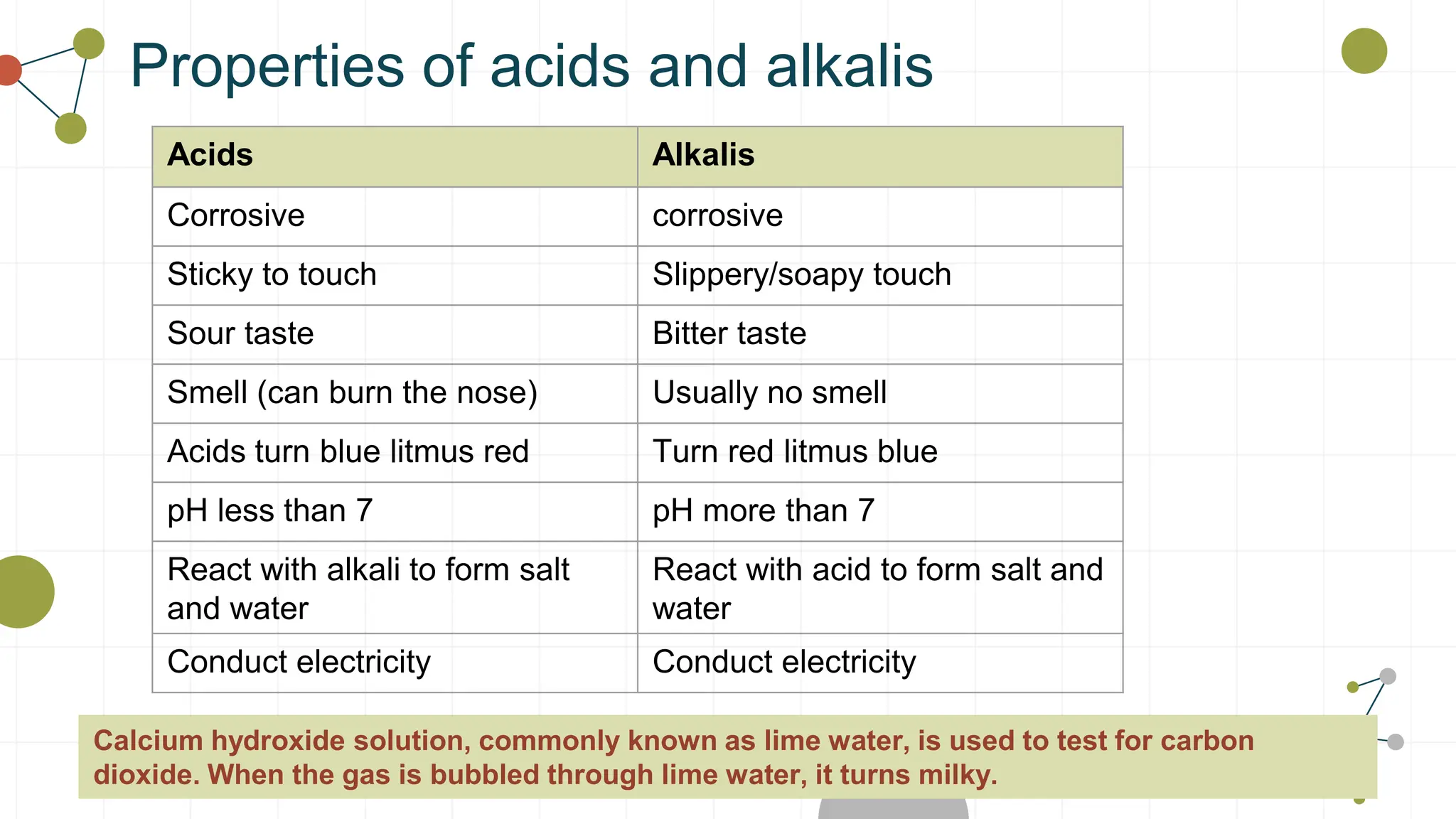
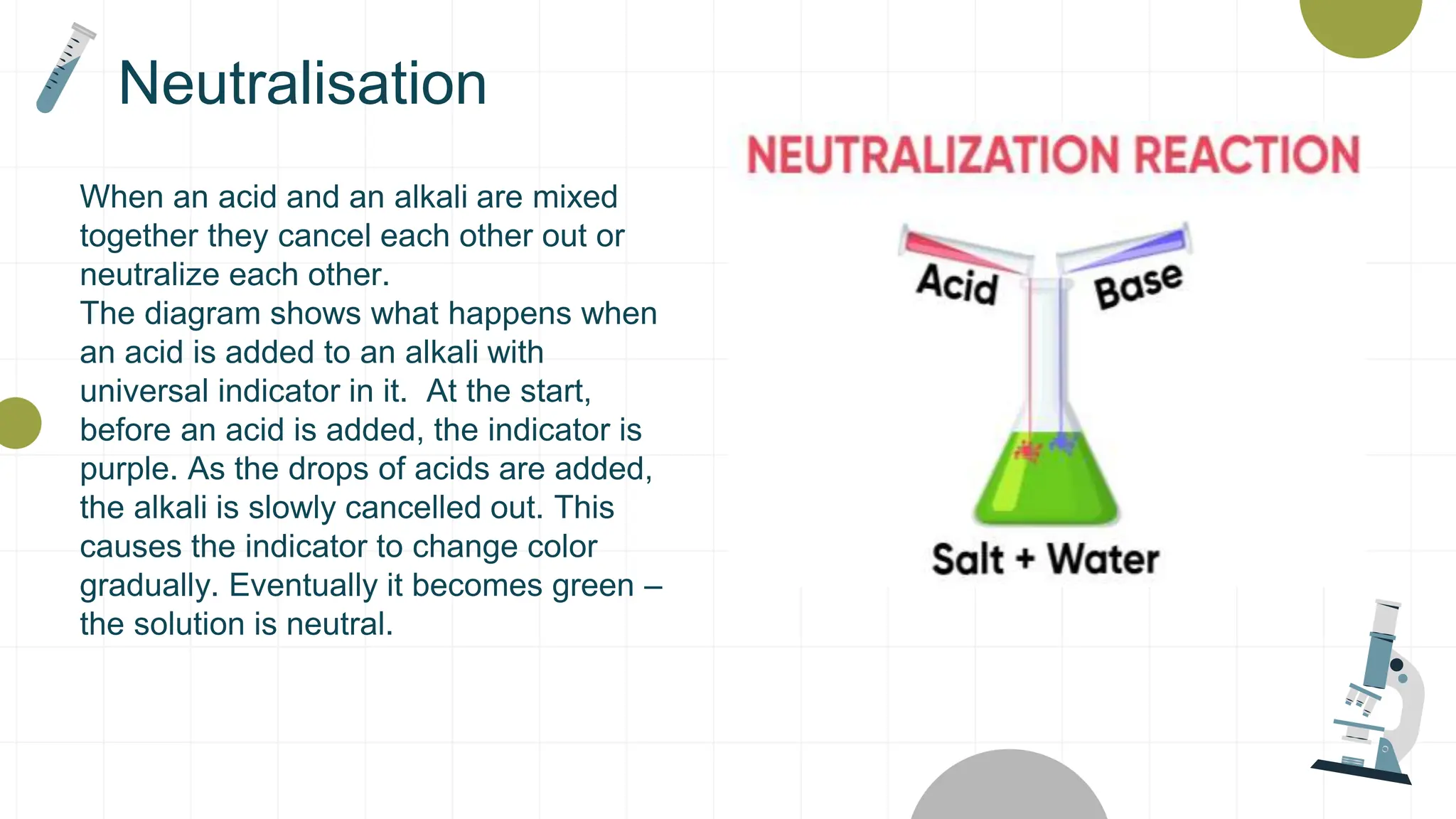
The document covers the properties and reactions of acids and alkalis, including their characteristics, common examples, and the use of indicators to determine pH levels. It explains the process of neutralization, how alkalis can treat excess stomach acid and support dental health by counteracting acidic conditions. Safety guidelines for handling these substances are also provided.