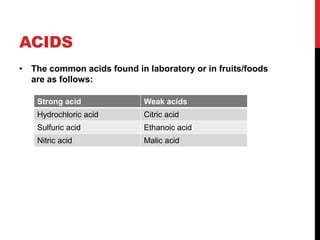
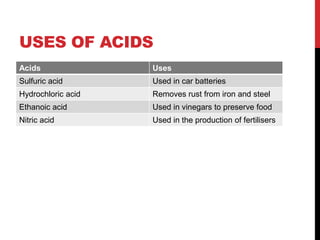
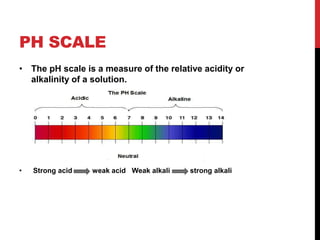
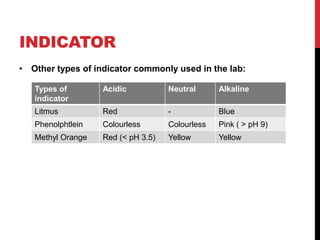
This document discusses acids and alkalis. It defines strong and weak acids and lists some common examples. It explains that acids have properties like sour taste and ability to turn litmus paper red. The document outlines how acids react with metals, carbonates, and alkalis. Common uses of sulfuric, hydrochloric, ethanoic, and nitric acids are provided. Properties and uses of common alkalis like sodium hydroxide are also described. The document introduces the pH scale and how indicators like universal indicator and litmus paper can be used to test the acidity or alkalinity of solutions.