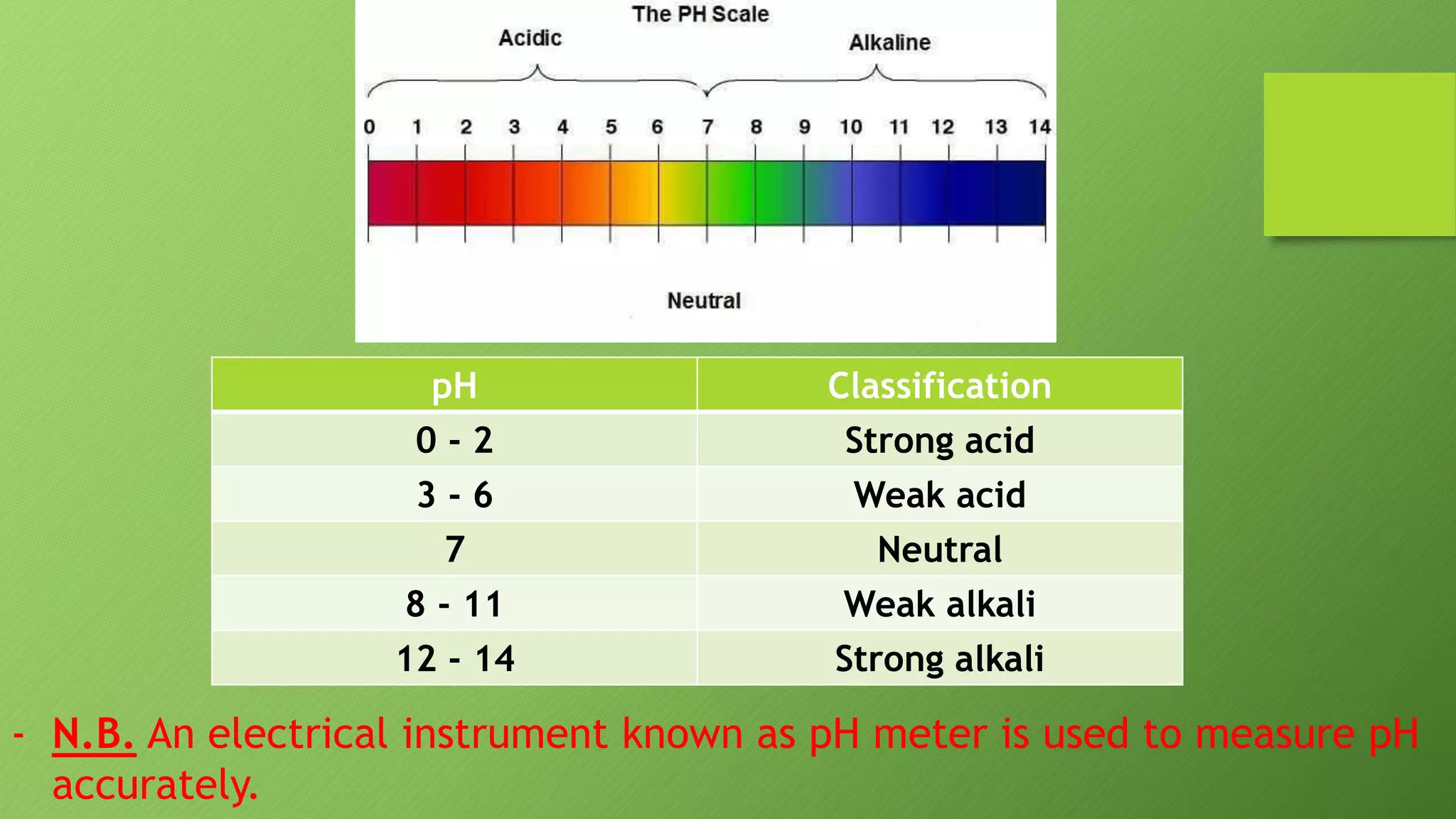
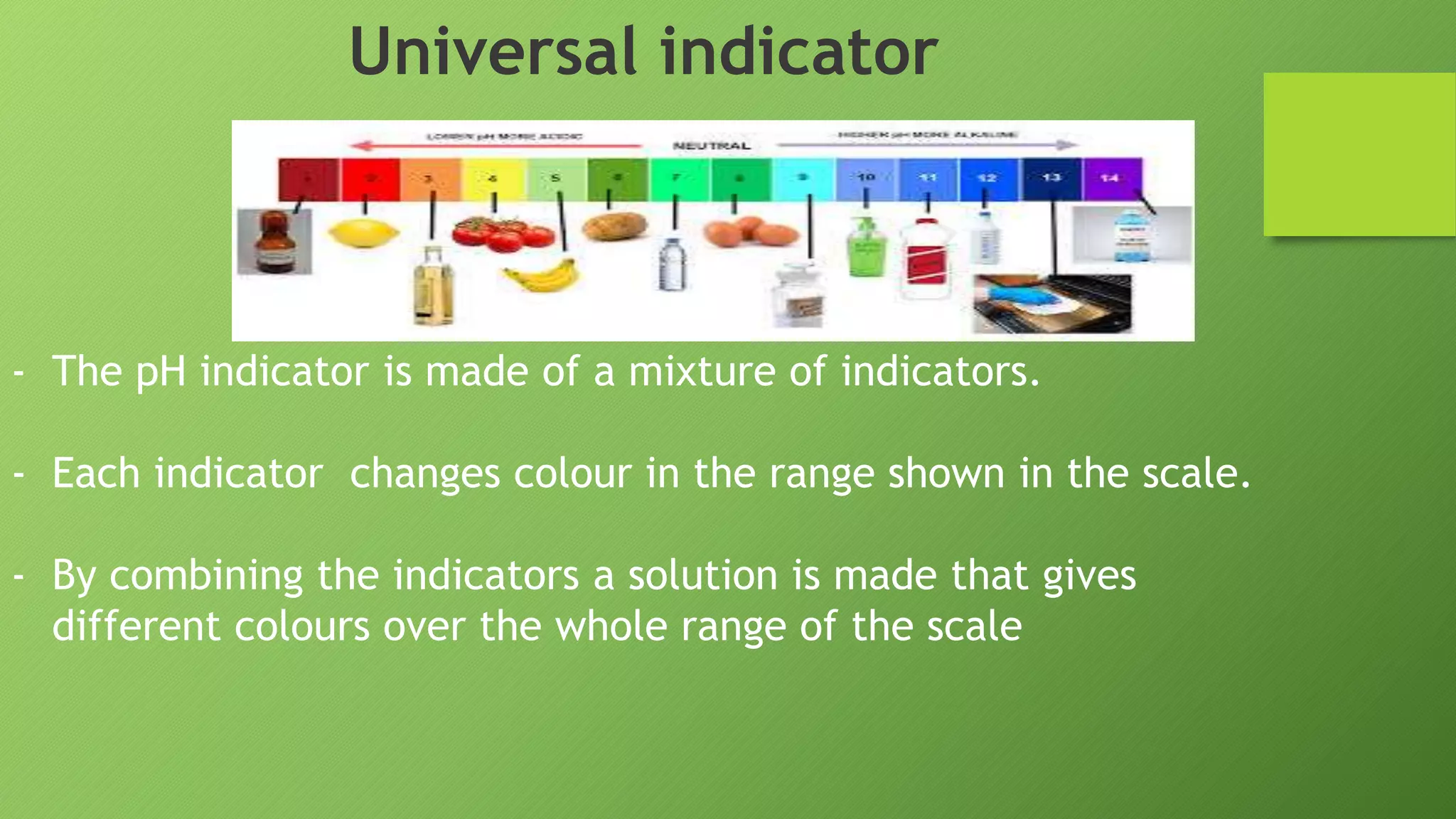
This document discusses acids and alkalis and how they can be detected and measured. It explains that Robert Boyle discovered plant juices like red cabbage juice and litmus could detect acids and alkalis through color changes. The juice would turn red in acids and green in alkalis. This led to the development of pH indicators that scientists now use to measure the strength of acids and alkalis on the pH scale, from 0-14, invented by Soren Sorensen. Common indicators and their color changes in acids and alkalis are also described.