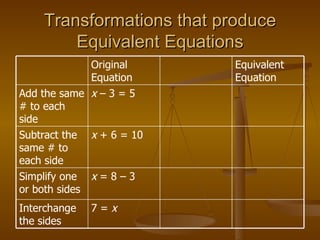
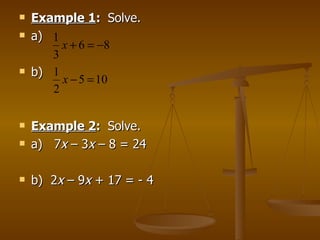
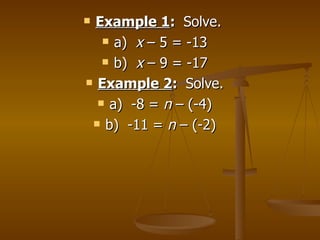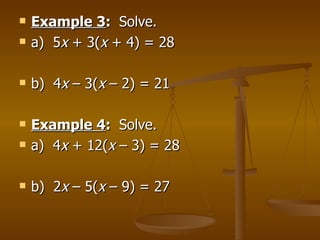The document discusses solving linear equations by using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division properties. It provides examples of solving single-step and multi-step equations, including equations with decimals that require rounding. It also covers rewriting formulas to make one variable a function of another and solving real-world application problems involving formulas.