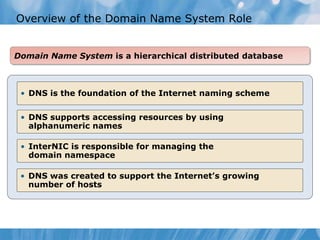
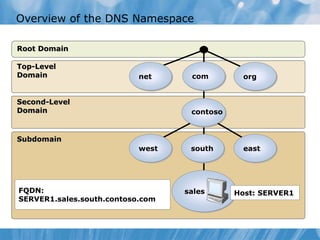
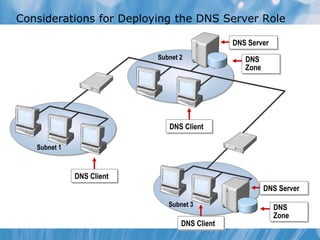
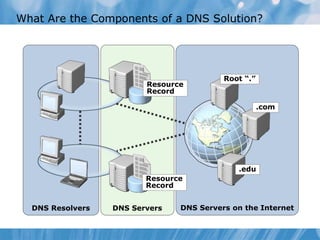
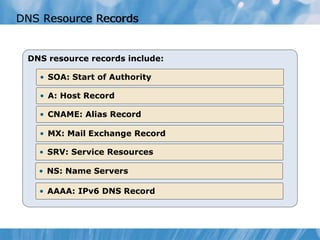
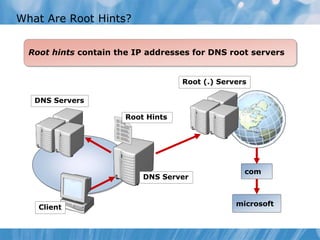
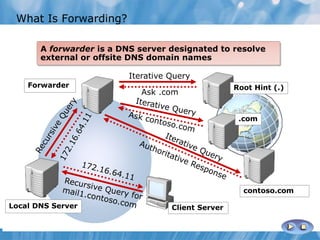
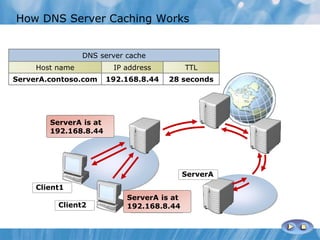
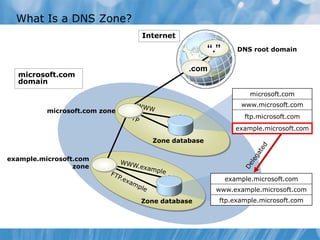
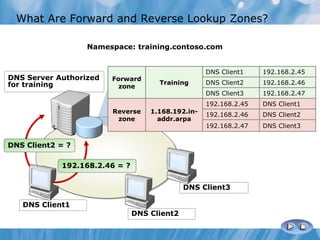
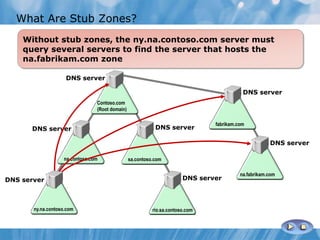
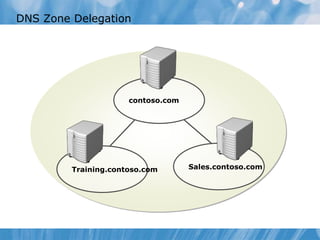
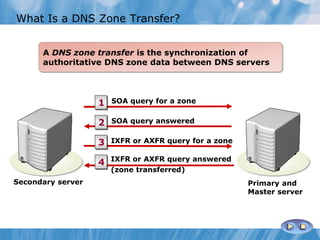
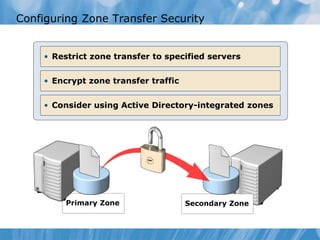
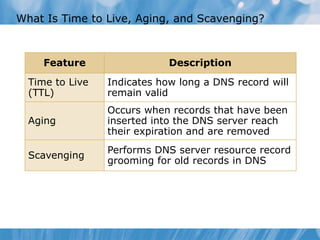
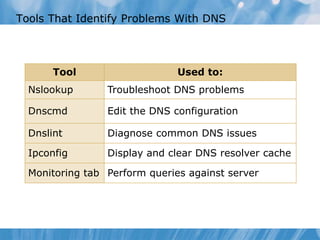
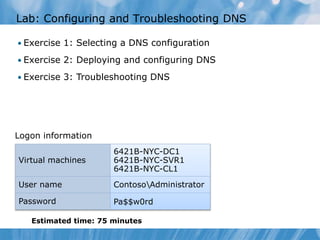
This document covers the installation, configuration, and troubleshooting of DNS (Domain Name System) in Windows Server environments. It details the components of a DNS solution, DNS zones and their types, as well as the management and monitoring of DNS servers. Key improvements in DNS for Windows Server 2008 and 2008 R2 are highlighted, along with practical demonstrations and lab exercises for hands-on experience.