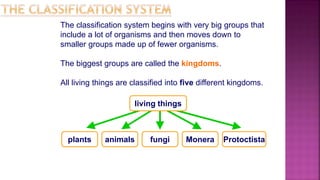
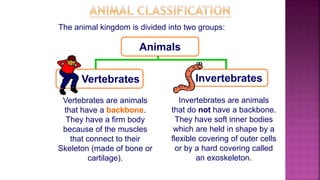
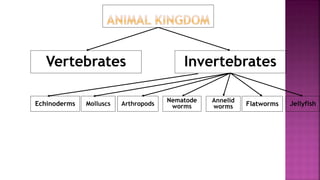
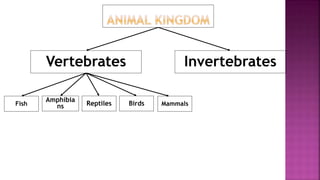
This document discusses the classification of living things. It explains that organisms can be classified into groups like kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus and species based on their common features. The classification system moves from the biggest groups that include many organisms to smaller groups with fewer organisms. All living things are divided into five kingdoms - plants, protoctista, animals, monera and fungi. Within the animal kingdom, organisms are divided into vertebrates and invertebrates based on whether they have a backbone or not. Examples of invertebrate groups include arthropods, annelids, nematodes, jellyfish and flatworms. Vertebrate groups include mammals, fish, birds,