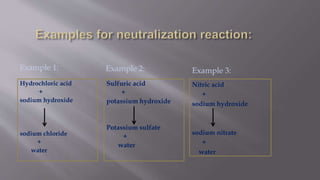
Neutralization is a chemical reaction between an acid and a base that produces a salt and water. Common examples of neutralization include:
1. Hydrochloric acid reacting with sodium hydroxide to produce sodium chloride and water.
2. Sodium bicarbonate reacting with hydrochloric acid to produce sodium chloride, carbon dioxide, and water.
3. Baking powder containing an acid and sodium bicarbonate that undergoes neutralization when mixed with water to release carbon dioxide and leaven baked goods.