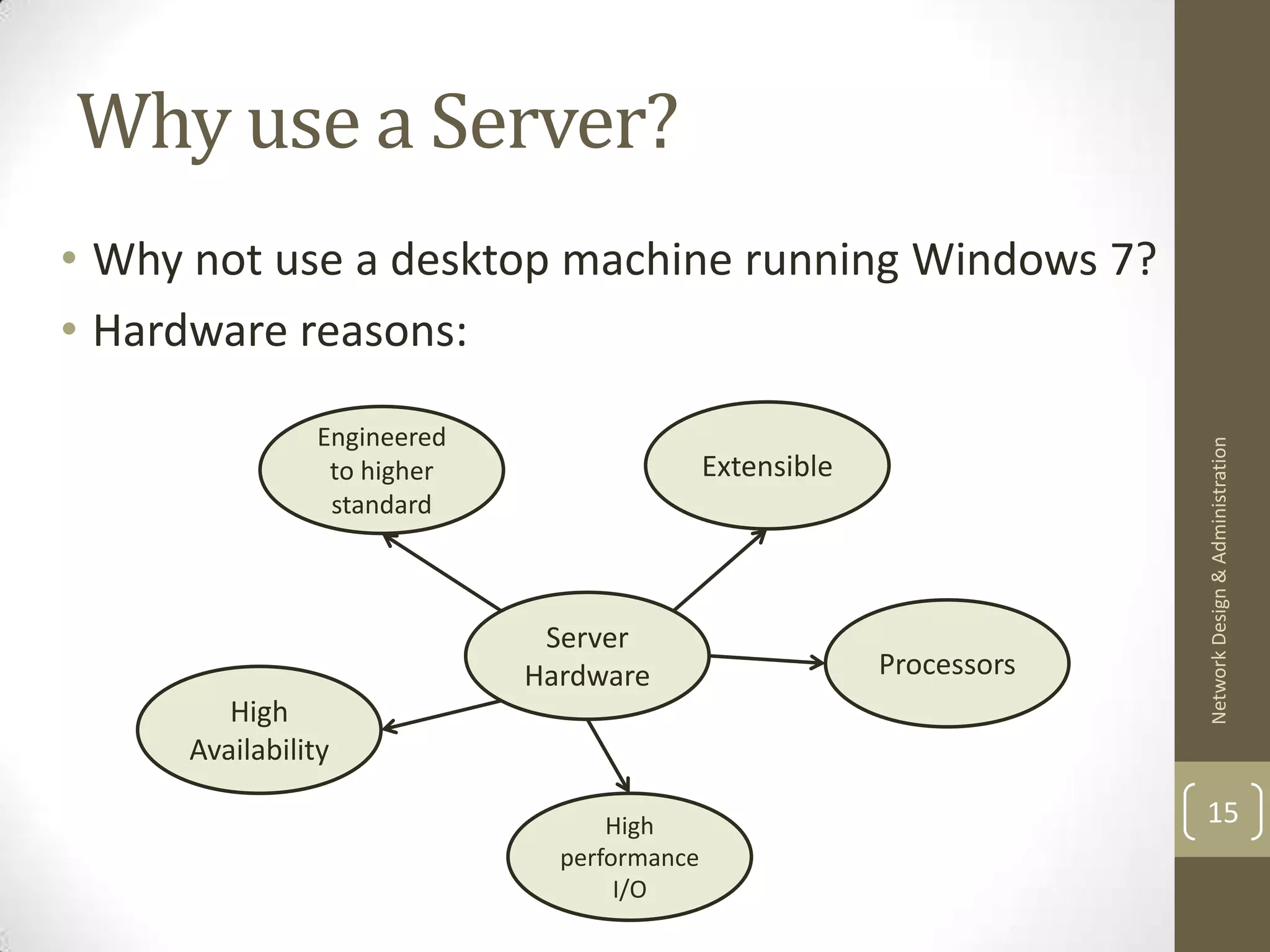
This document discusses servers and services in a computer network. It describes the similarities between client and server operating systems like Windows and Linux. Servers can take on different roles to provide services like file storage, printing, email, and more. The document explains DHCP and how it automatically assigns IP addresses to devices on the network. It also discusses the advantages of using server hardware designed for high availability, performance, and reliability over desktop machines.

![XP/Server 2003 Architecture
Diagram[1]
Network Design & Administration
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture2-serversandservices-130204184323-phpapp02/75/Lecture-2-servers-and-services-3-2048.jpg)
![Vista/7 Architecture Diagram[1]
Network Design & Administration
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture2-serversandservices-130204184323-phpapp02/75/Lecture-2-servers-and-services-4-2048.jpg)
![Gnu/Linux [2]
Network Design & Administration
Board Support
Package (BSP)
Plugins to support
different file systems
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture2-serversandservices-130204184323-phpapp02/75/Lecture-2-servers-and-services-5-2048.jpg)


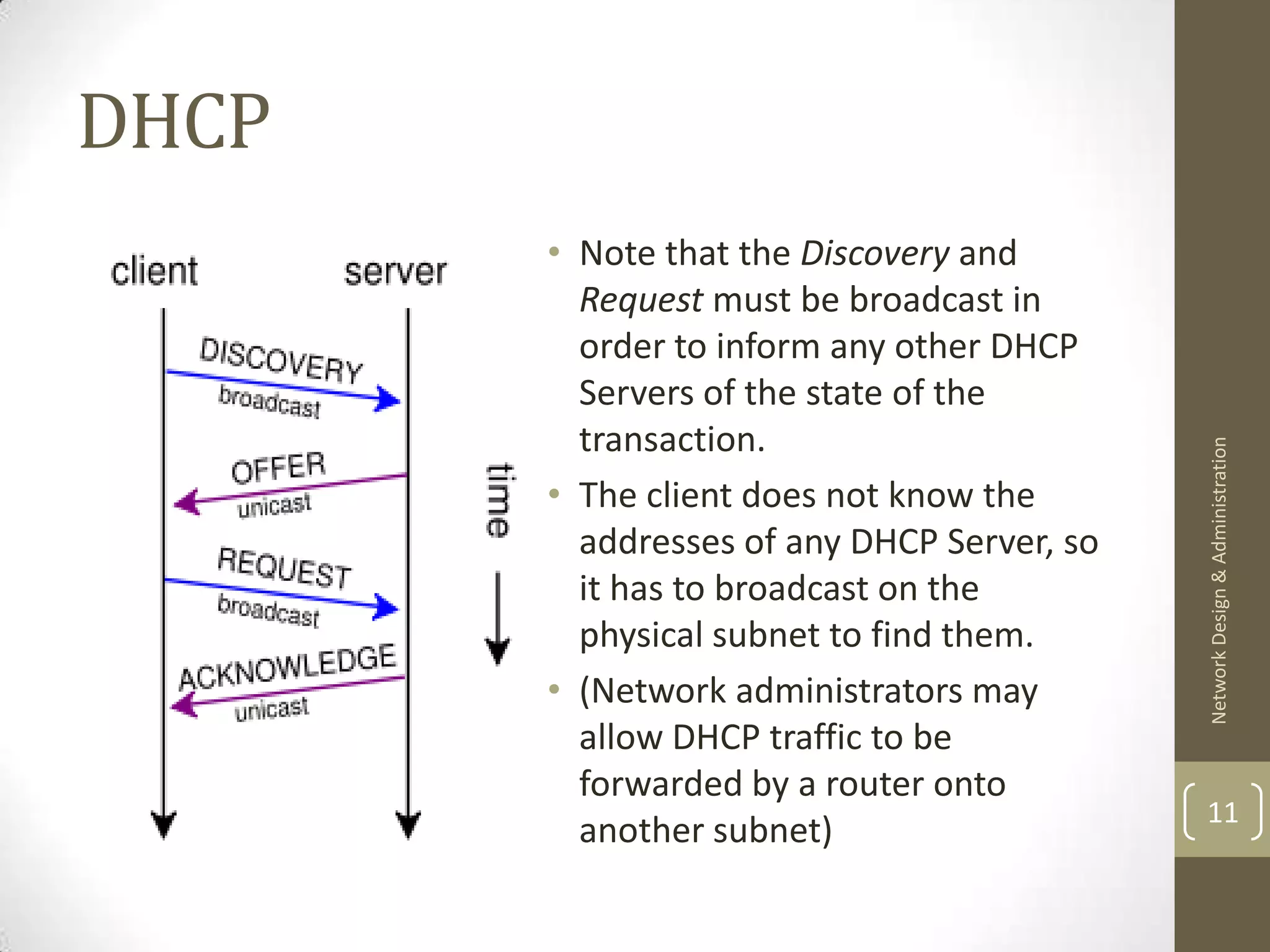
![DHCP
• Address allocation has a few variants[2] –
• Dynamic: the address is allocated for a lease period from
a pool and then re-used after the lease has expired.
• Question:
Network Design & Administration
• What lease would be appropriate
• In the office?
• On the Dell production line where they are checking PC’s
before shipping?
• Automatic: the address is assigned permanently to a
client and the client is preferentially given the same
address next time it asks.
13
• Static: a list of MAC/IP address pairs is used to assign to
the client.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture2-serversandservices-130204184323-phpapp02/75/Lecture-2-servers-and-services-13-2048.jpg)
![DHCP
• Microsoft seem to have slightly different definitions of
these terms[4]:
• Static – certain machines (e.g. DHCP, DNS, WINS
Servers, Print Server, Firewall, Router) have defined
addresses which are also excluded from a dynamic
Network Design & Administration
range (also called permanent lease)
• Client Reservation (as above, but for ordinary clients)
• Automatic (Automatic Private IP Addressing, APIPA) –
if DHCP Server unavailable, client can configure itself
in the 169.254.0.1 to 169.254.255.254 range and talk
to other clients in the same range. Client polls
regularly (but not frequently) for a DHCP Server to
14
return, to get back to normal.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture2-serversandservices-130204184323-phpapp02/75/Lecture-2-servers-and-services-14-2048.jpg)
![Next Time & References
• More on Servers and services
[1] “Modern Operating Systems”, Andrew Tanenbaum, 2008
[2] http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/linux/library/l-linux-
Network Design & Administration
kernel/
[3] Wikipedia, man pages for dhcpd
[4] "Windows Server 2008 - TCP/IP Fundamentals for Microsoft
Windows", eBook available at:
http://www.microsoft.com/download/en/details.aspx?displayla
ng=en&id=8781
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture2-serversandservices-130204184323-phpapp02/75/Lecture-2-servers-and-services-16-2048.jpg)