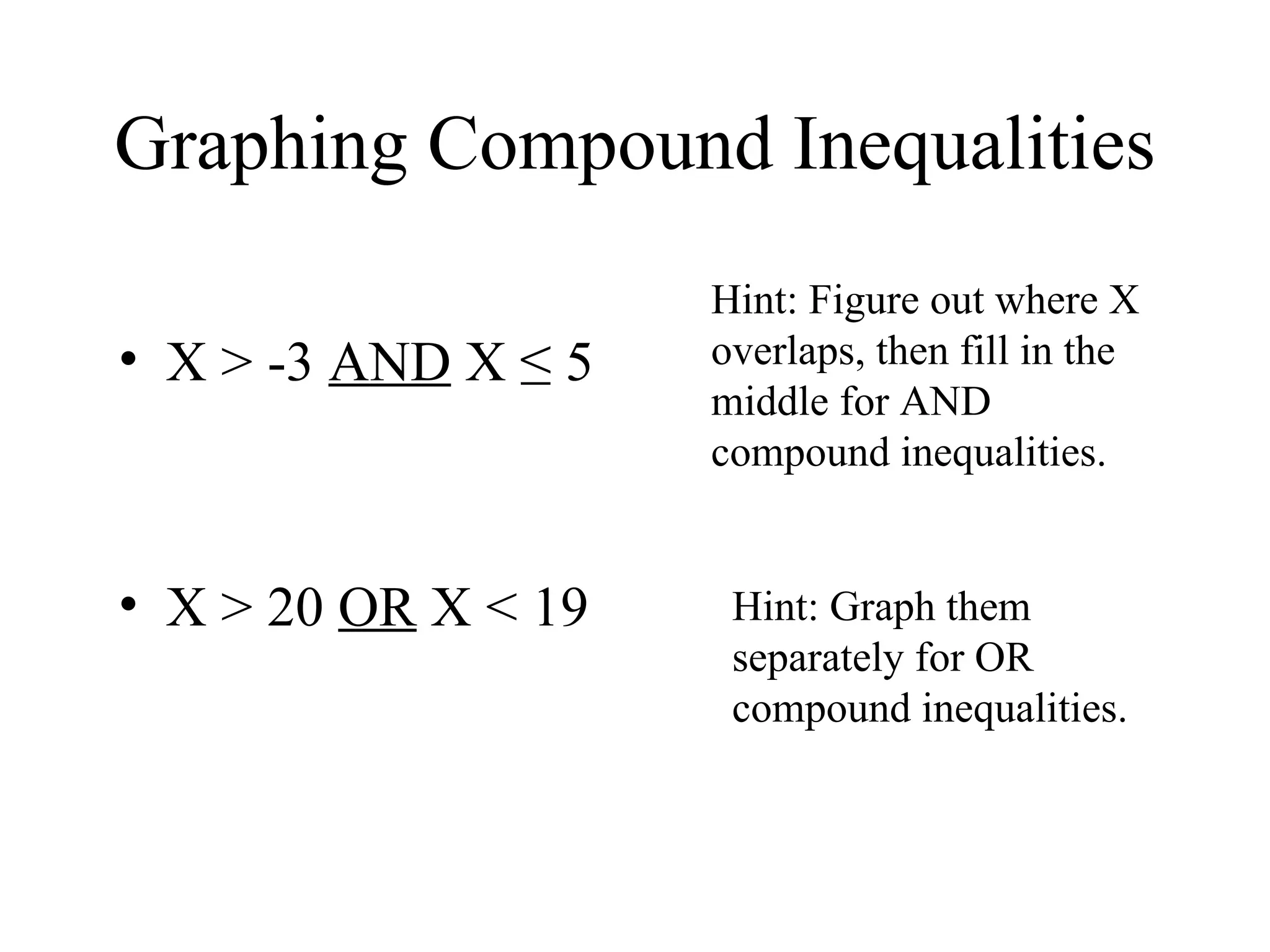
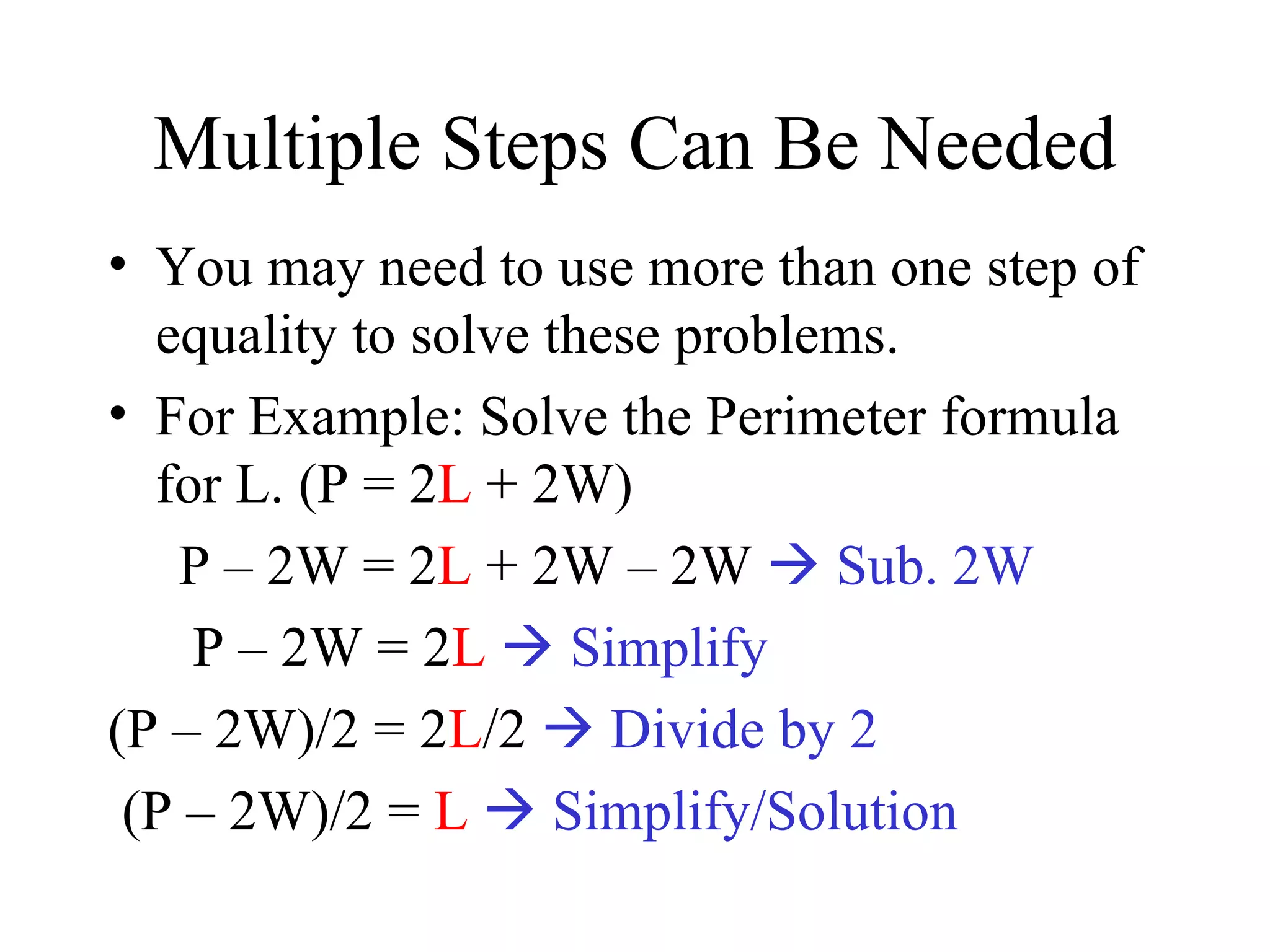
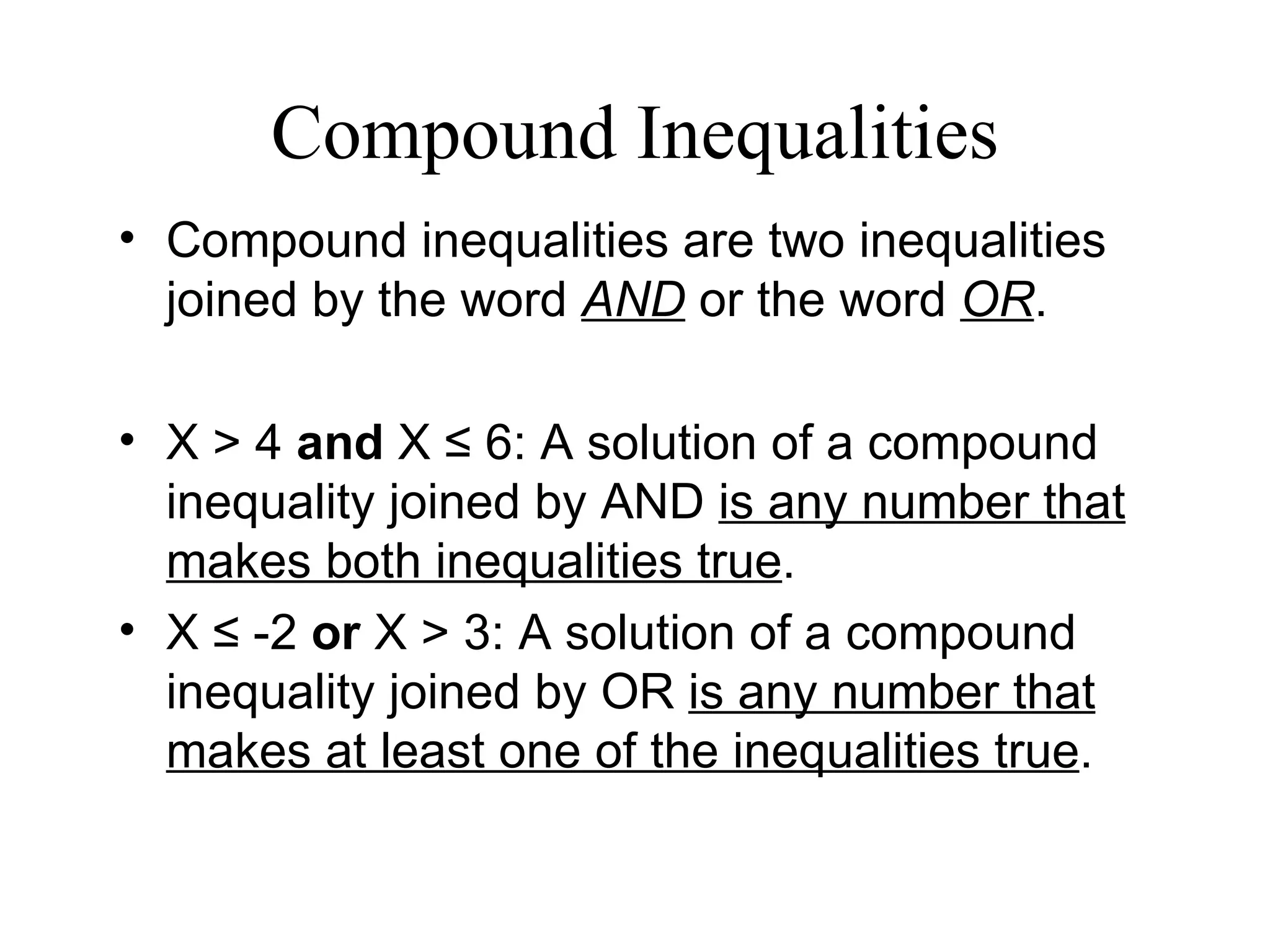The document discusses transforming formulas by rearranging them to solve for different variables. It provides examples of solving formulas for length, area, perimeter, and others. It emphasizes that when transforming a formula, the same operations must be applied to both sides. The document also gives real-world examples of using transformed formulas to solve for time, temperature, and number of hits in baseball.