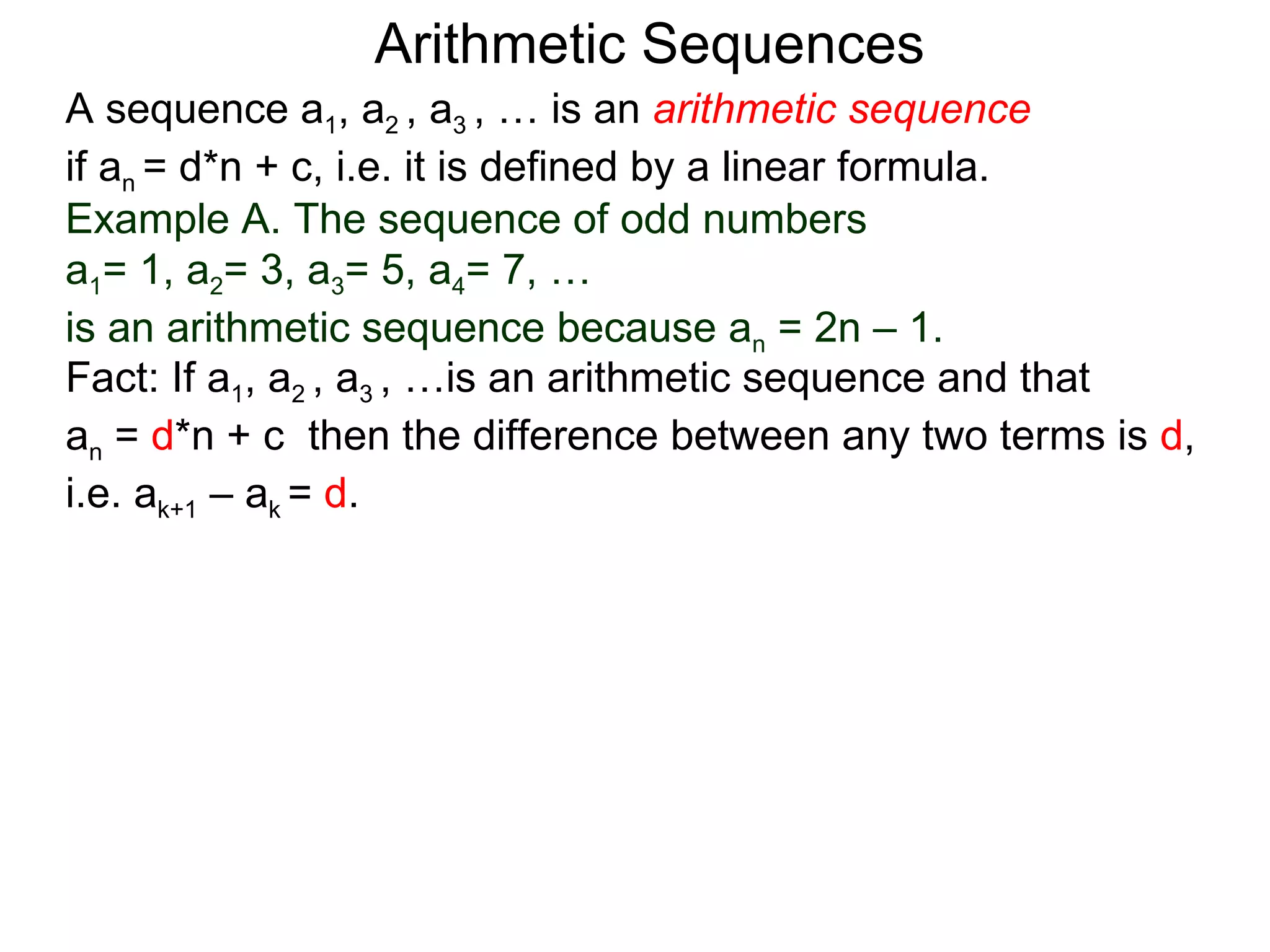
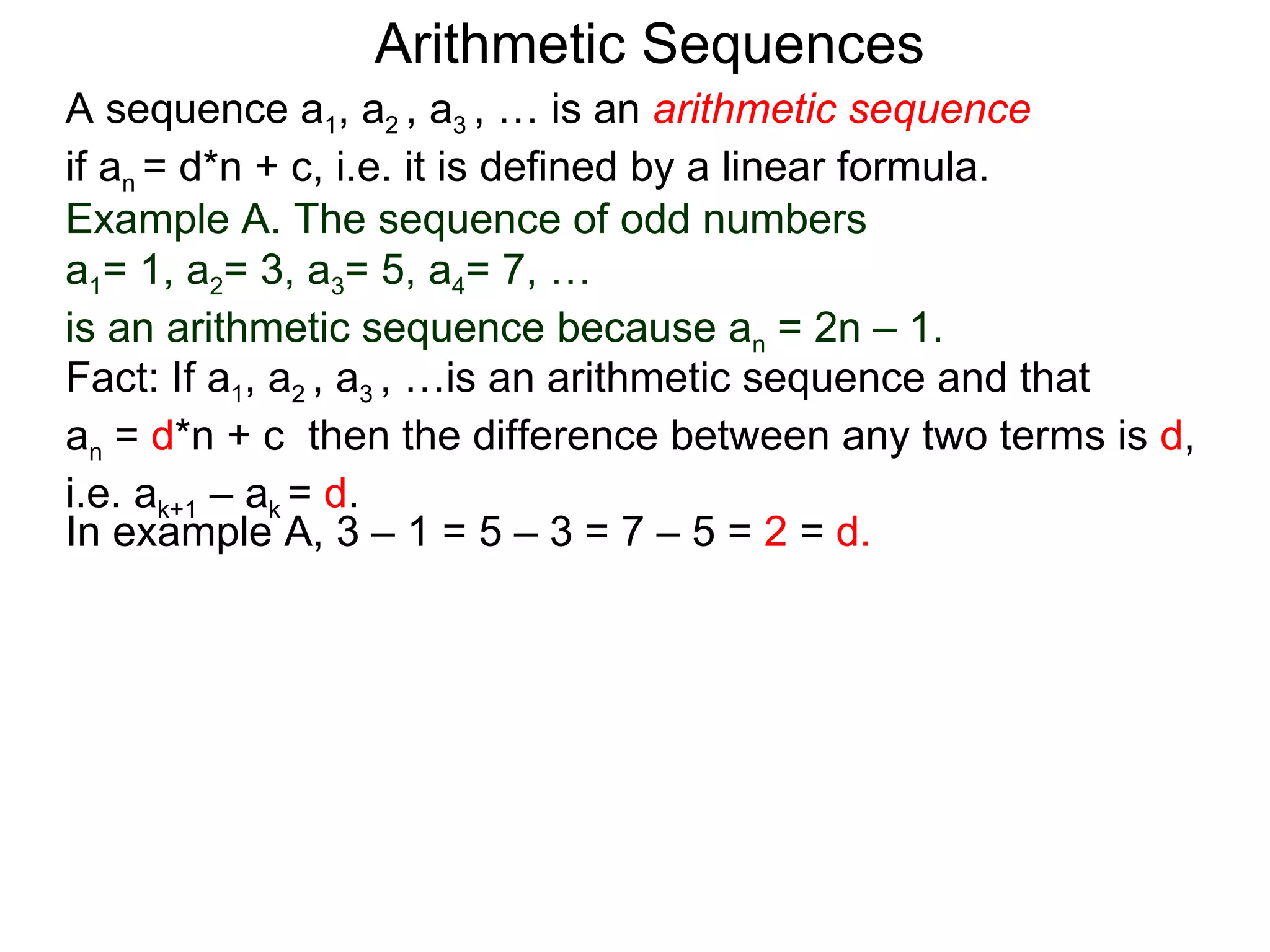
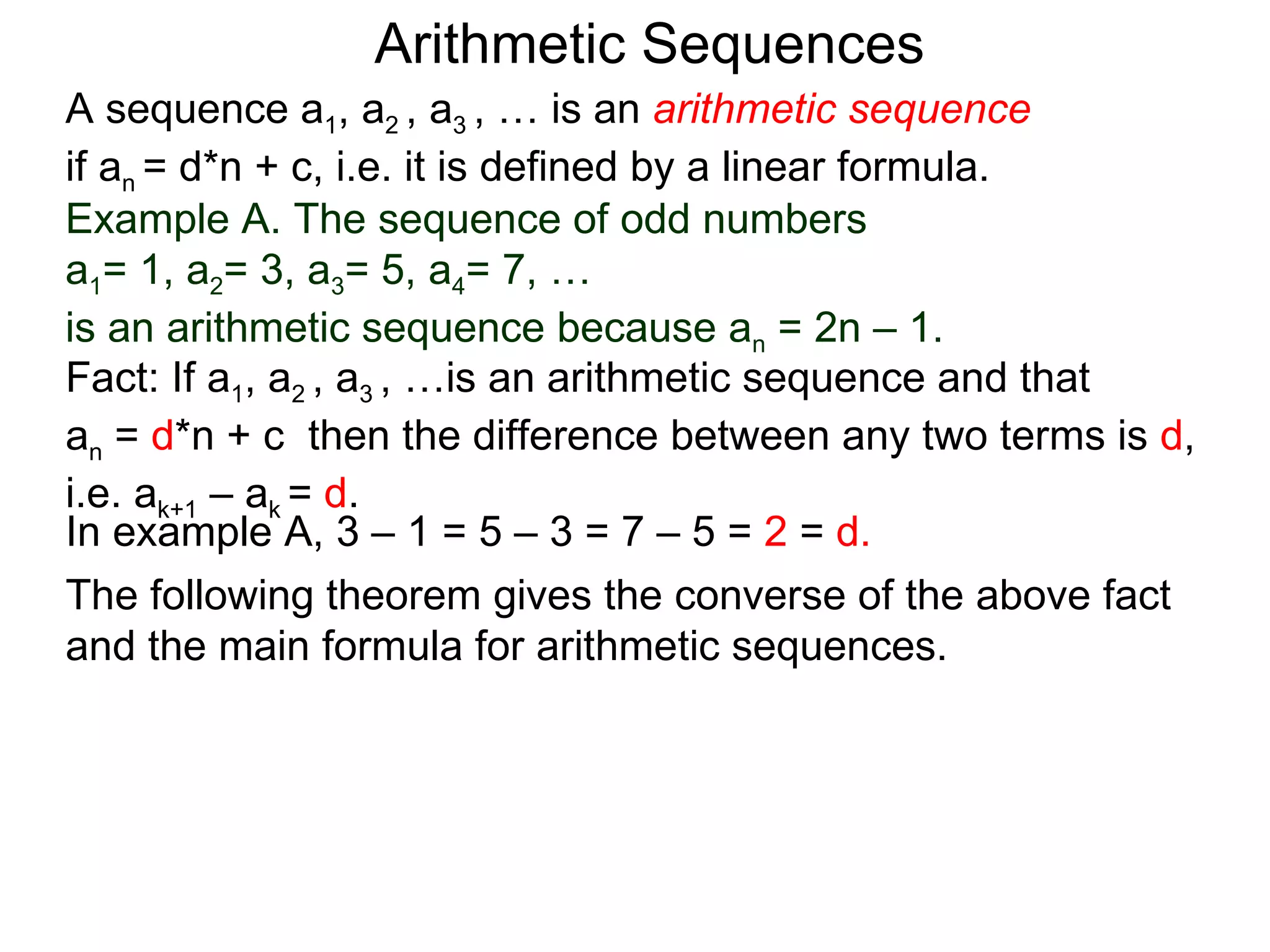
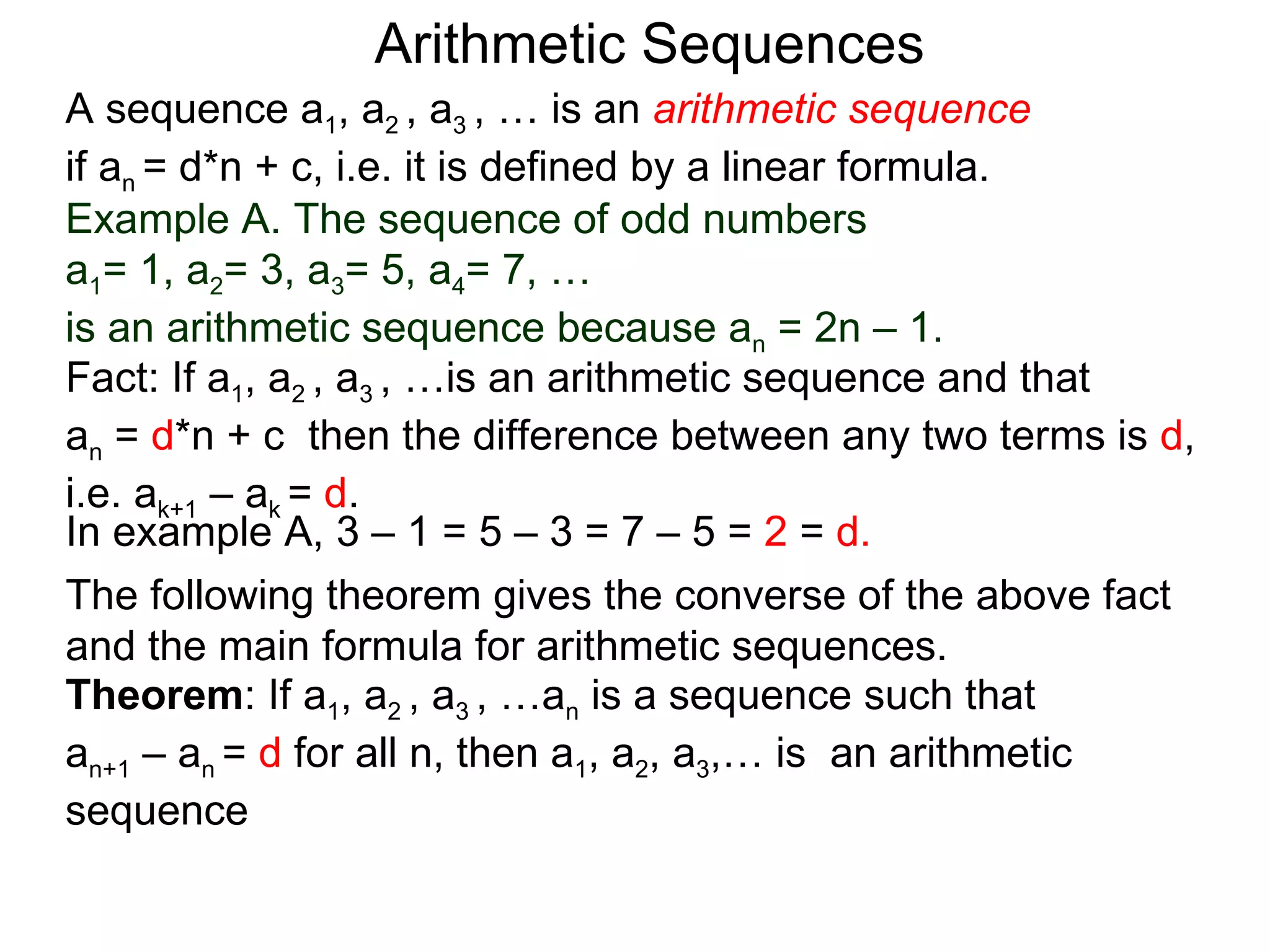
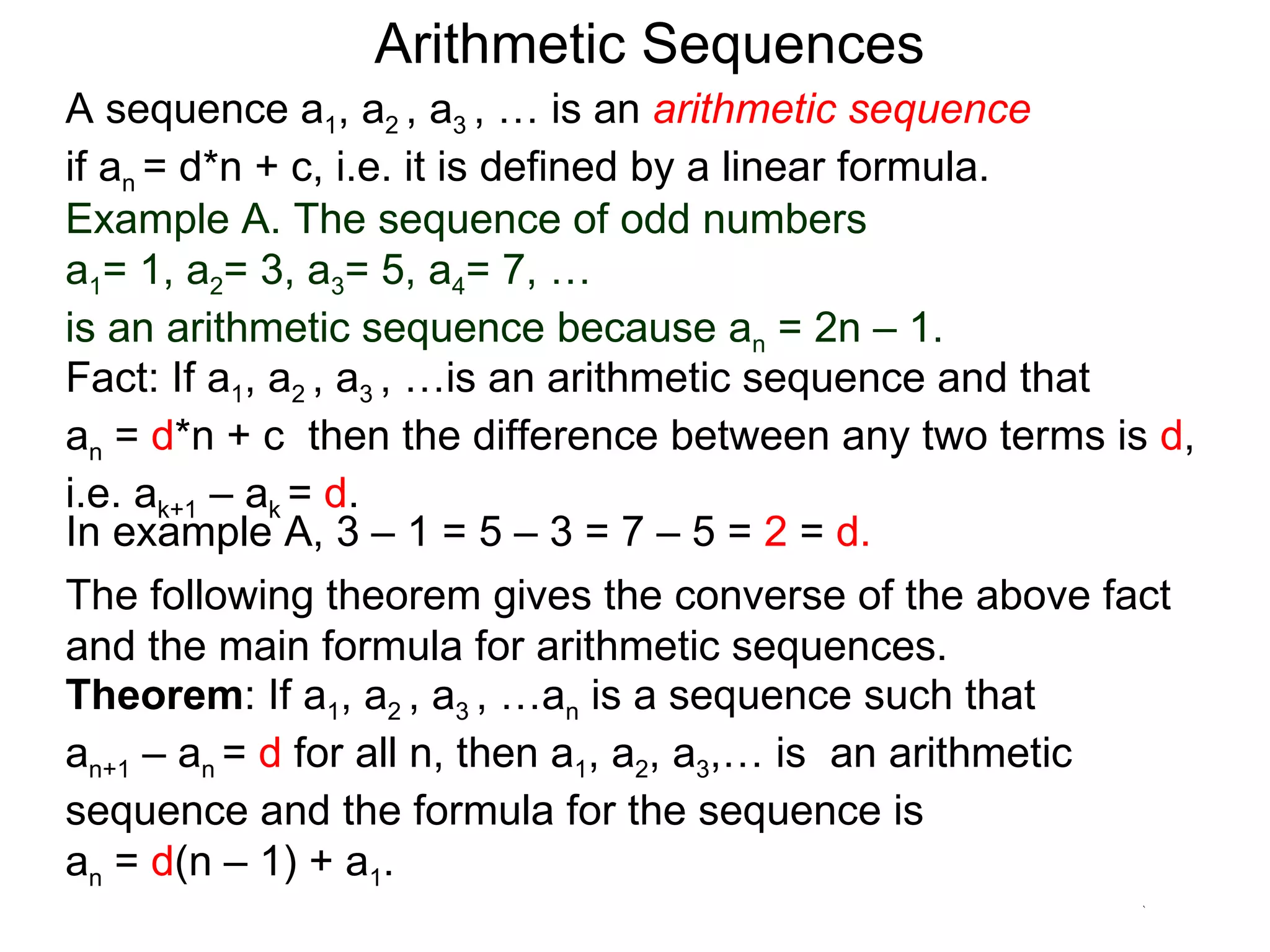
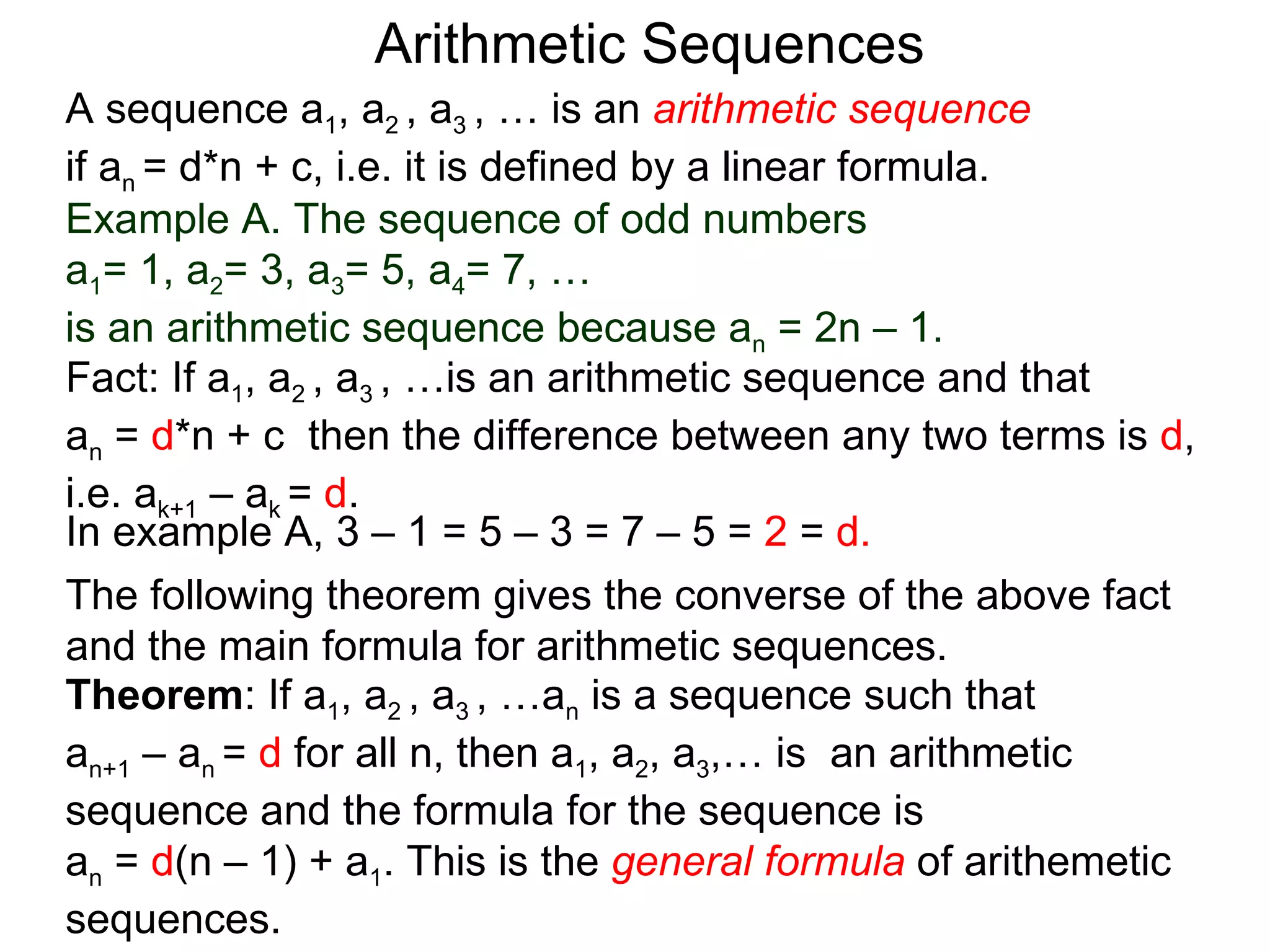
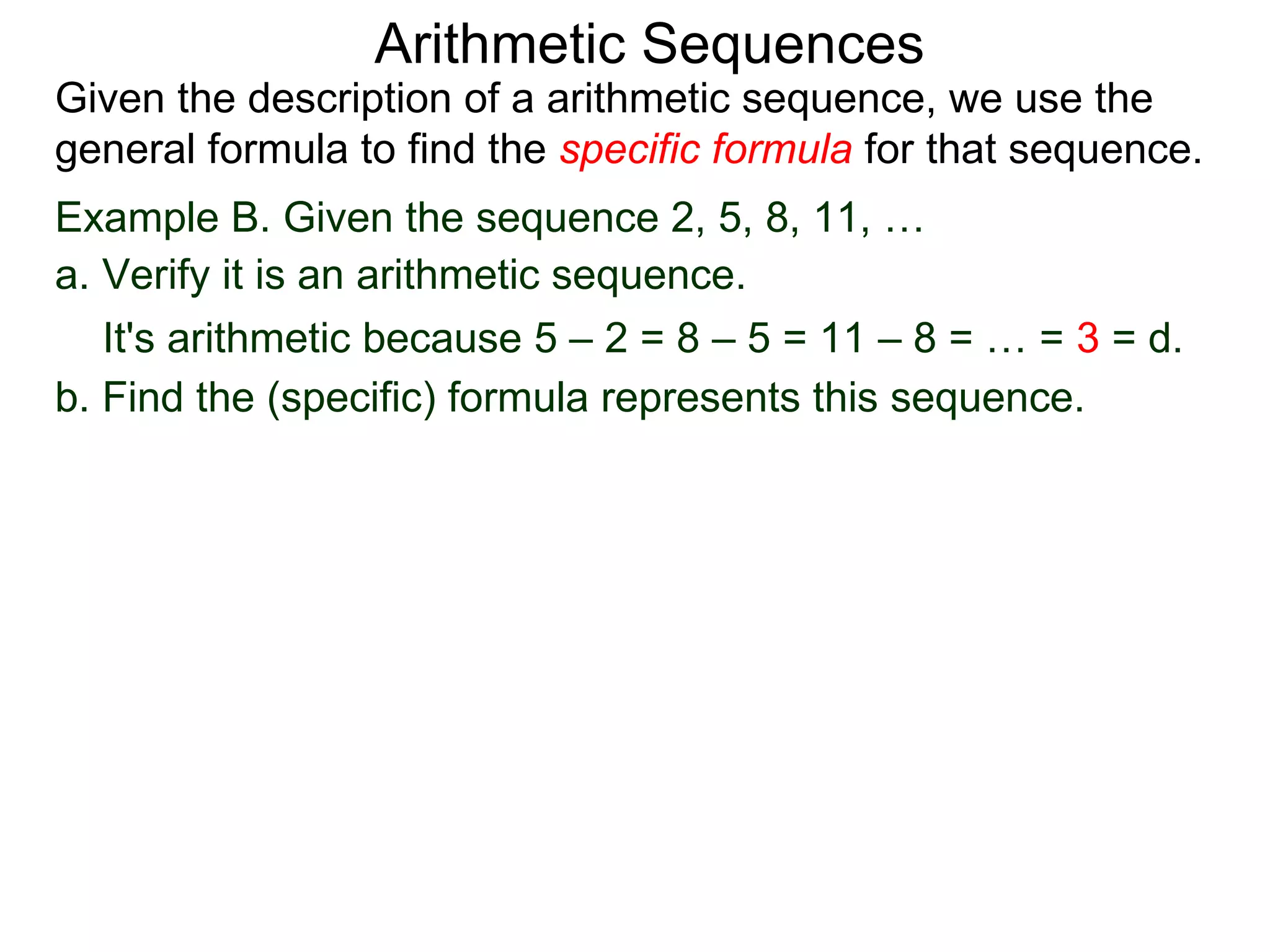
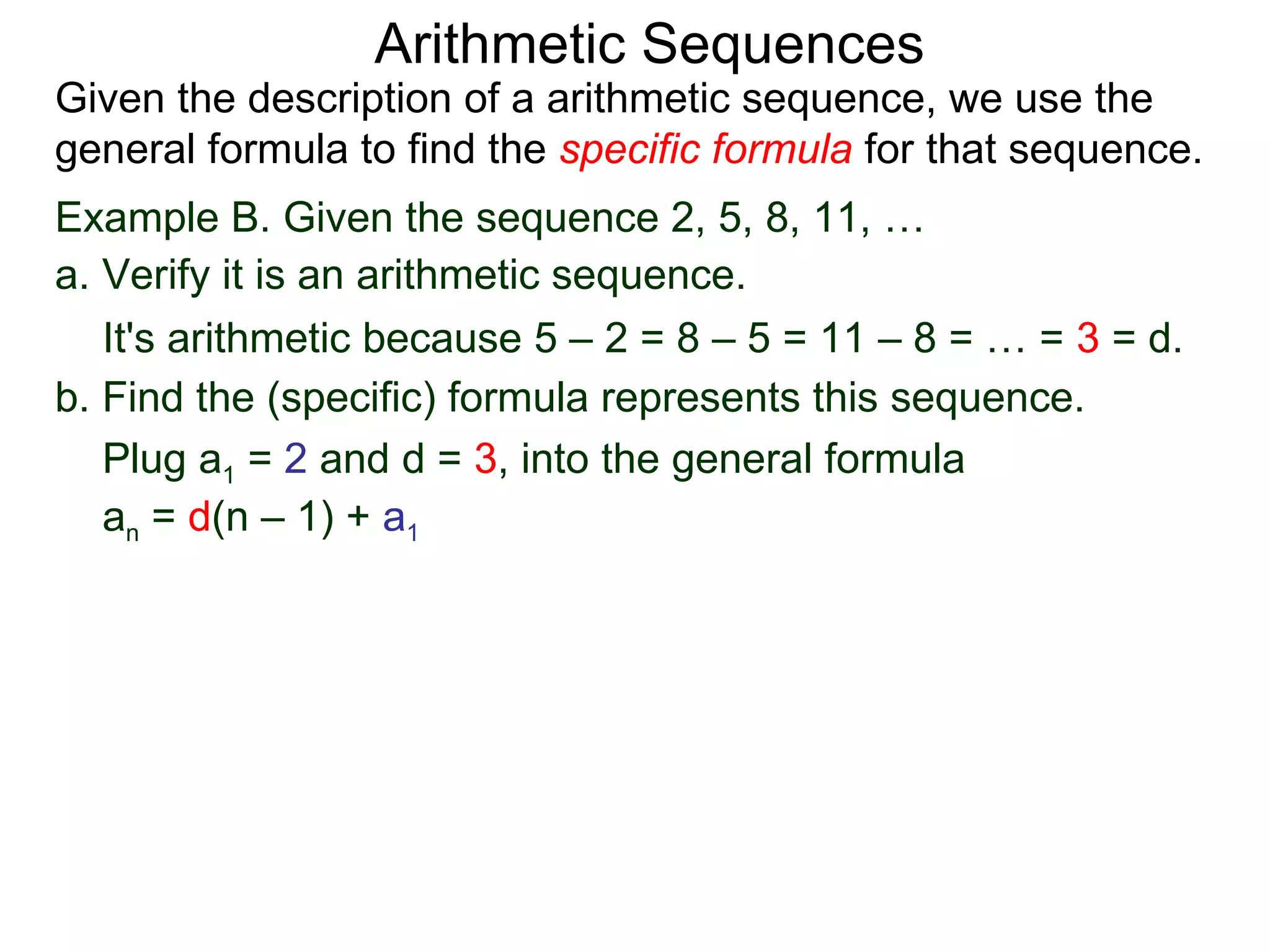
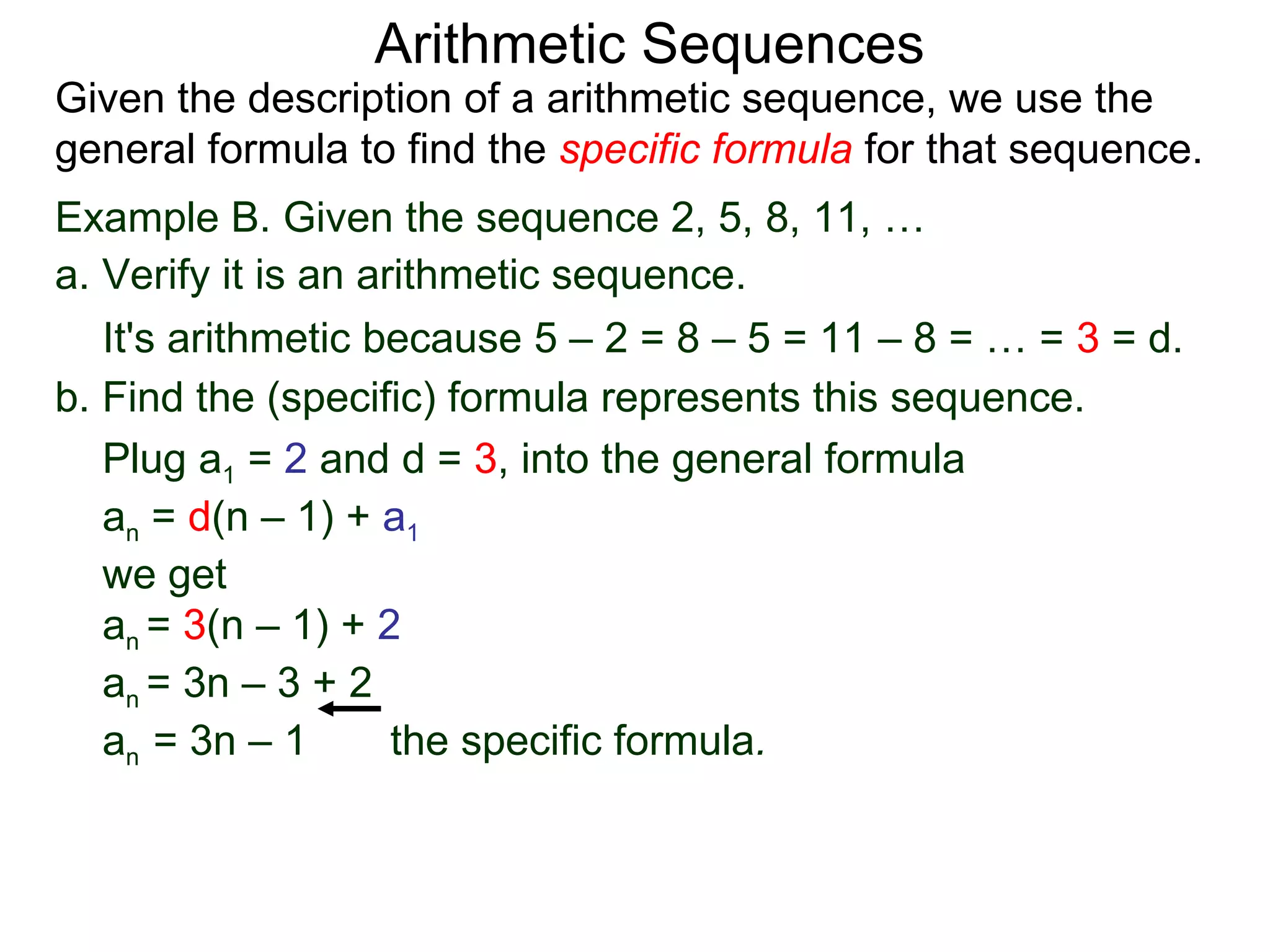
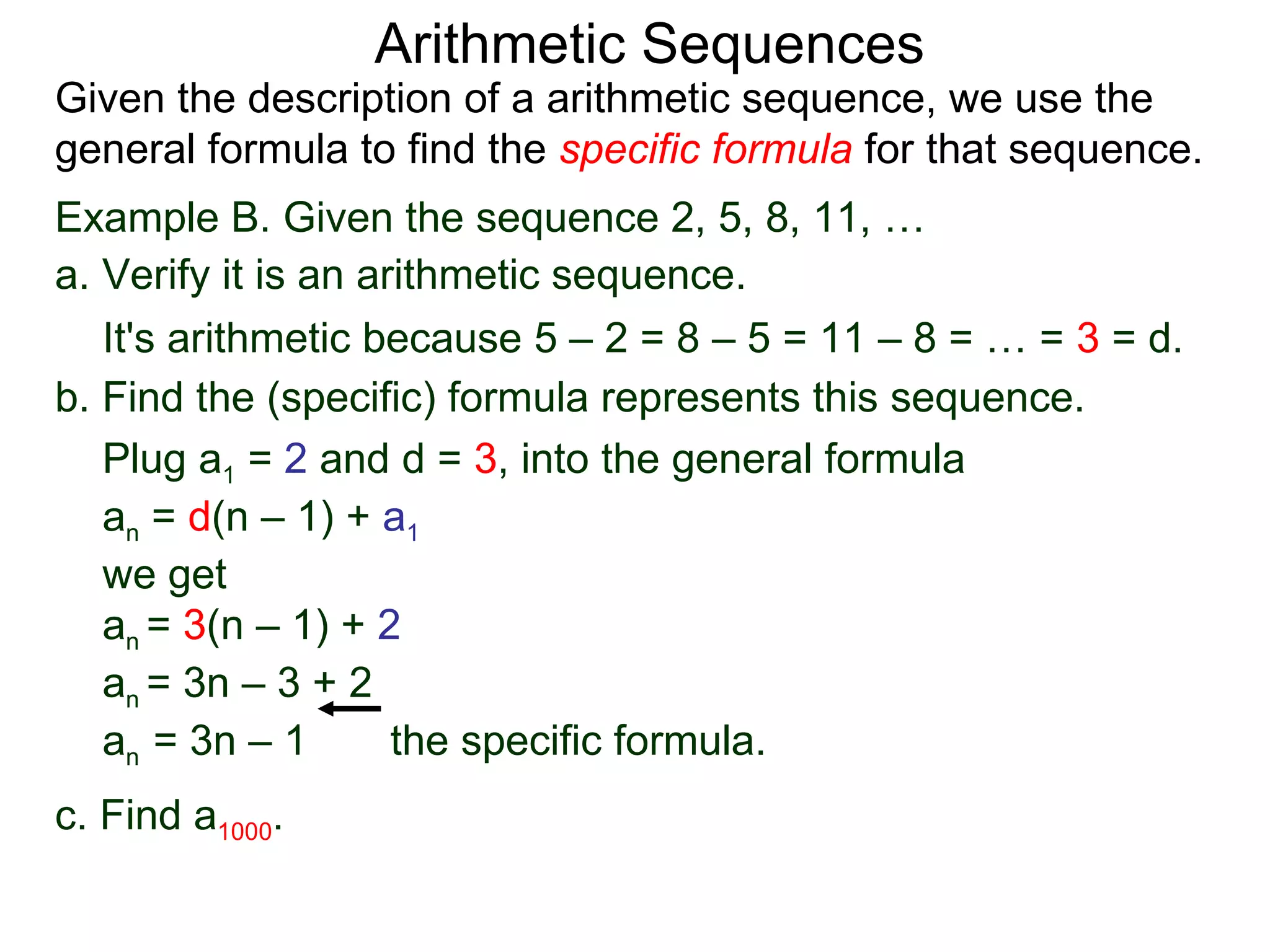
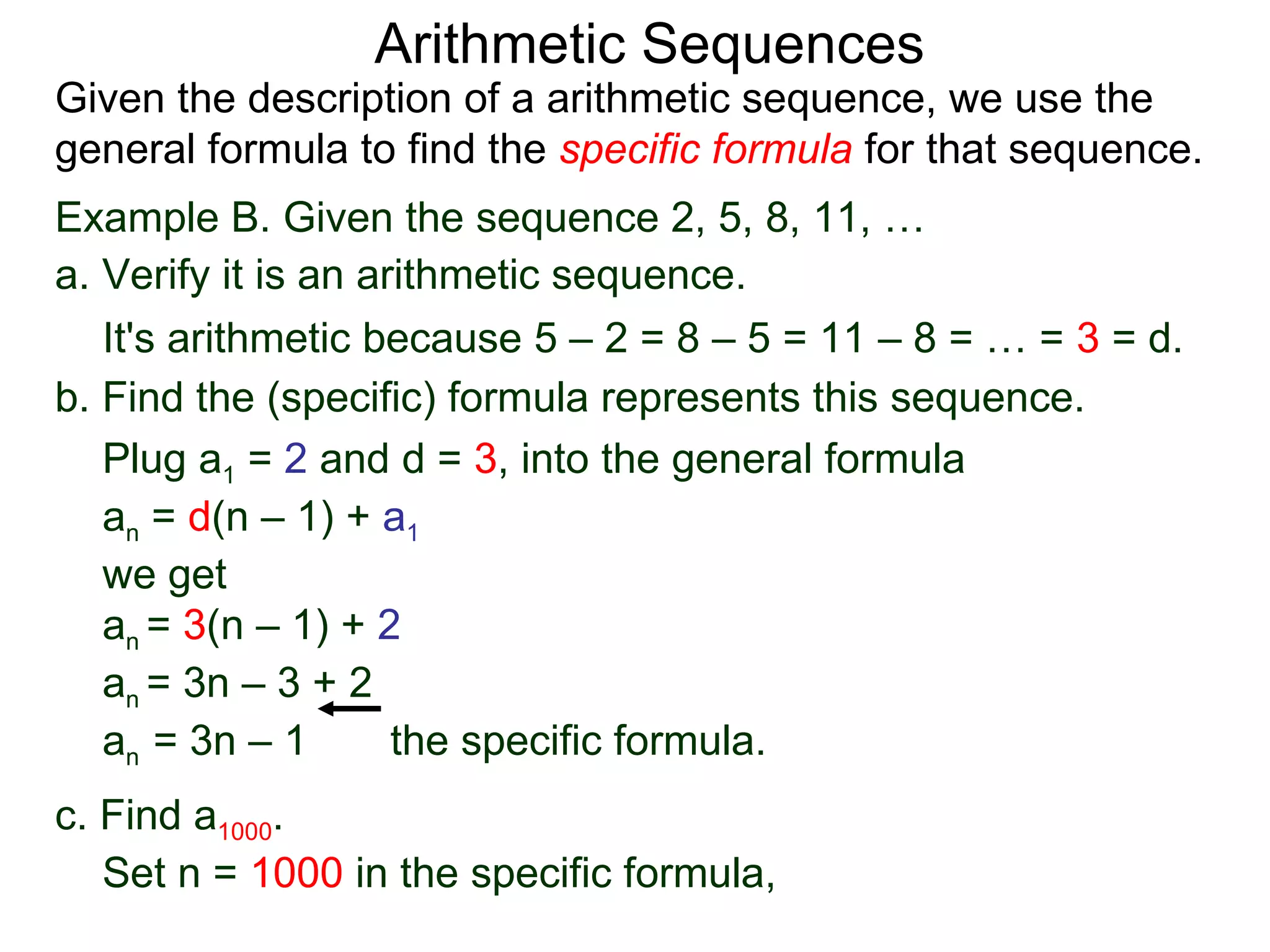
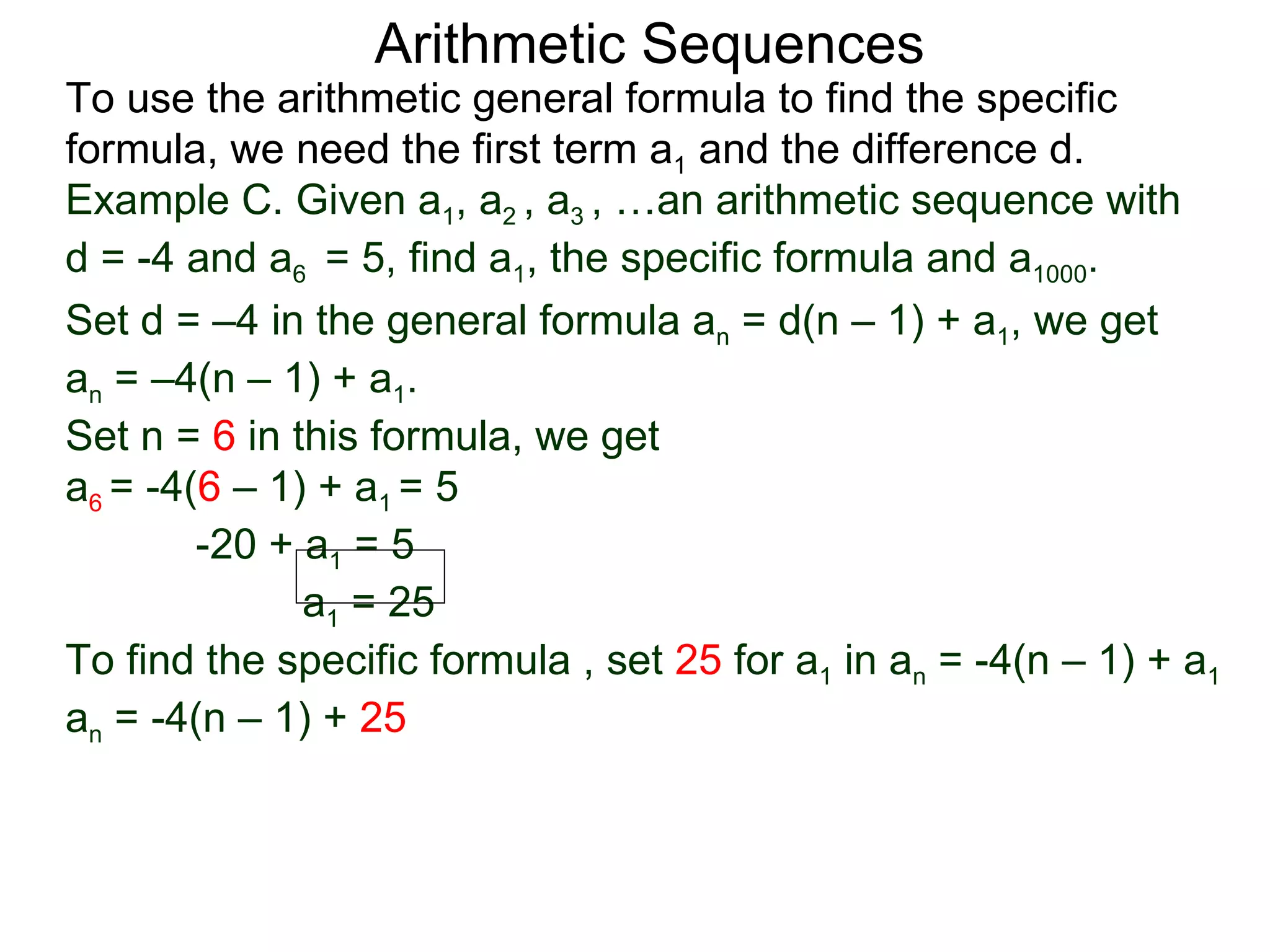
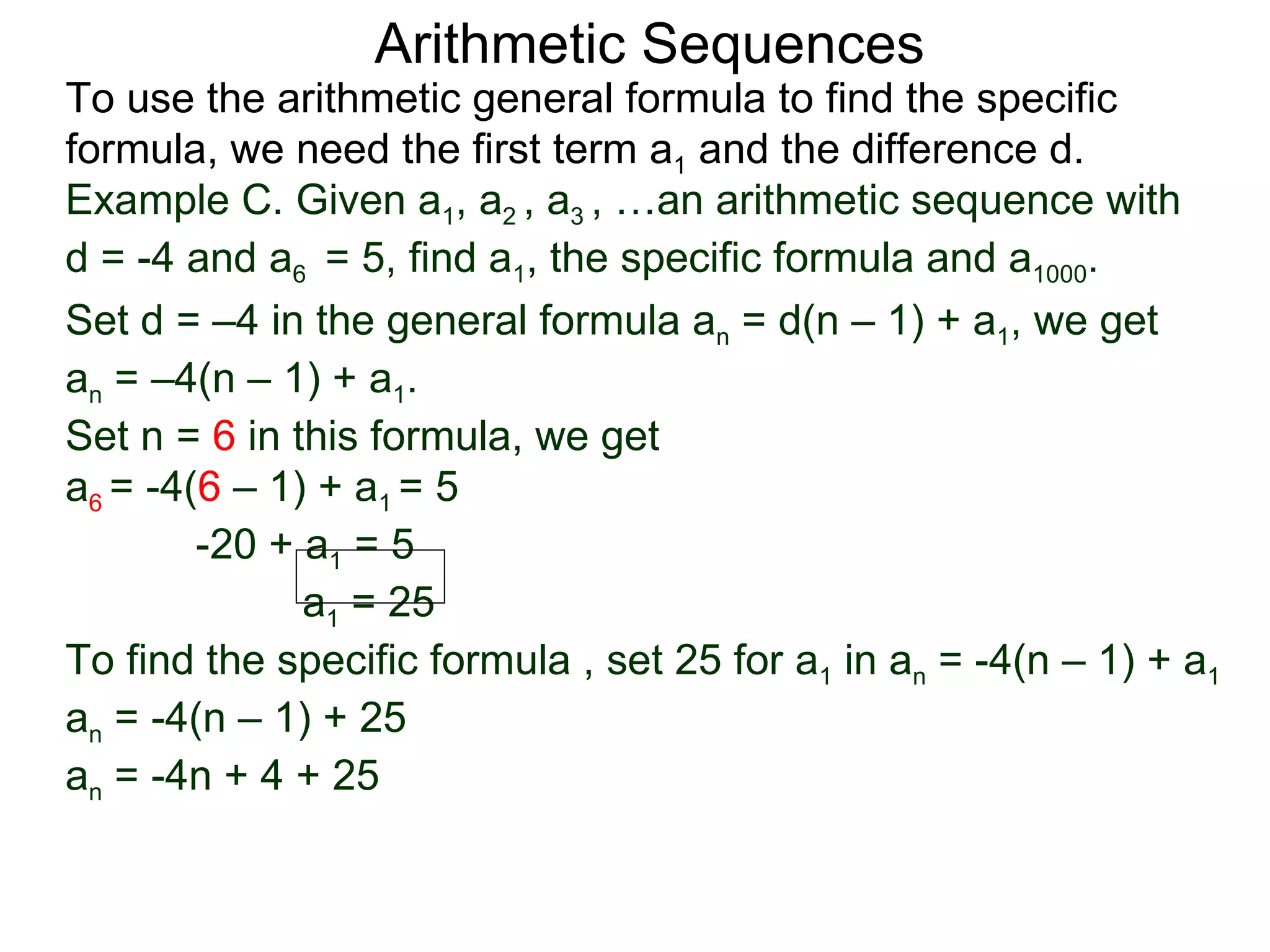
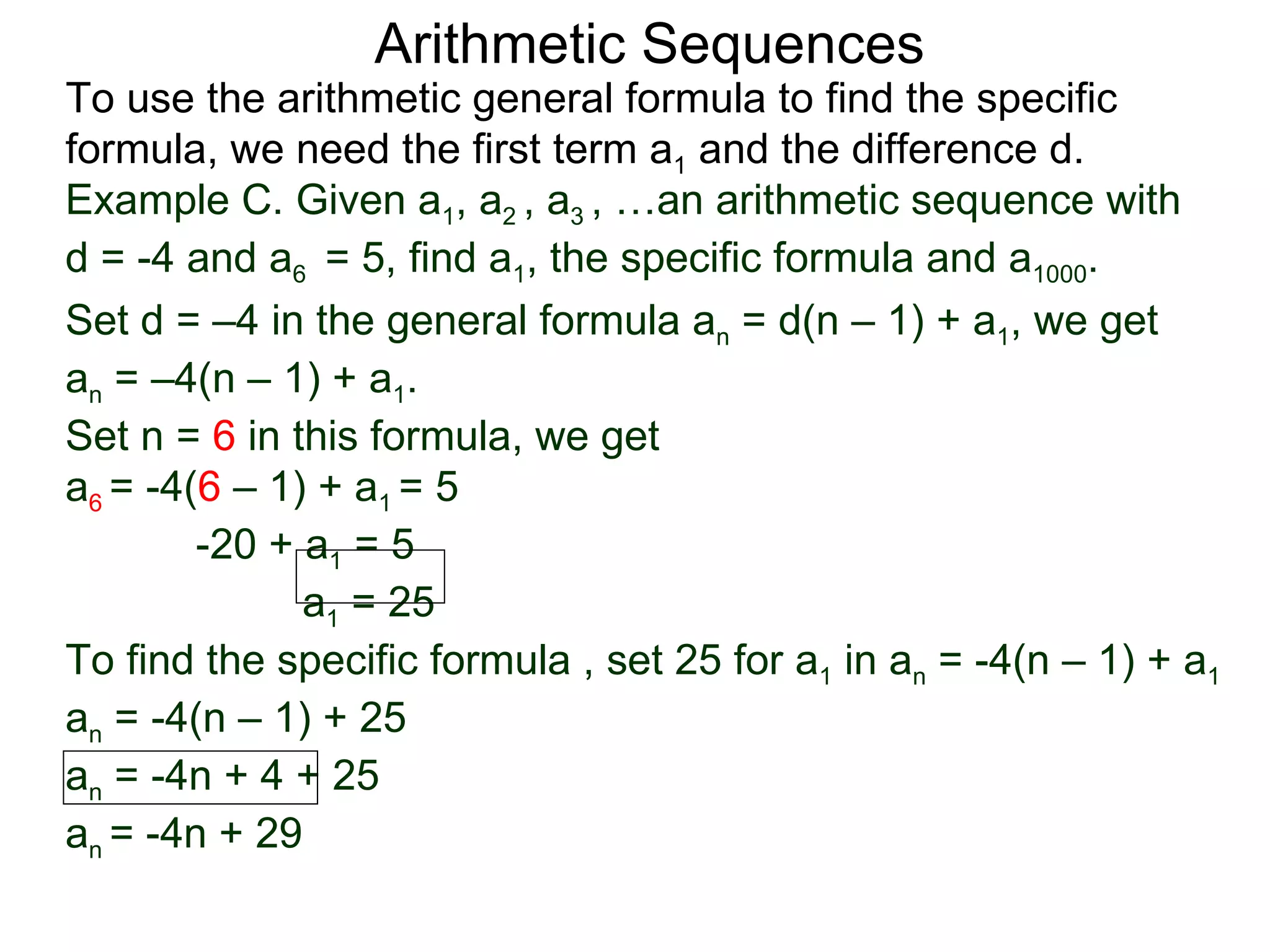
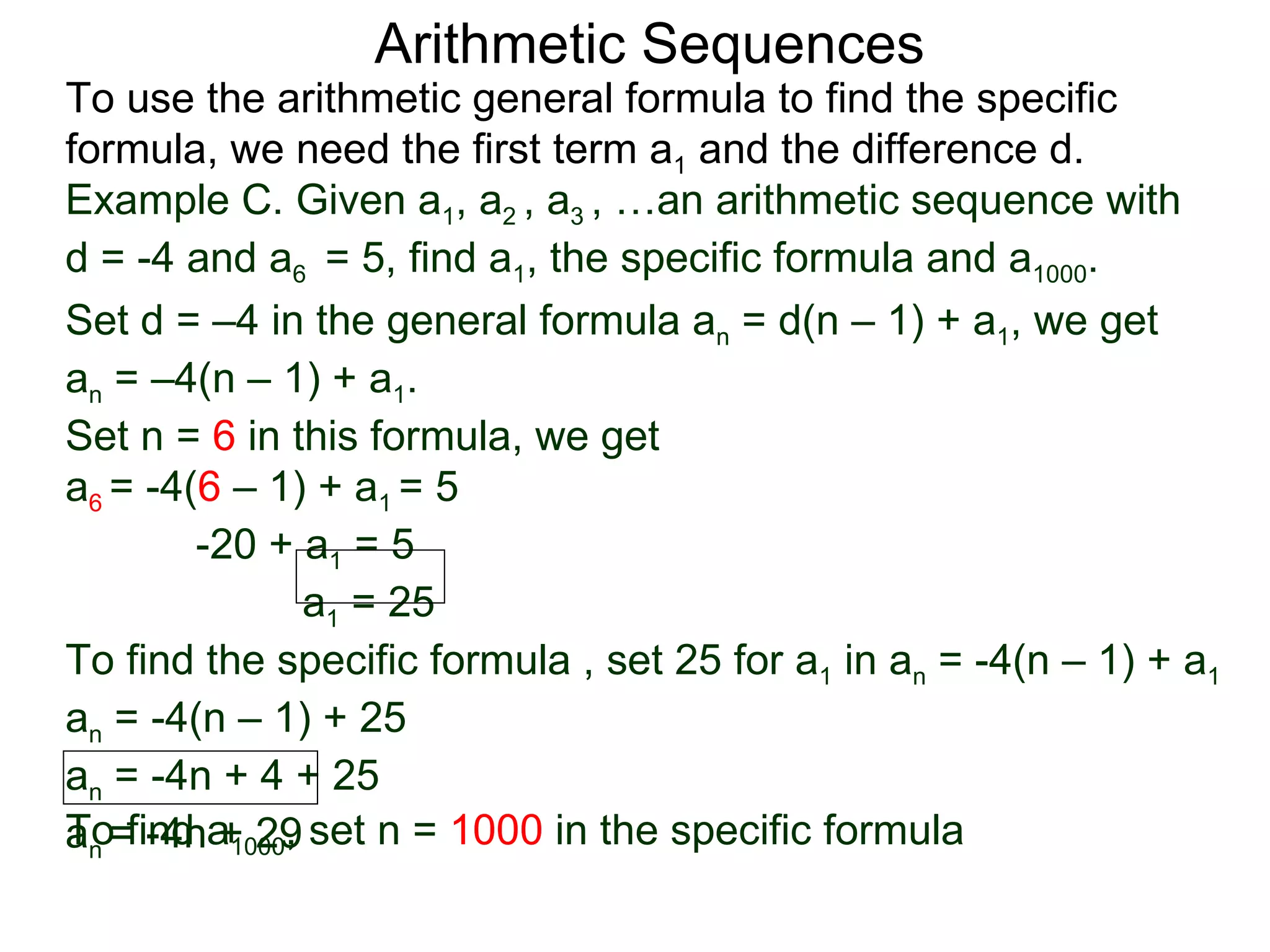
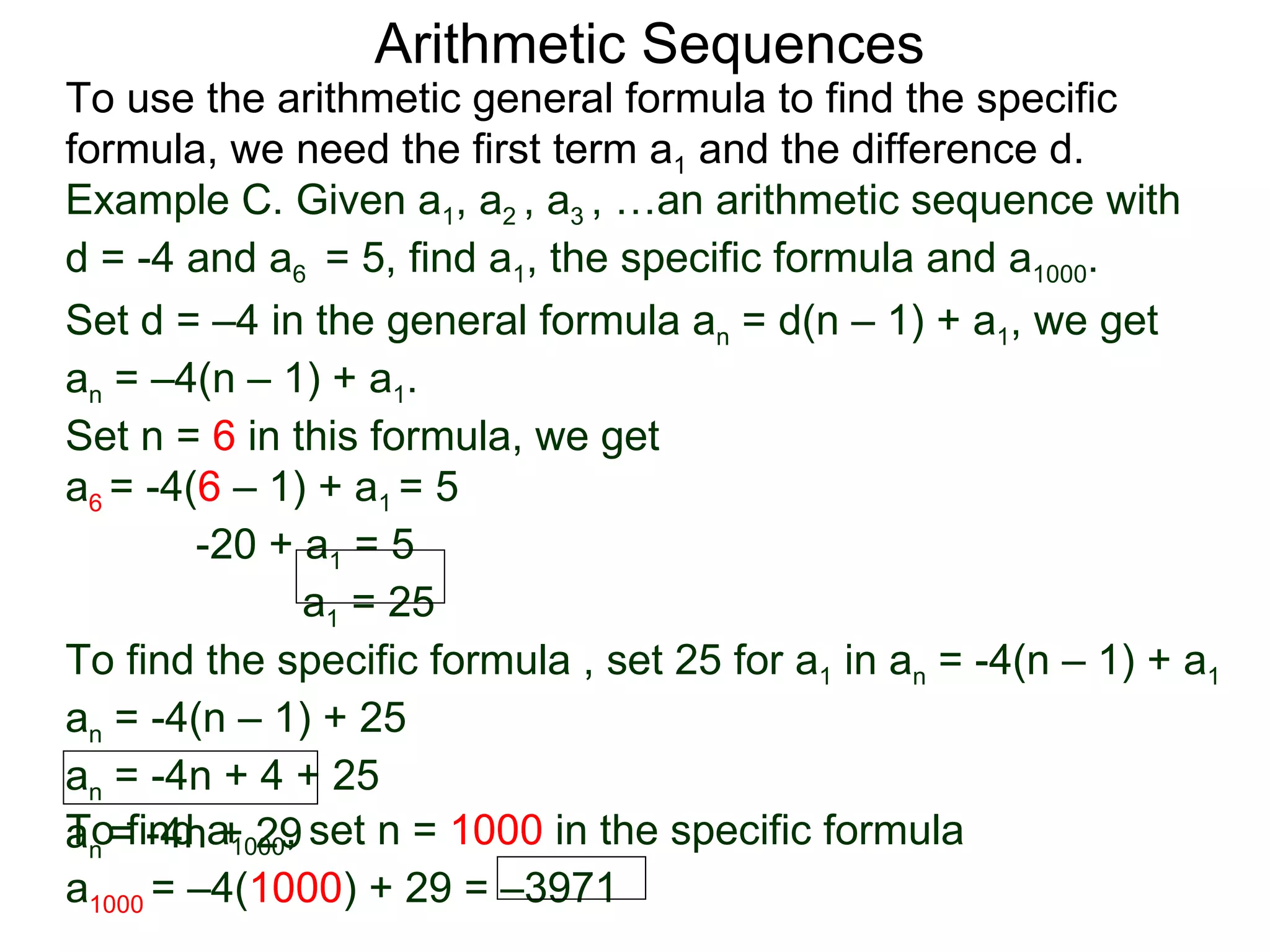
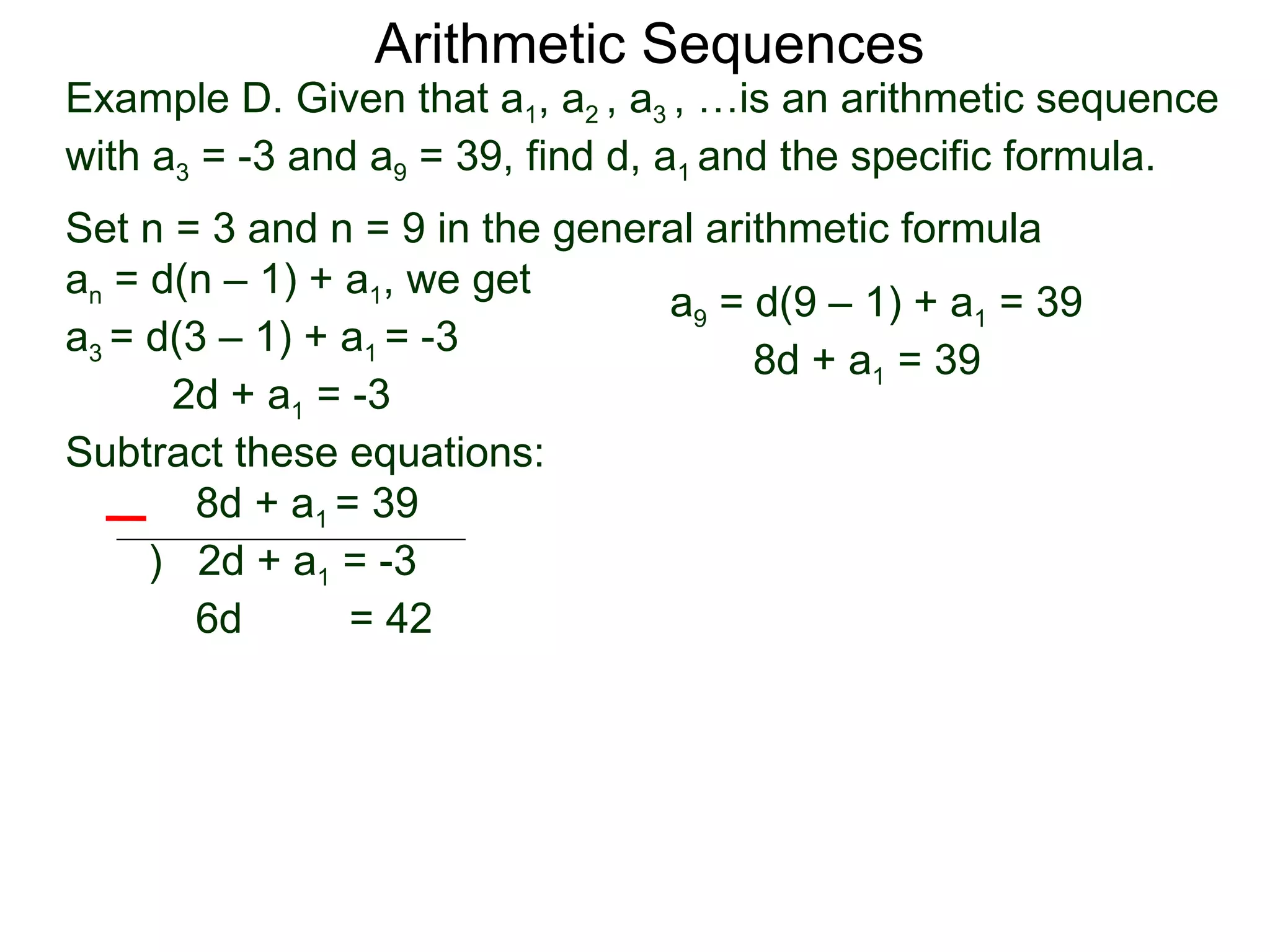
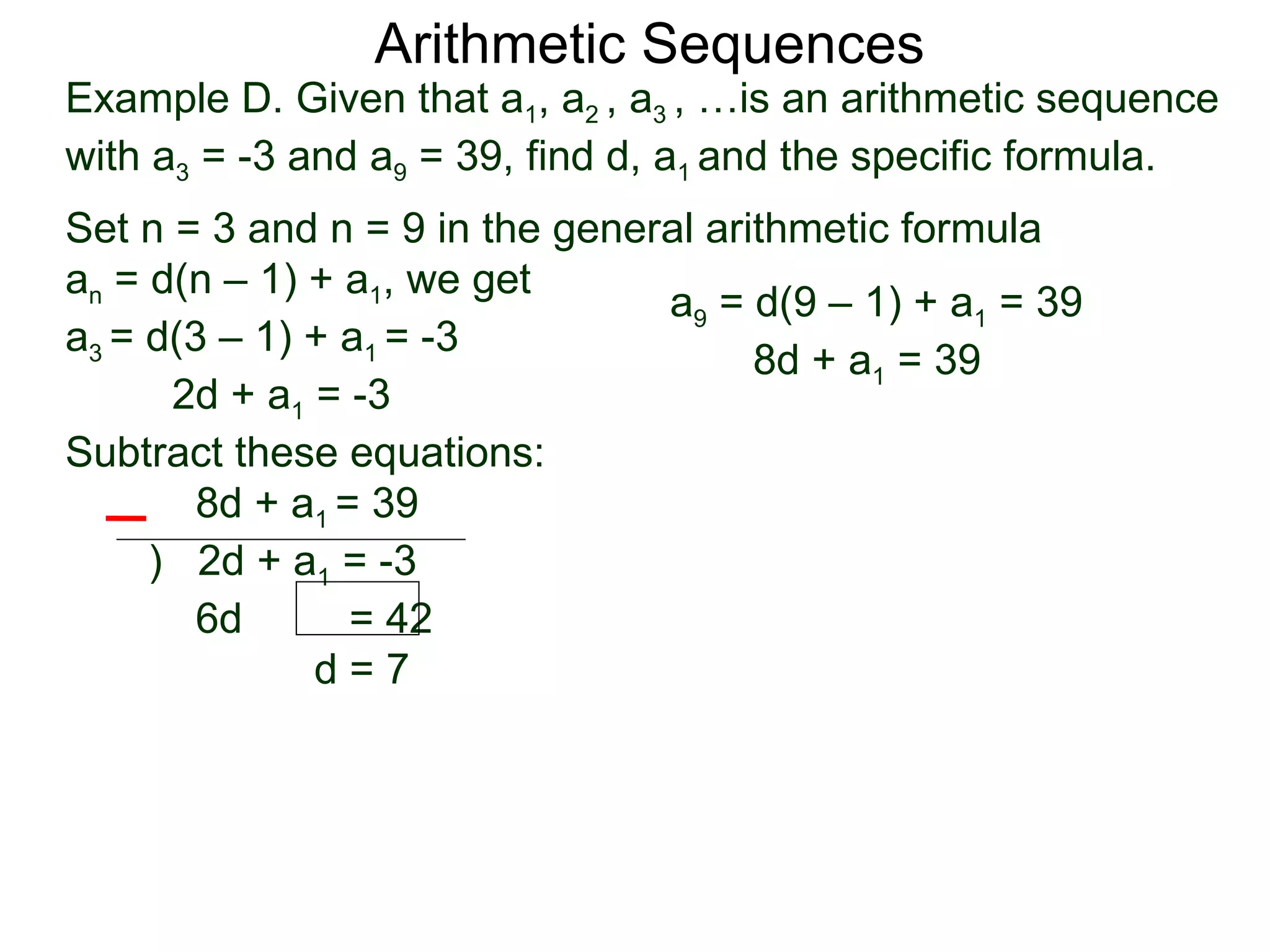
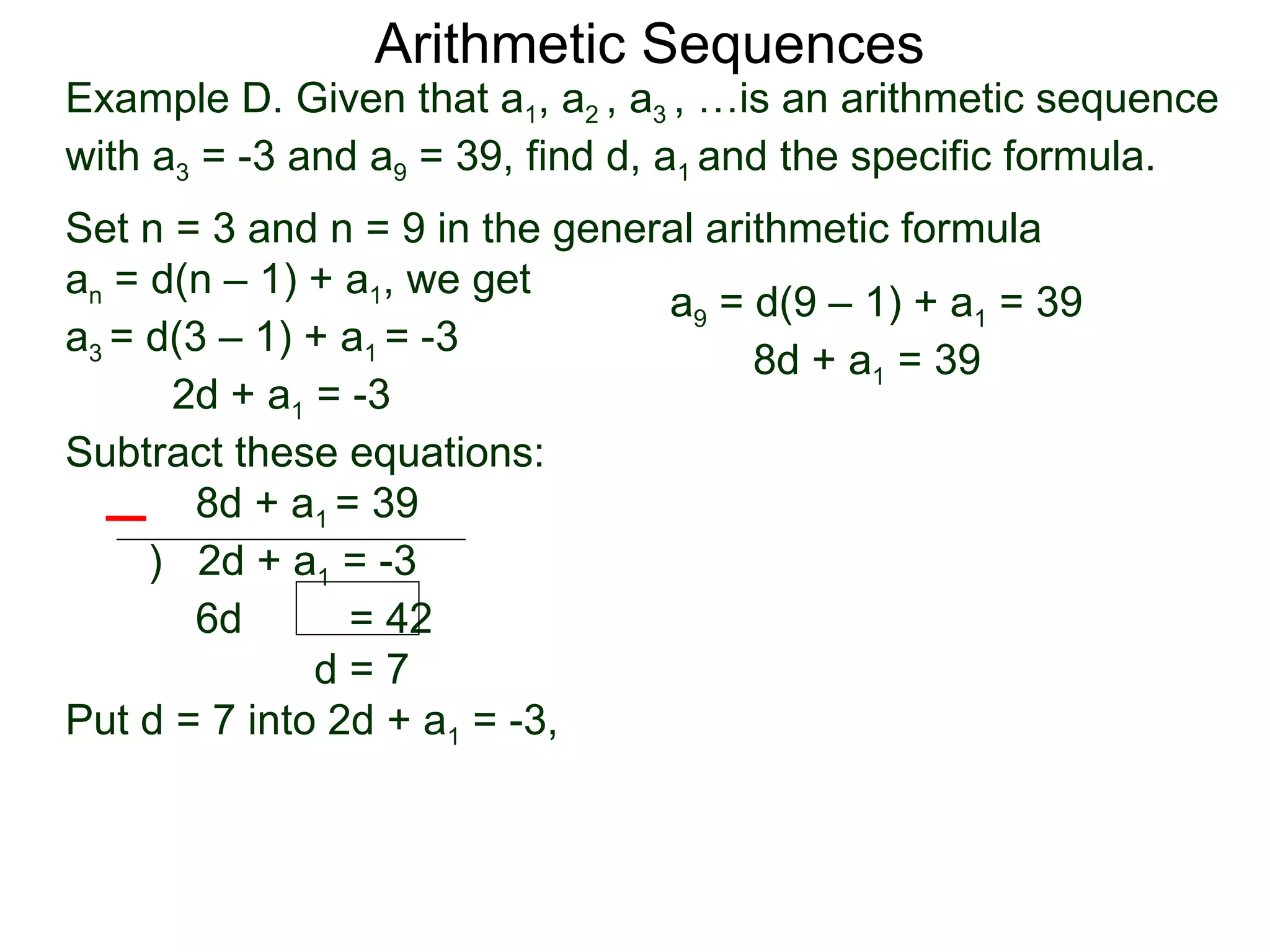
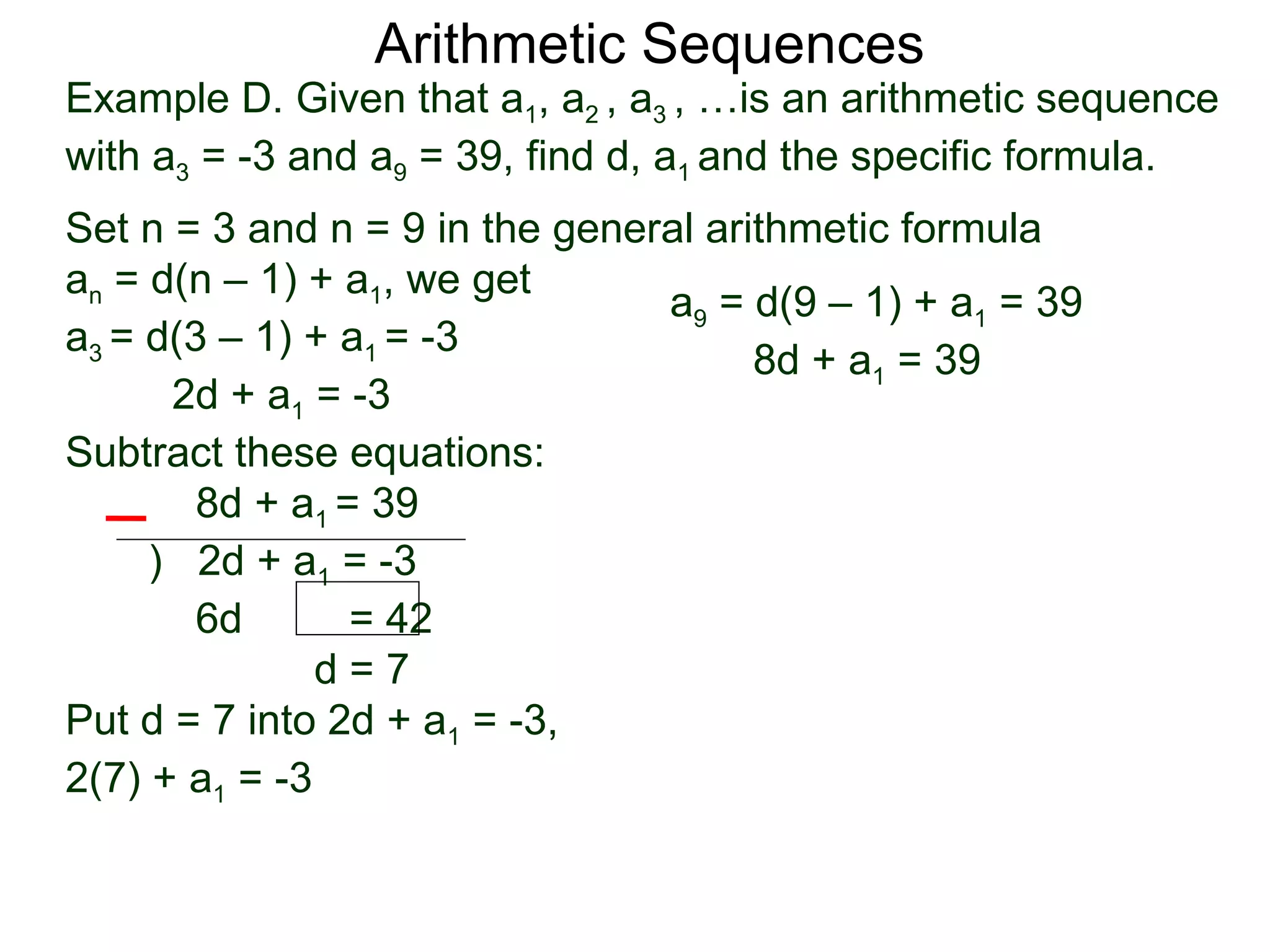
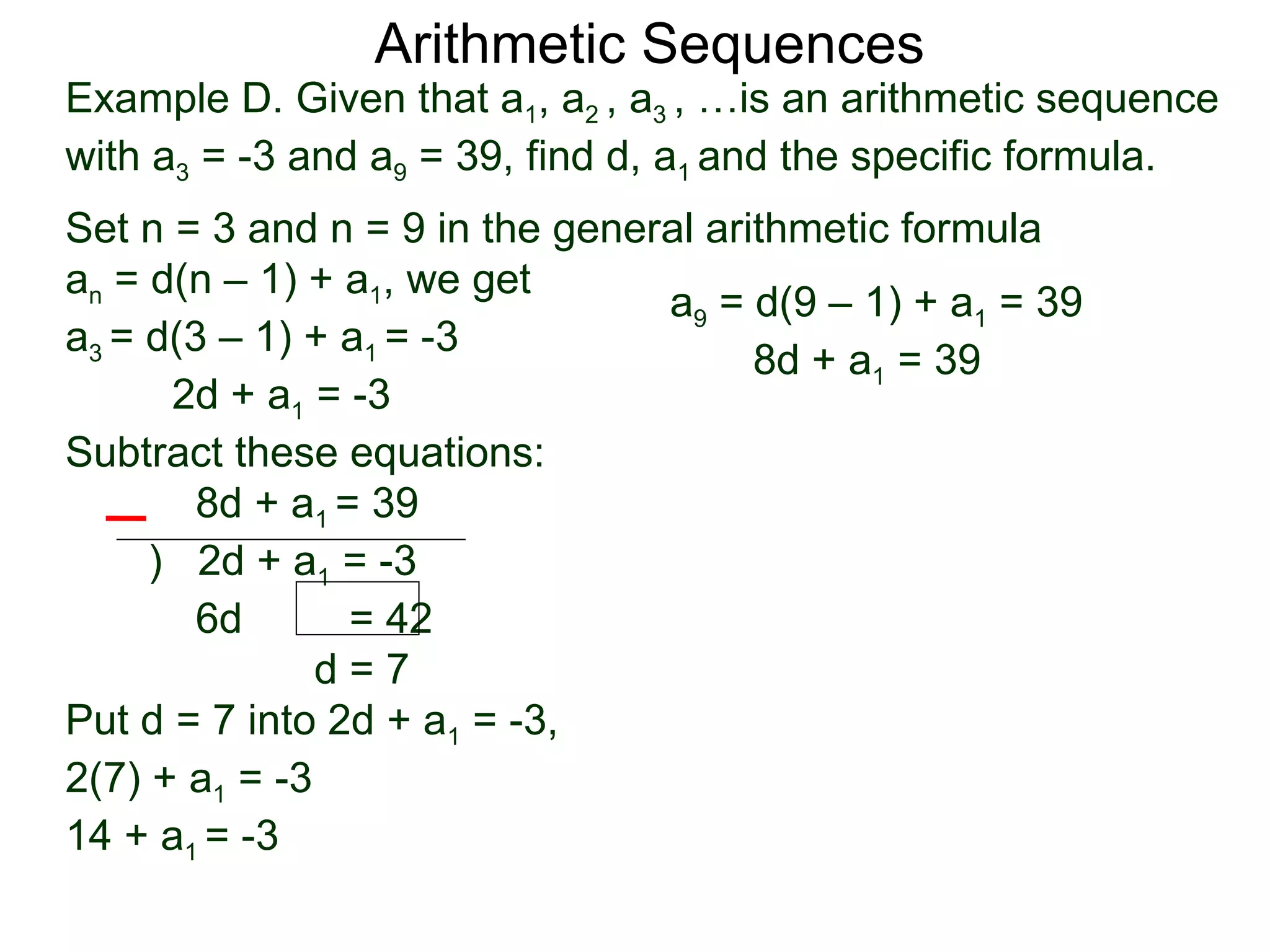
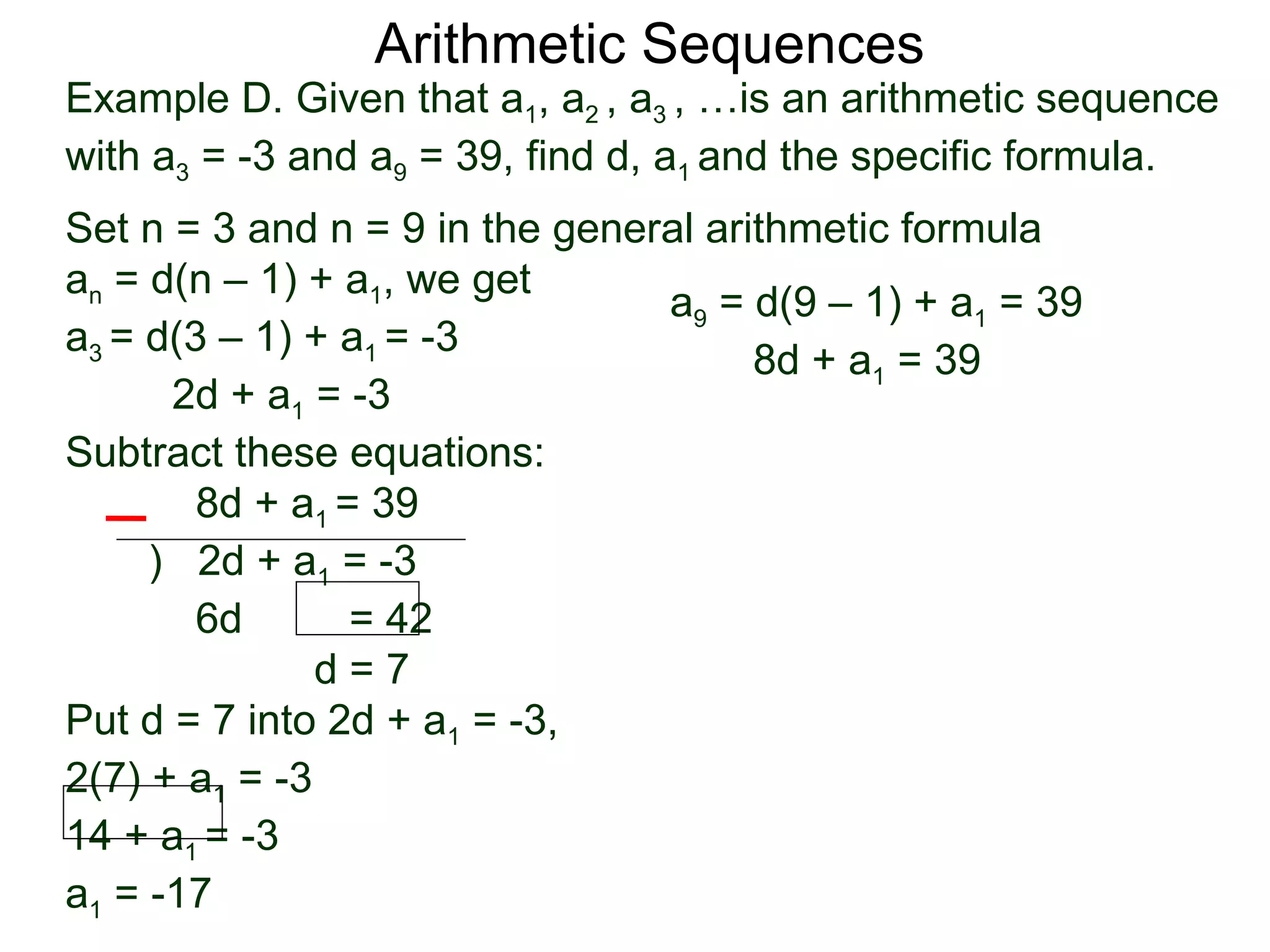
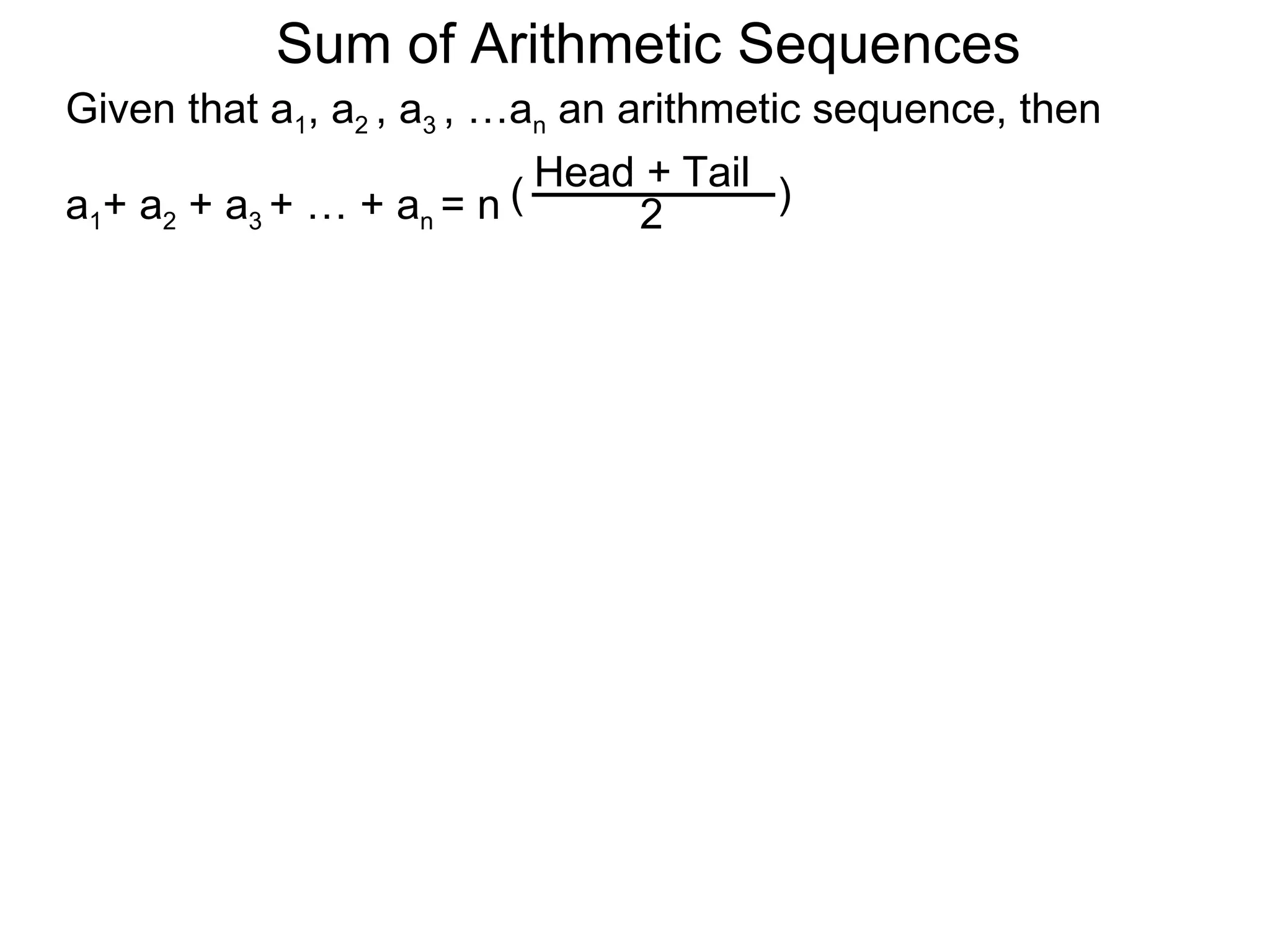
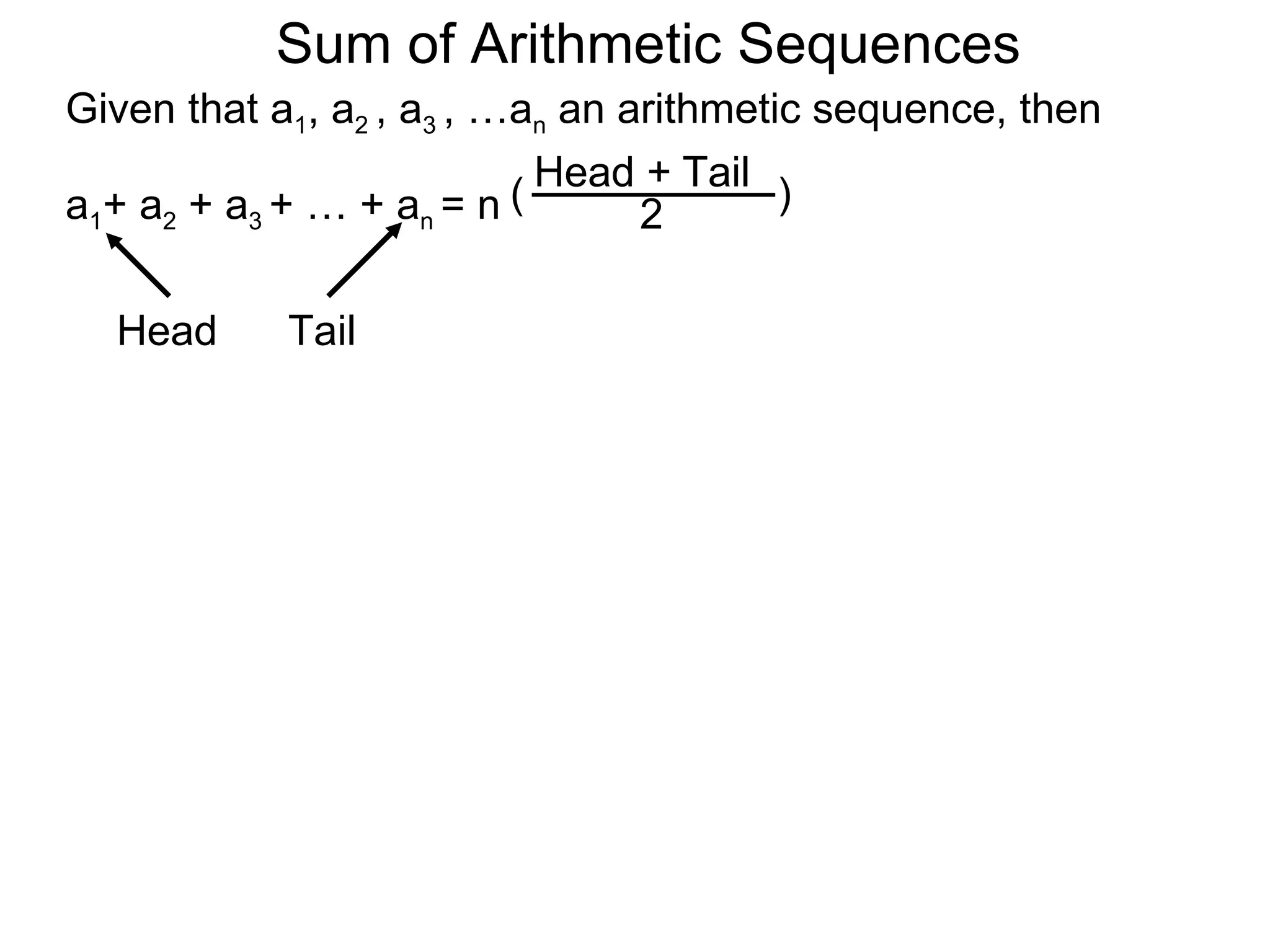
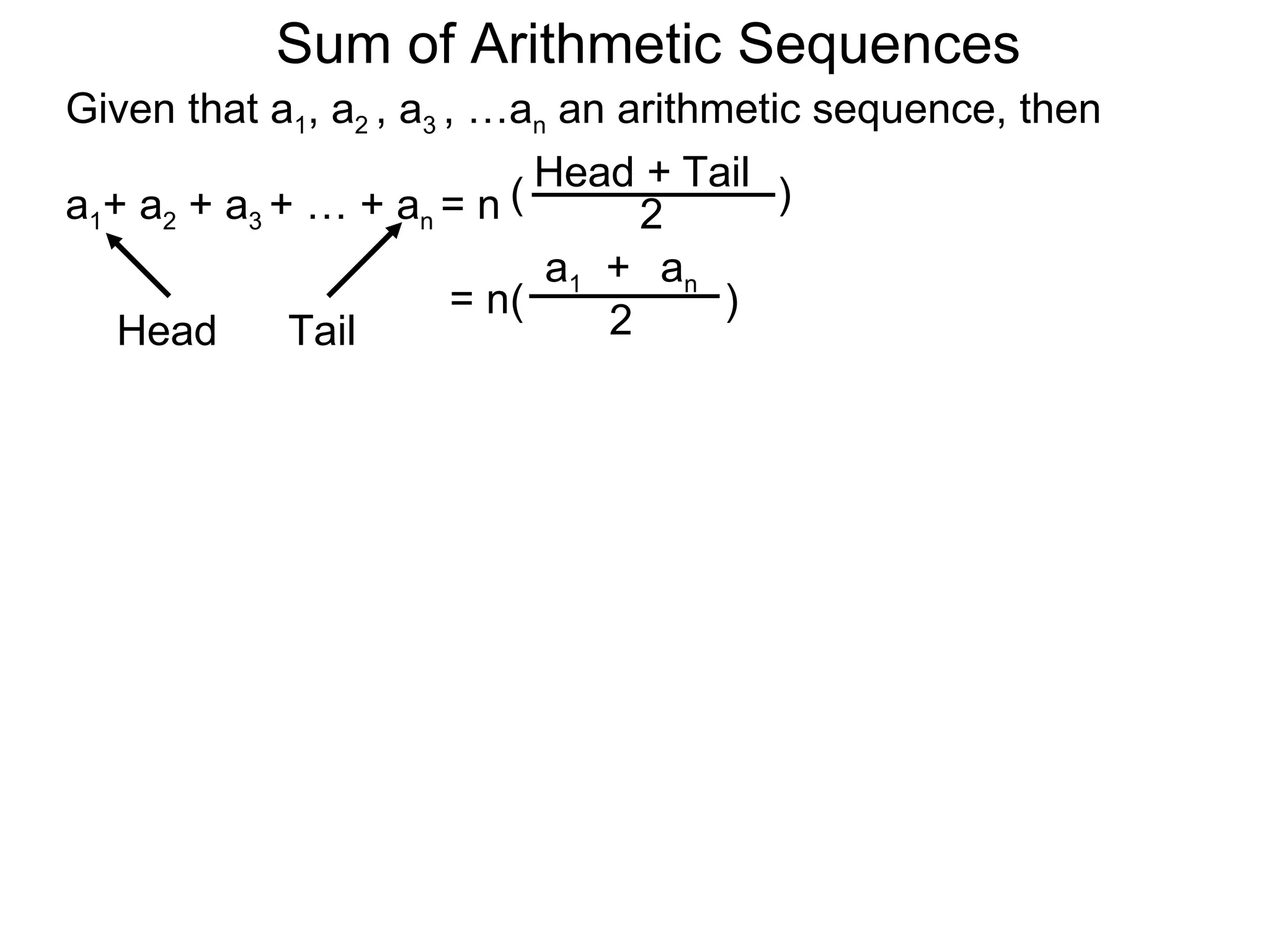
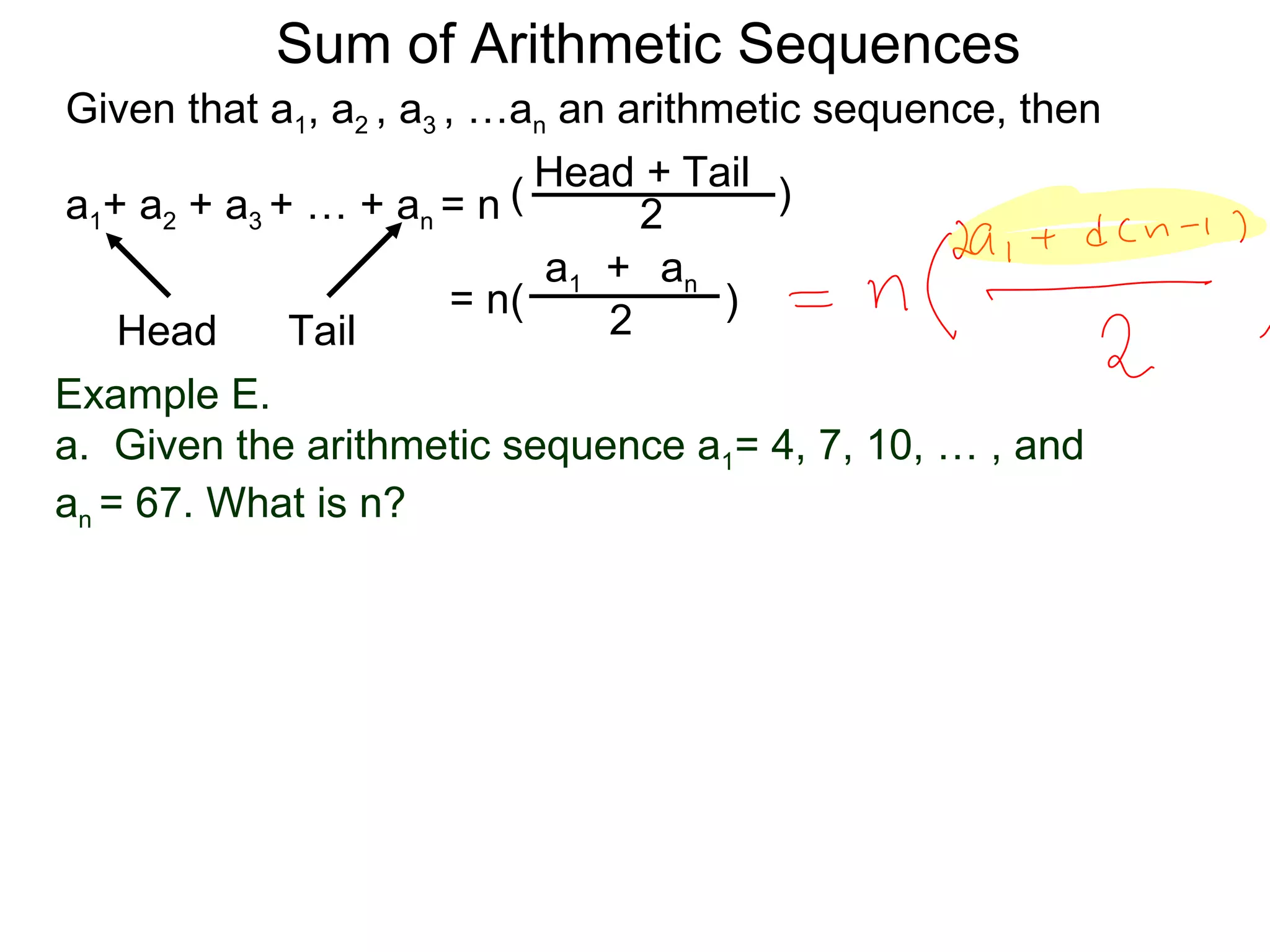
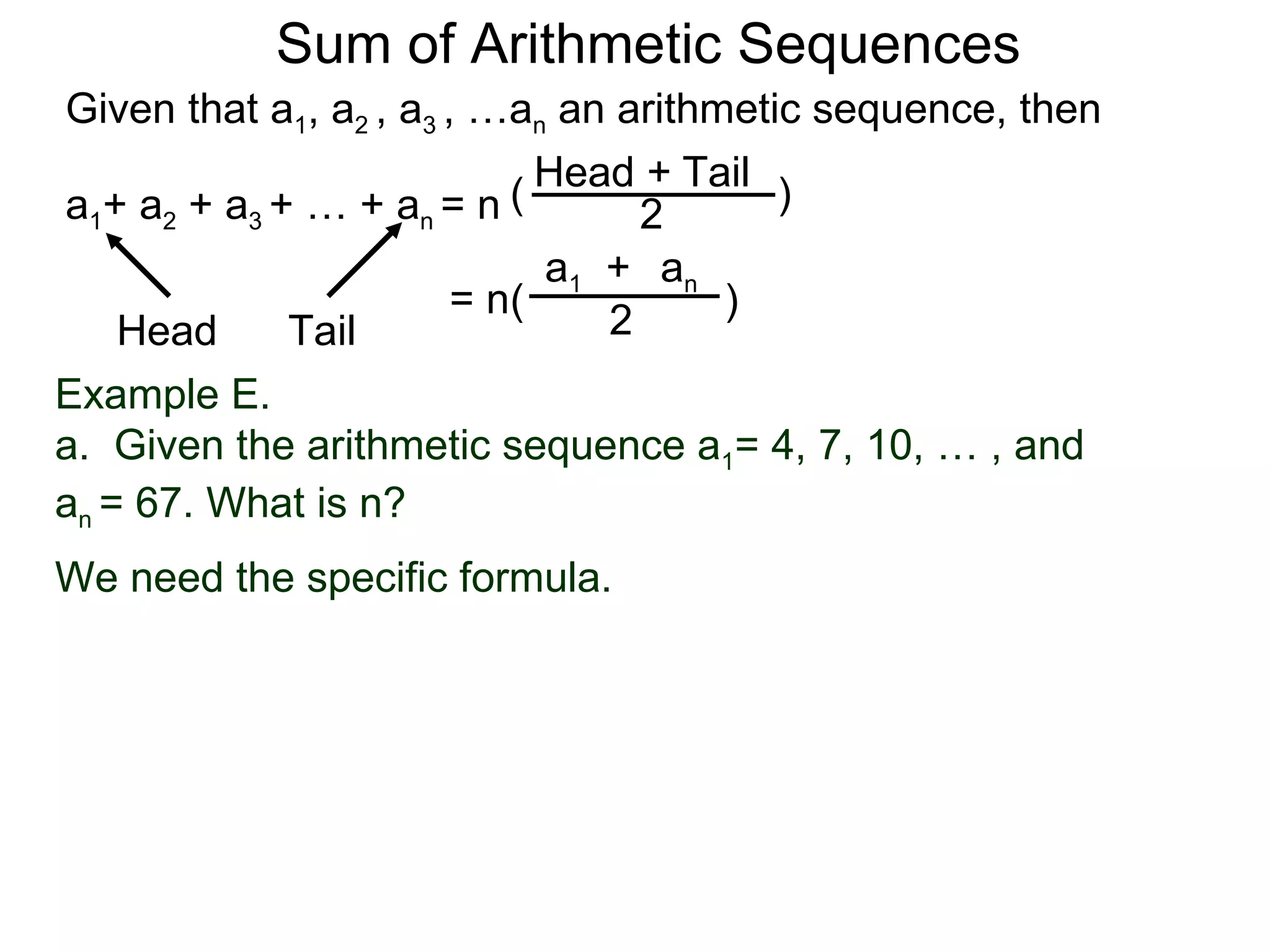
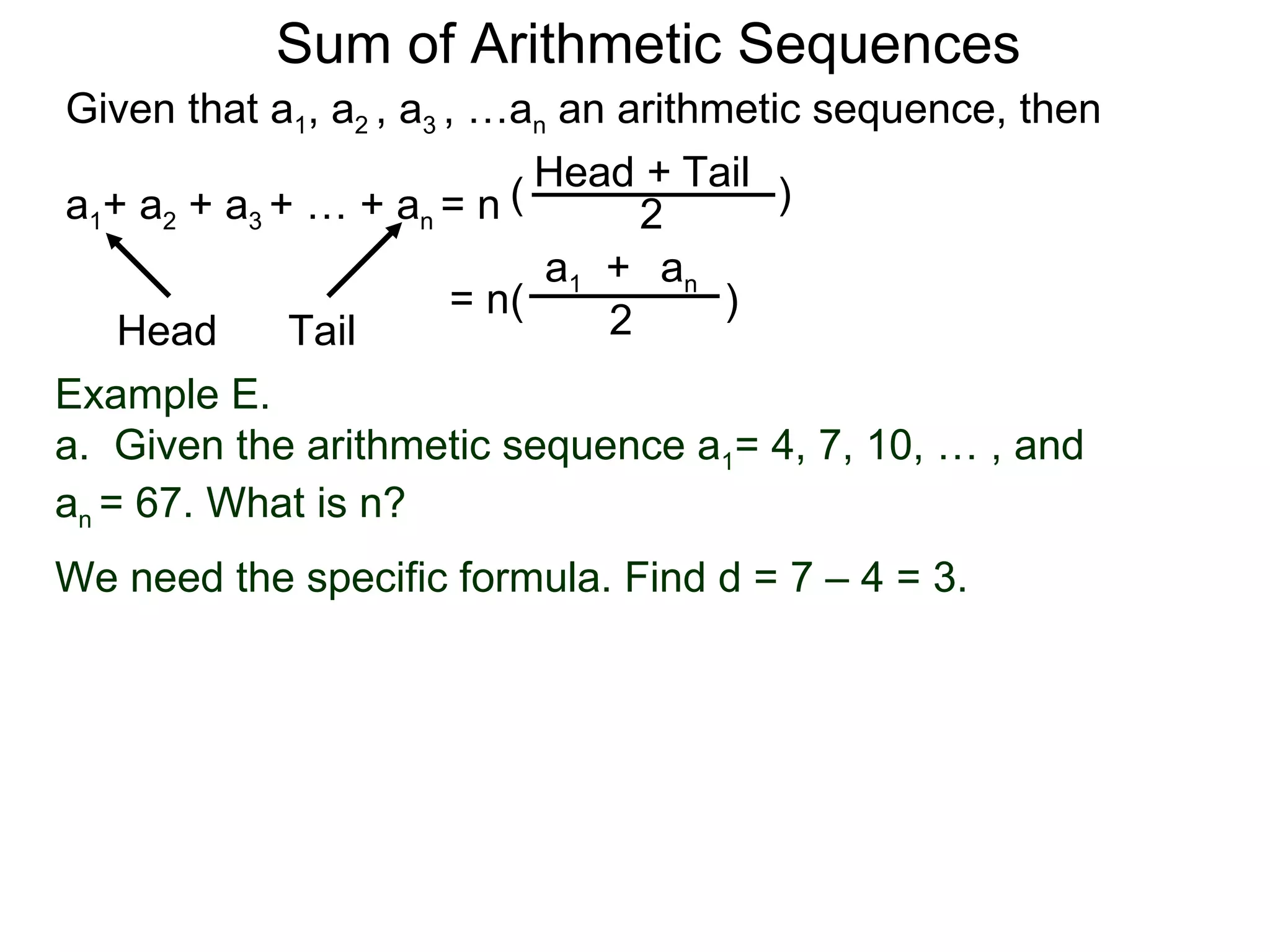
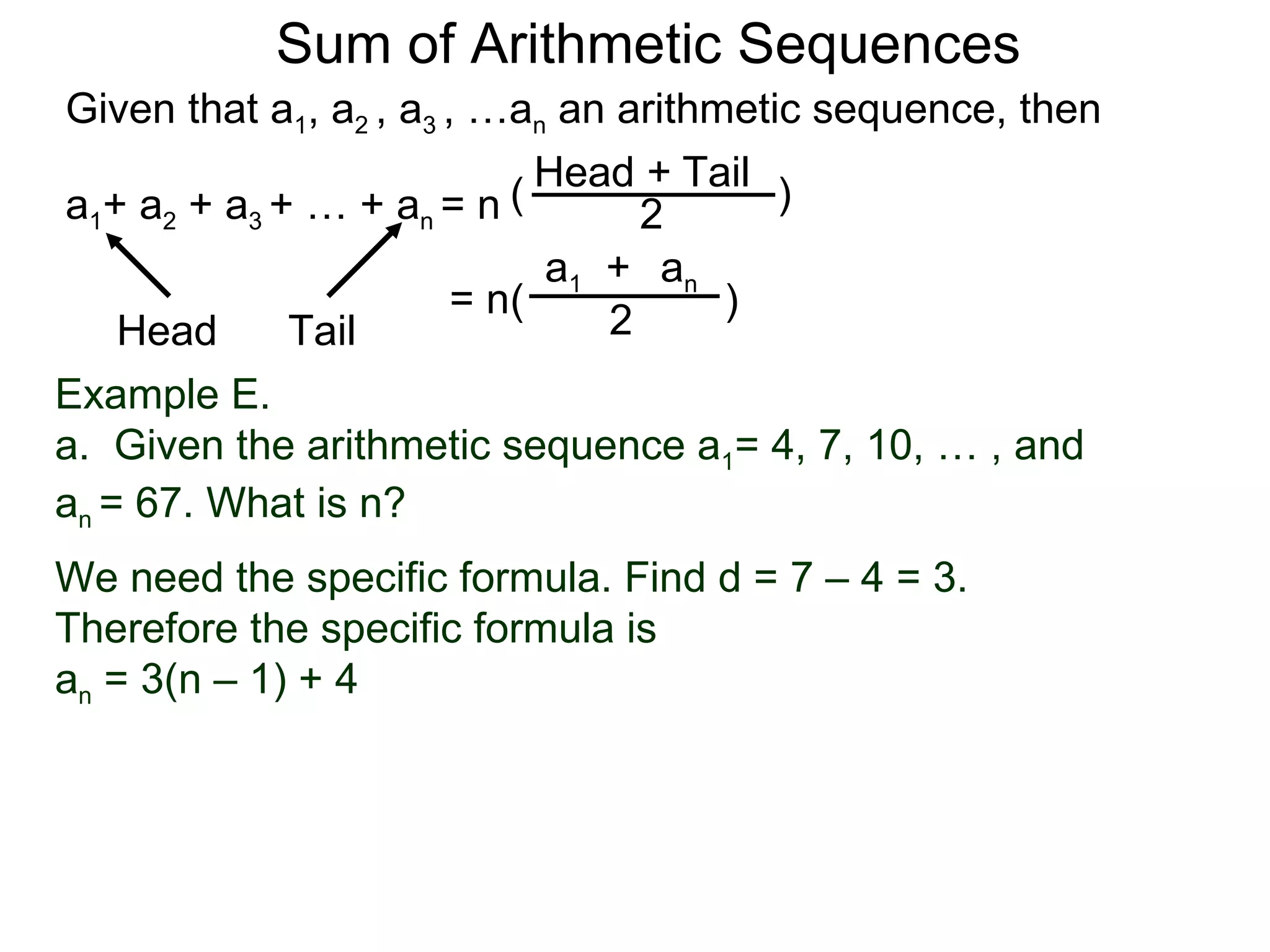
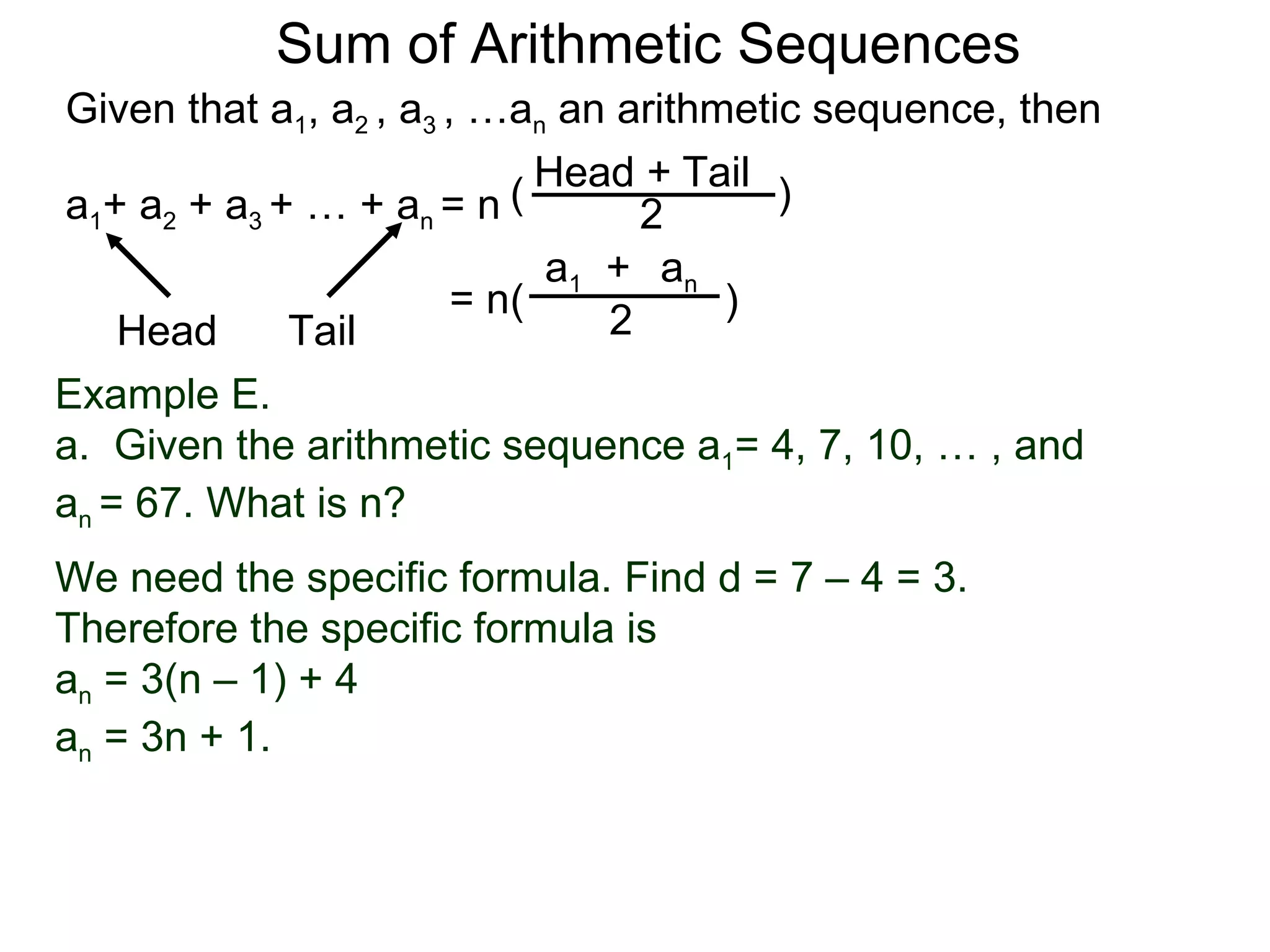
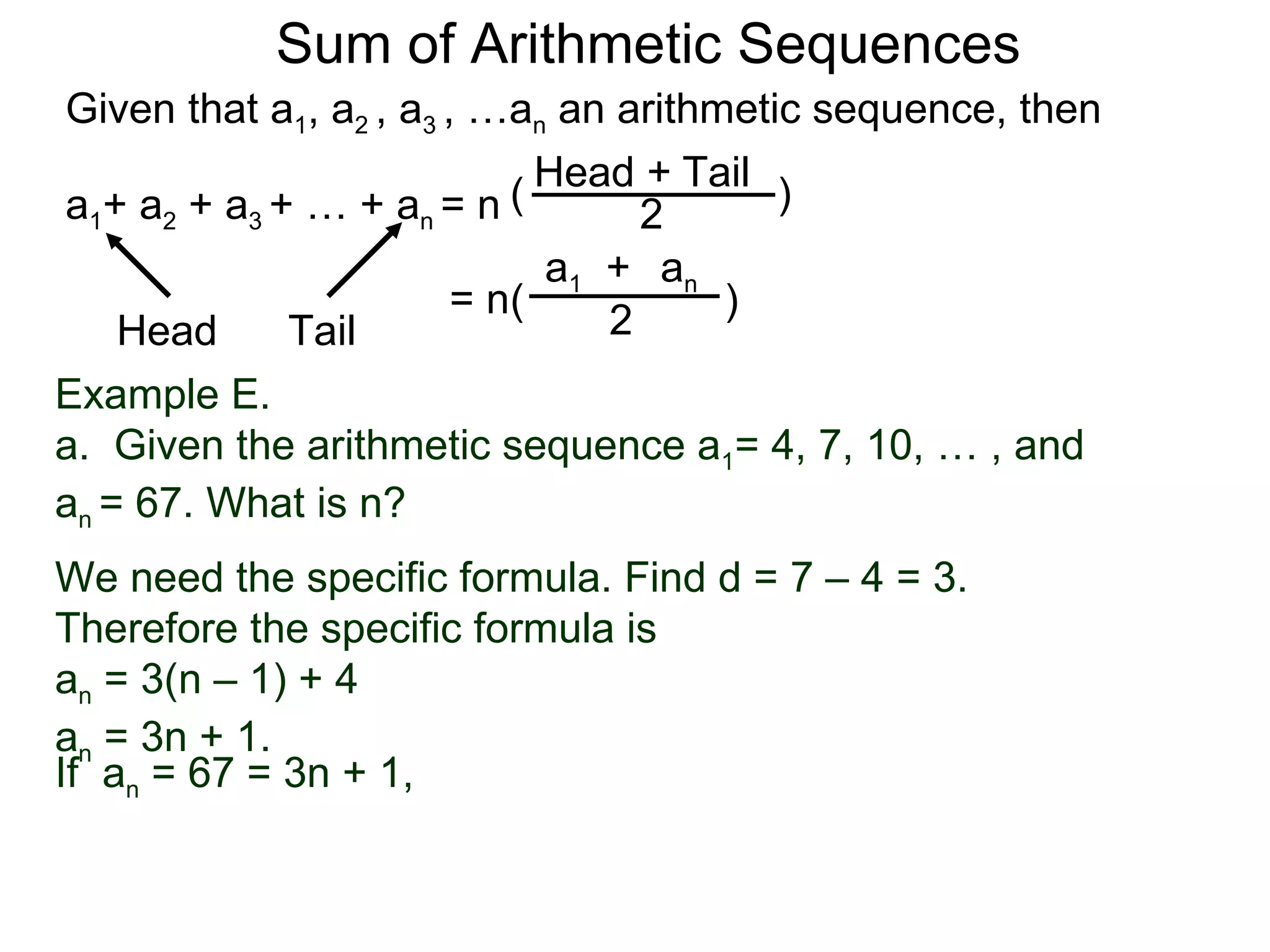
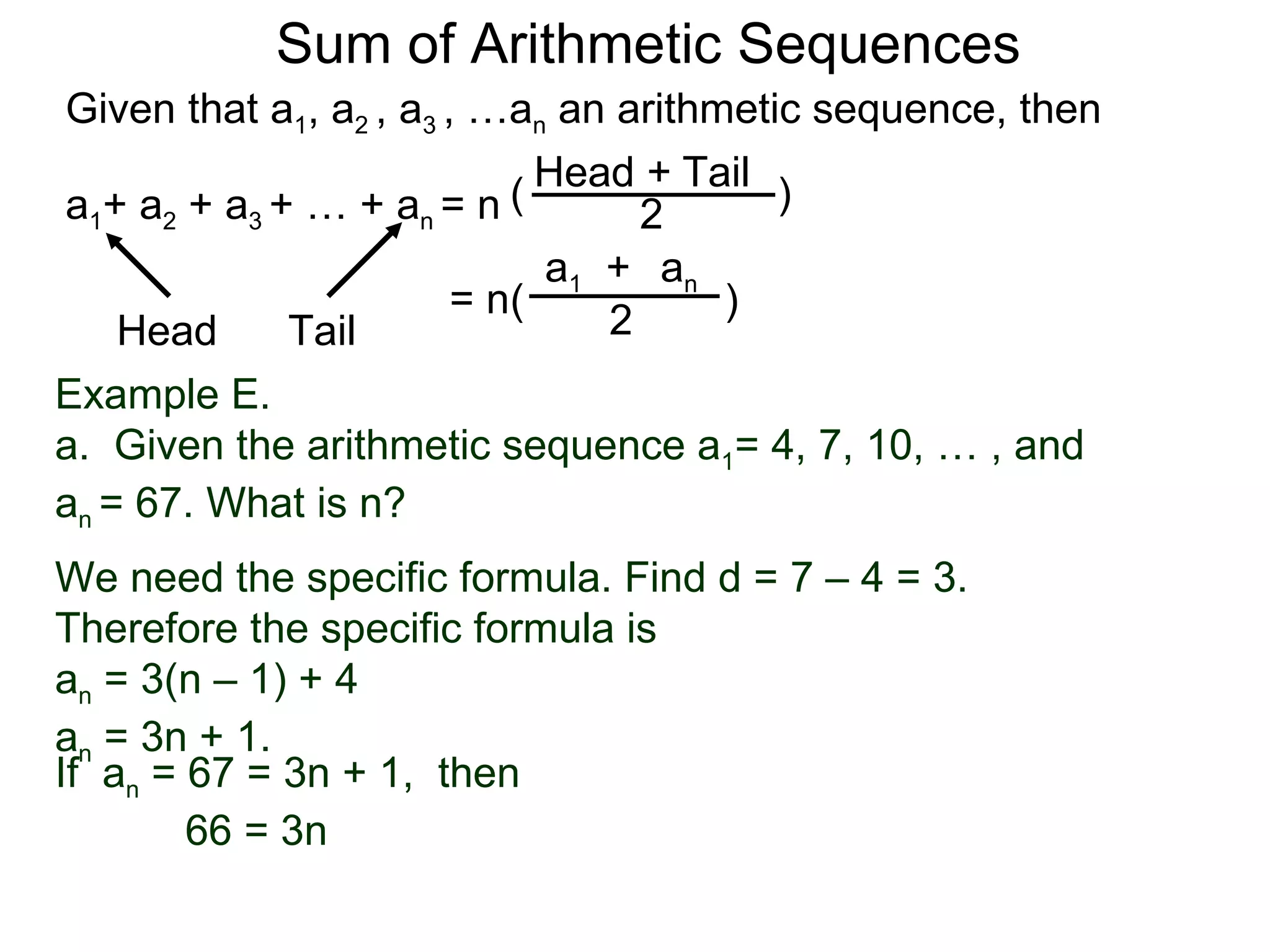
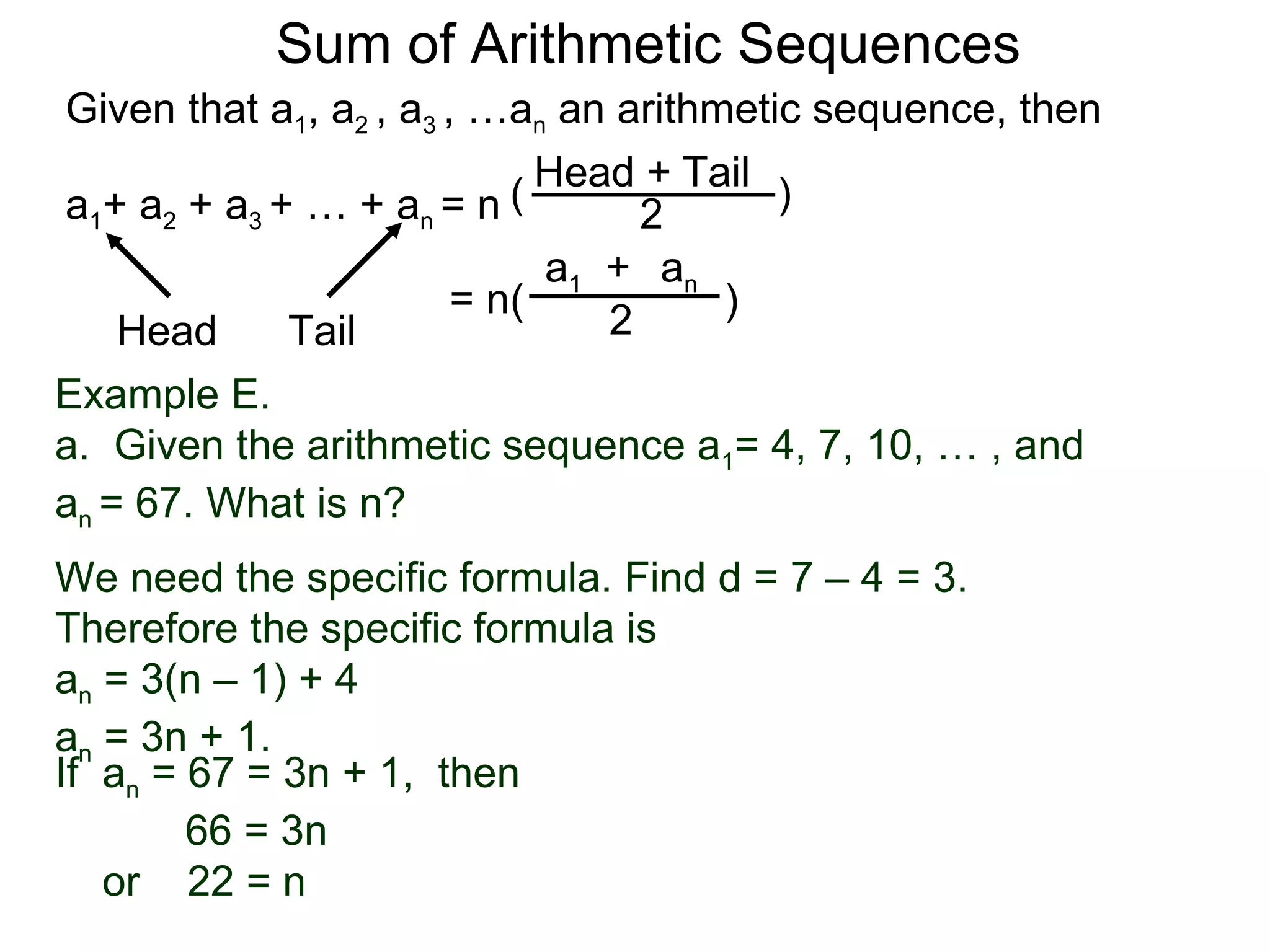
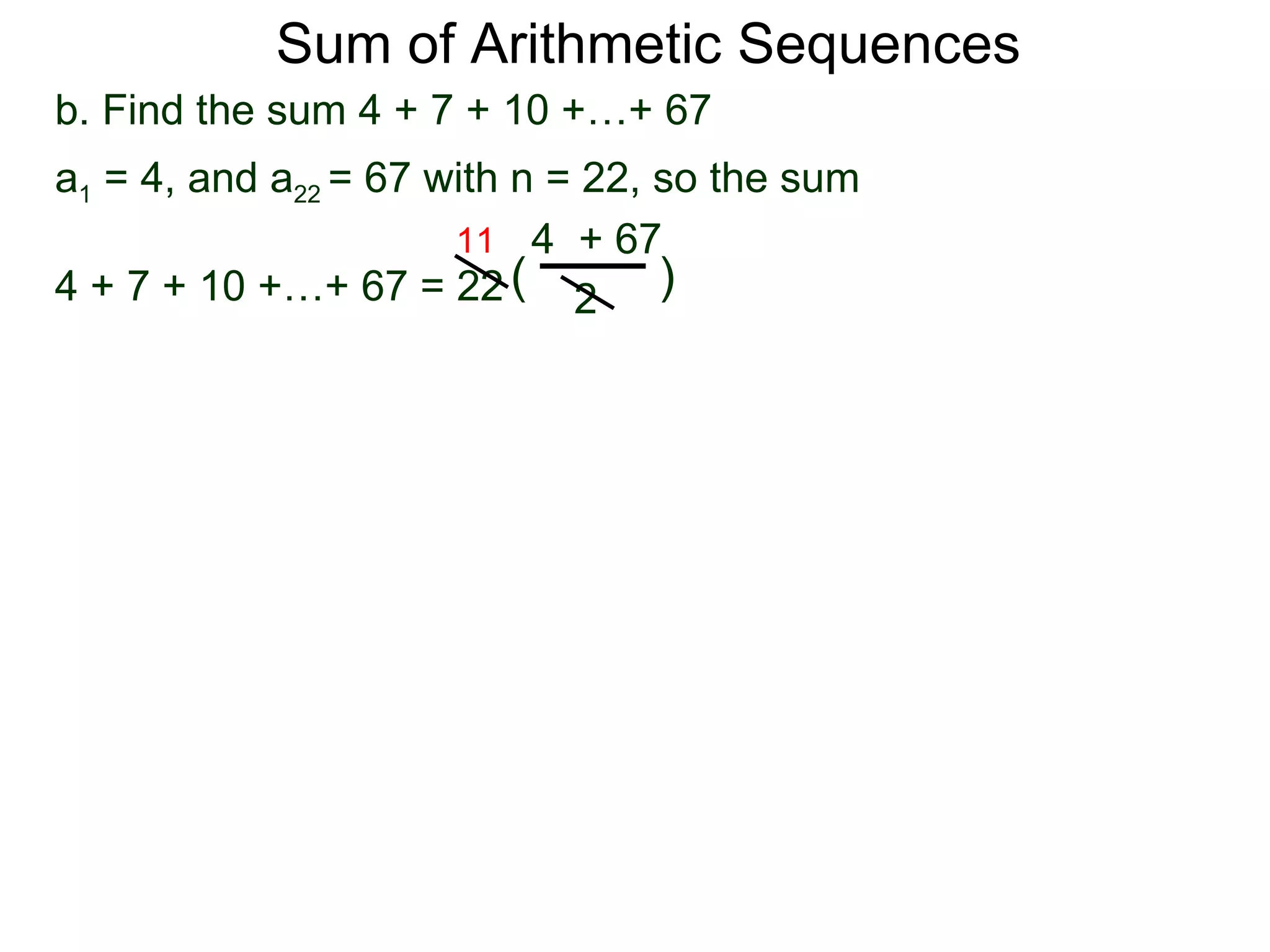
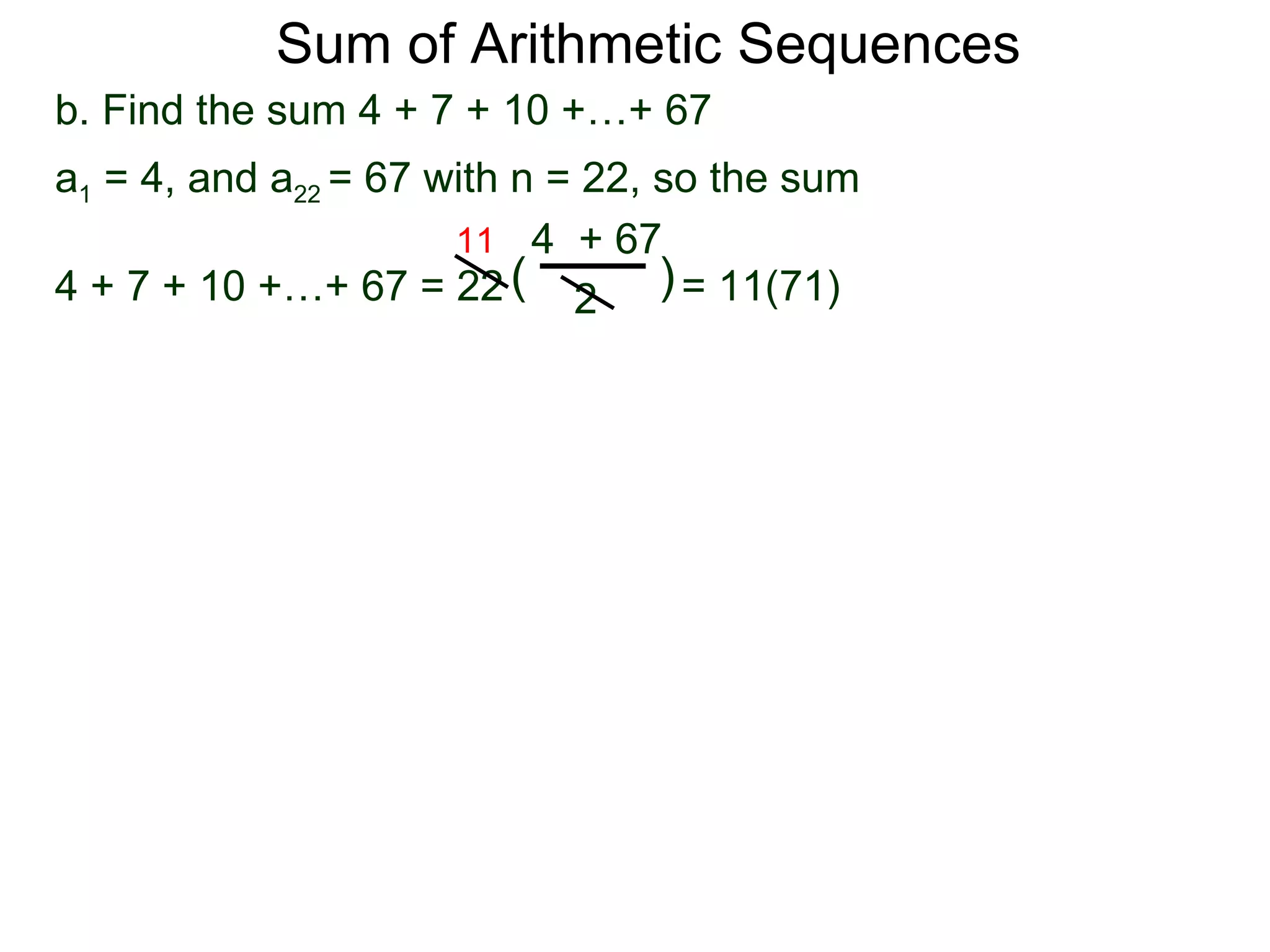
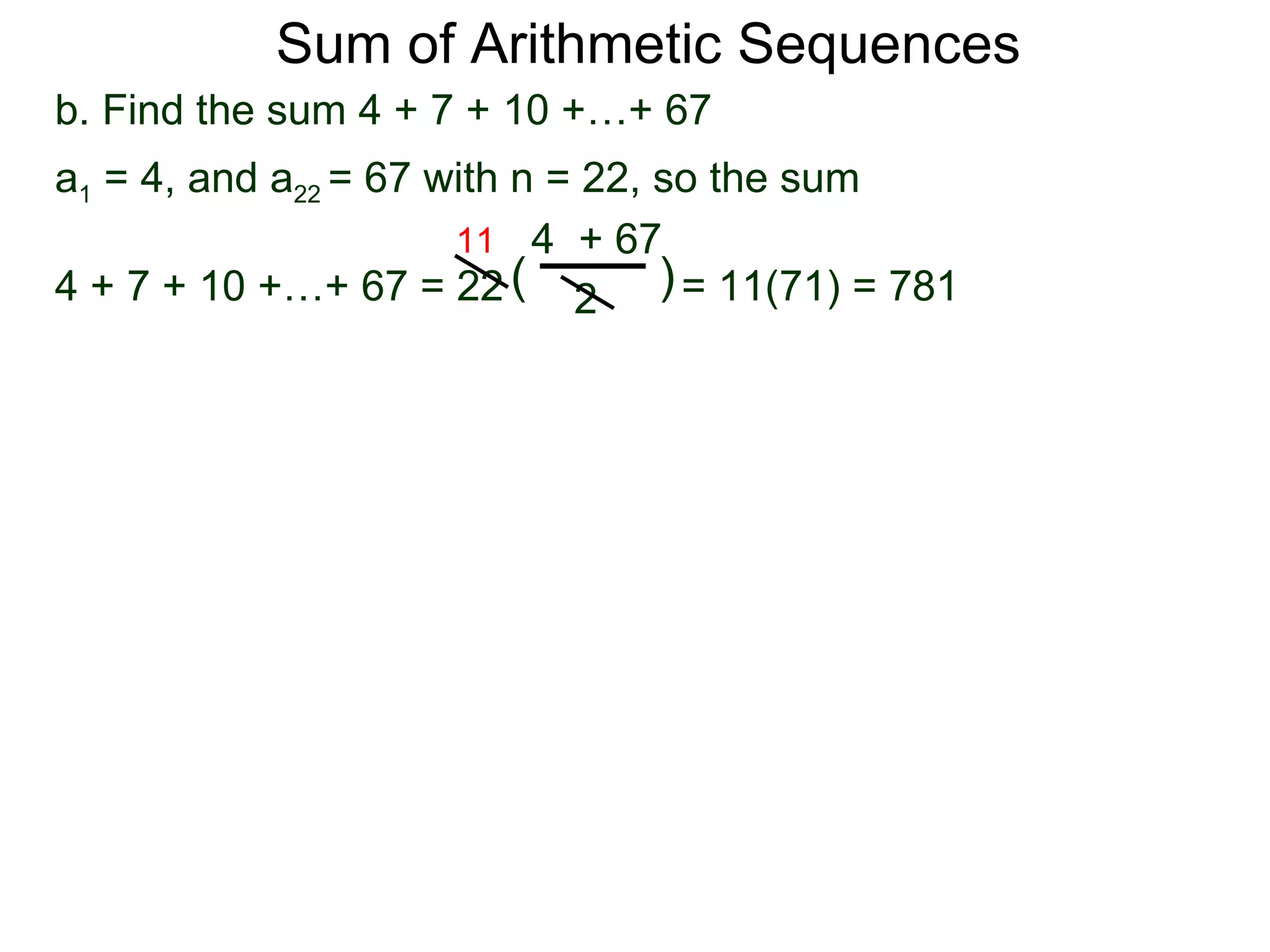
The document defines an arithmetic sequence as a sequence where the nth term is defined by a linear formula of the form an = d*n + c. It provides examples of arithmetic sequences and explains the general formula for finding any term in an arithmetic sequence if the first term (a1) and the common difference (d) between terms are known. It demonstrates using the general formula to find the specific formula for various arithmetic sequences given parts of the sequence.