This document summarizes key concepts in motion, including:
1) It defines types of velocity such as uniform, variable, and instantaneous velocity.
2) It also defines types of acceleration such as positive and negative acceleration as well as instantaneous acceleration.
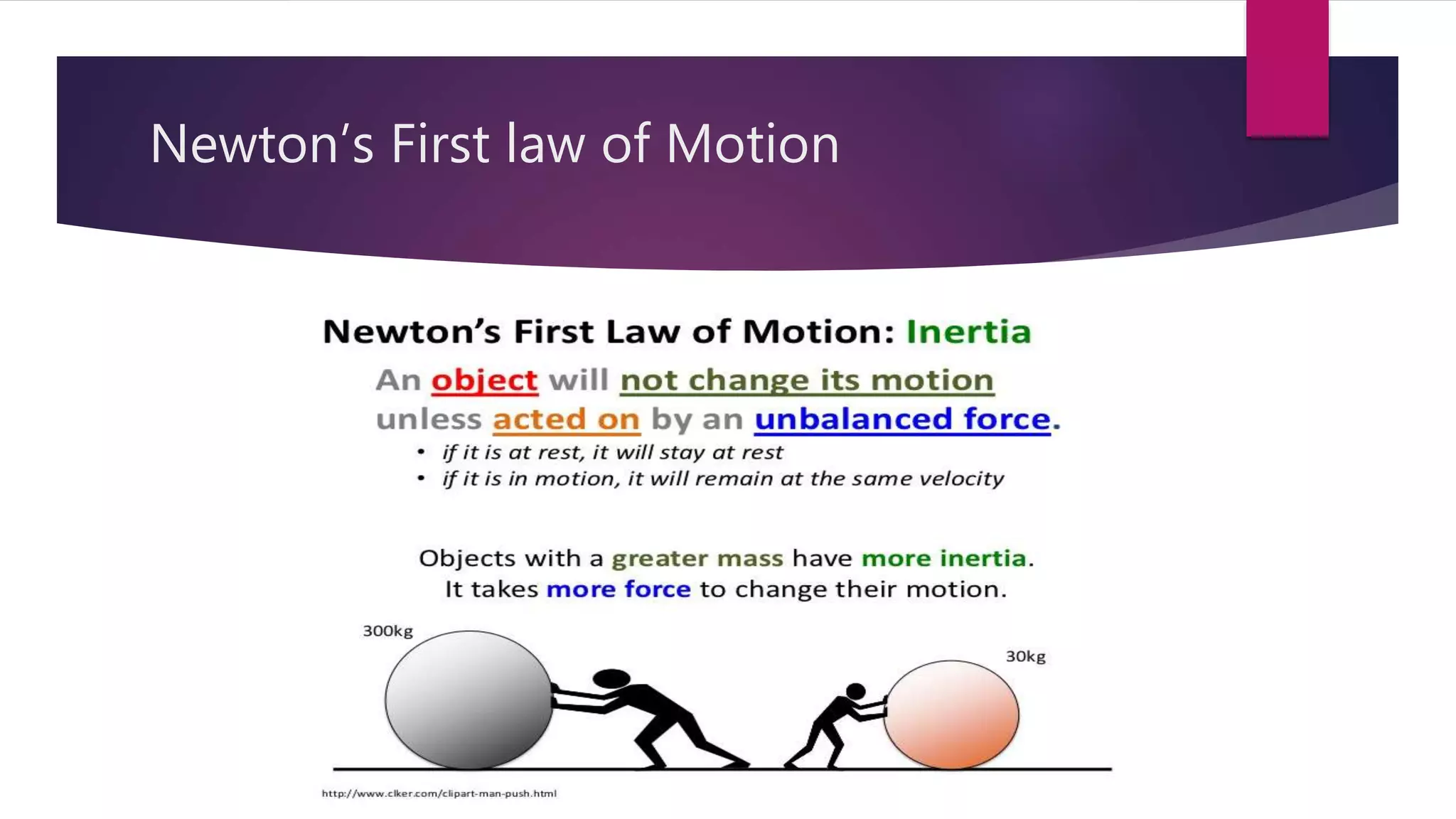
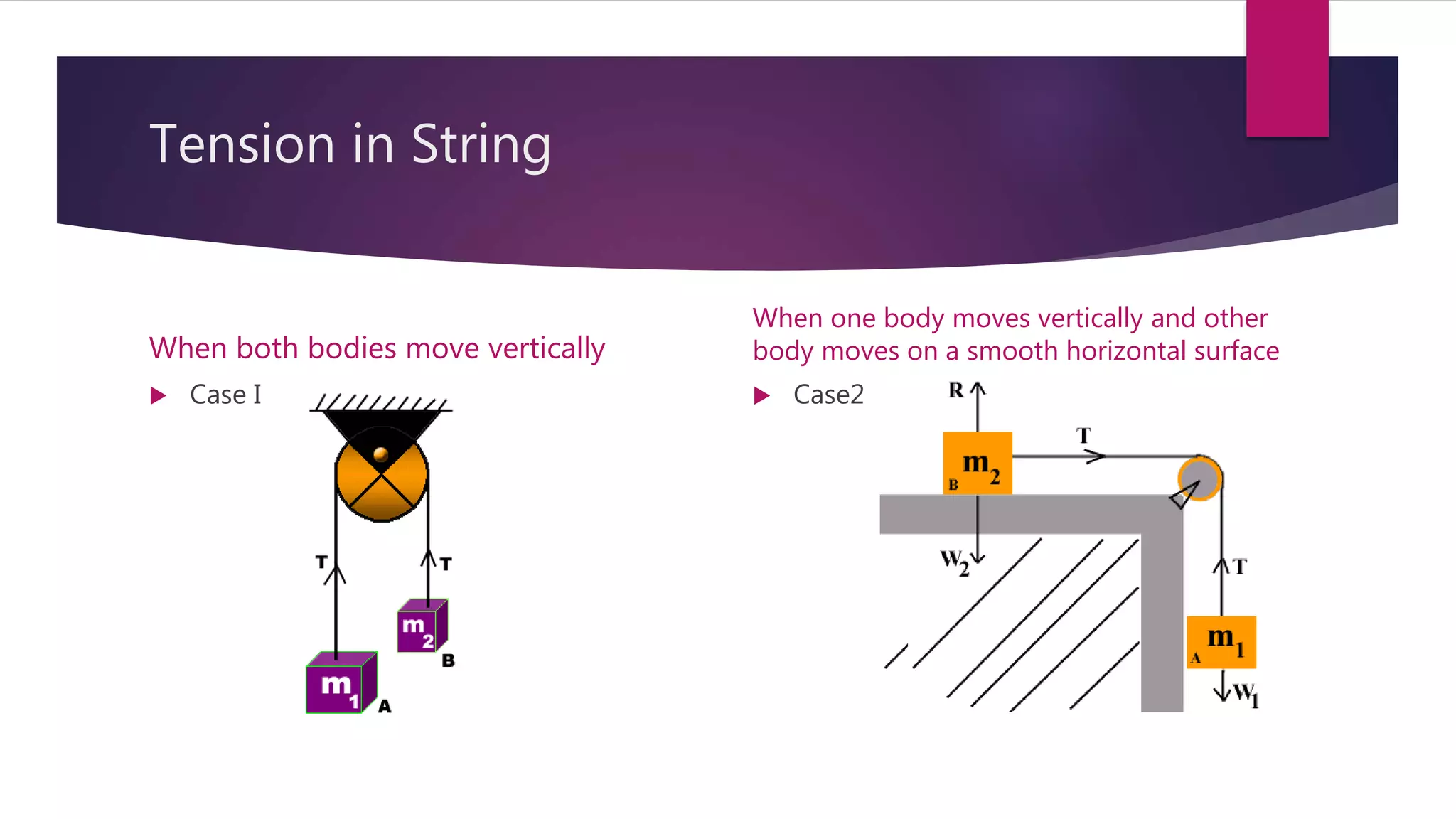
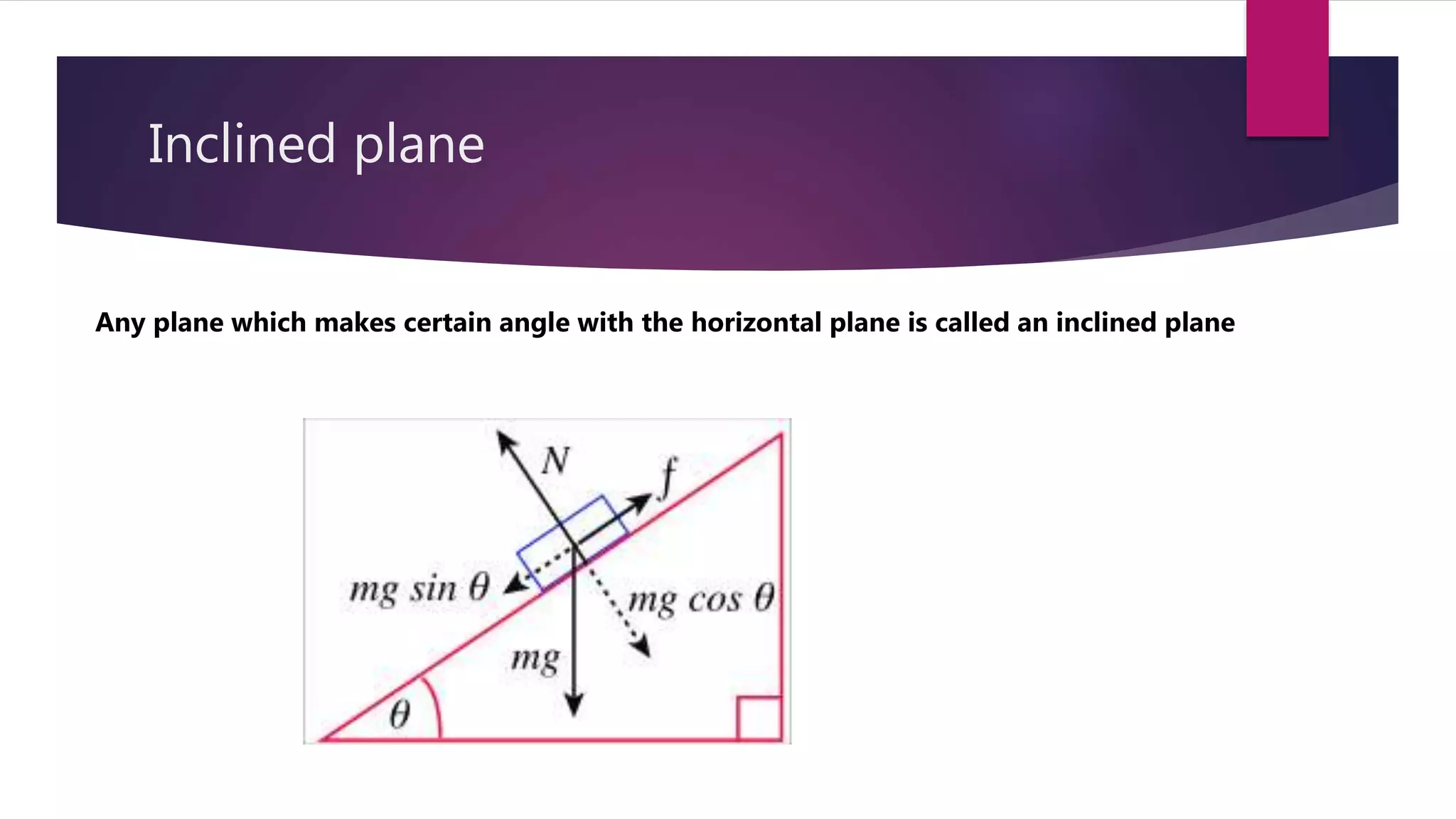
3) It provides overviews of Newton's Three Laws of Motion, linear momentum, friction, and inclined planes.