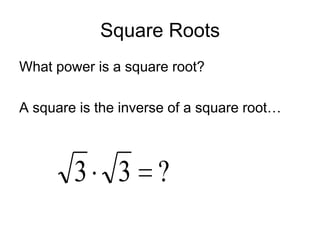
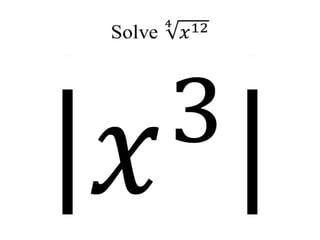1) The document discusses evaluating nth roots of numbers and expressions, including square roots, cube roots, and nth roots.
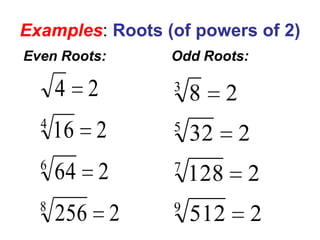
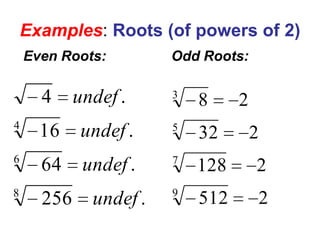
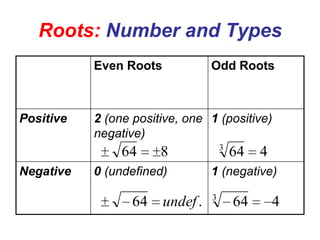
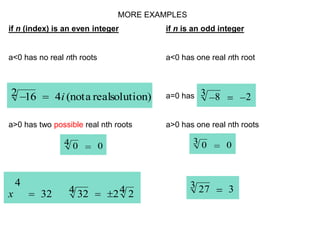
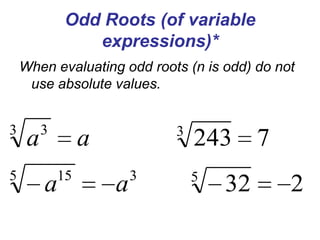
2) It provides definitions and examples of even and odd roots of positive and negative numbers. Even roots of negative numbers are undefined, while odd roots of negative numbers are negative.
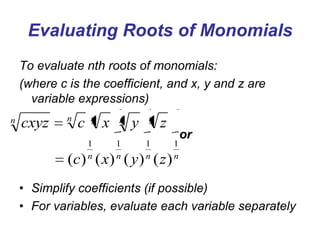
3) Methods are described for evaluating nth roots of monomial expressions by splitting them into factors and taking the nth root of each factor.