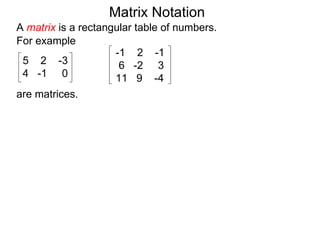
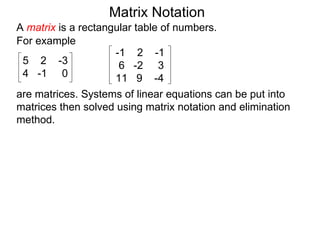
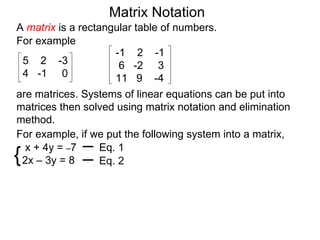
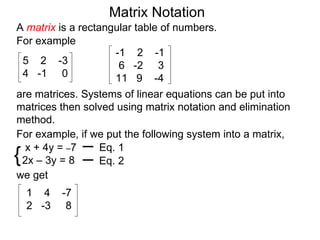
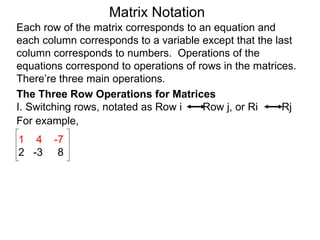
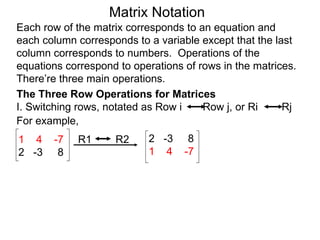
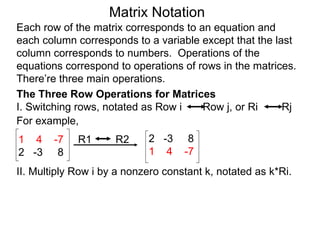
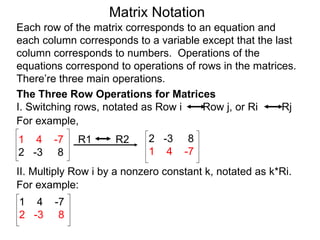
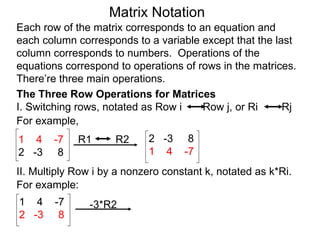
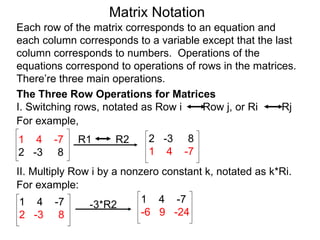
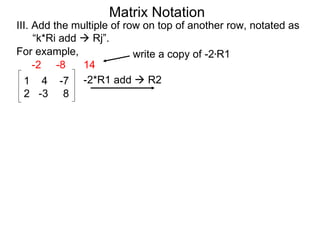
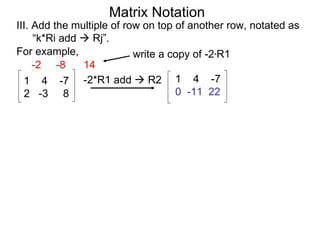
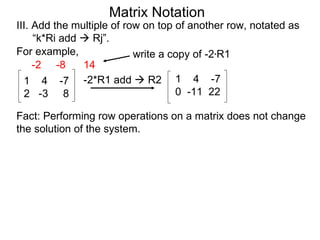
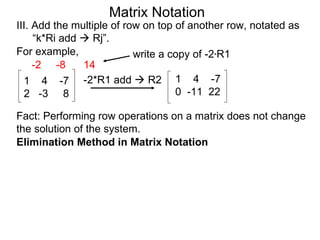
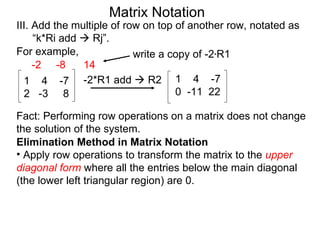
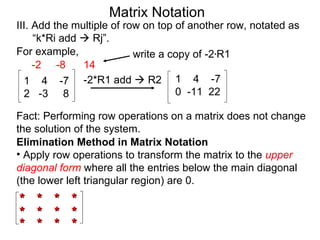
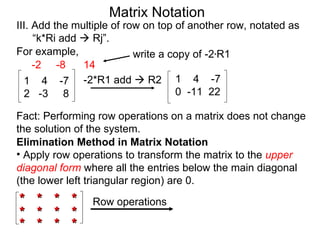
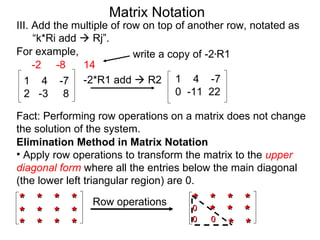
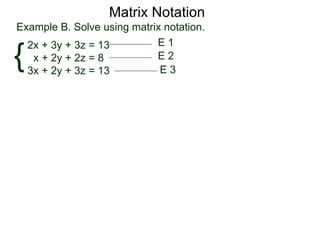
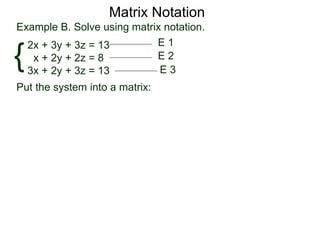
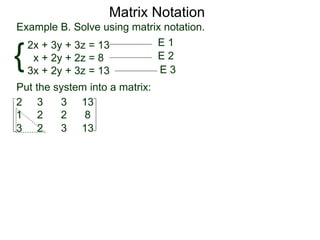
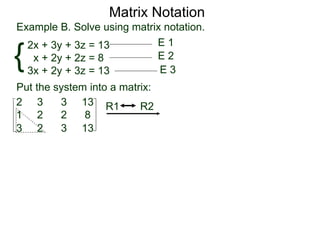
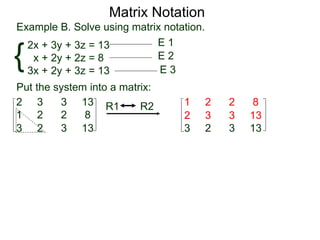
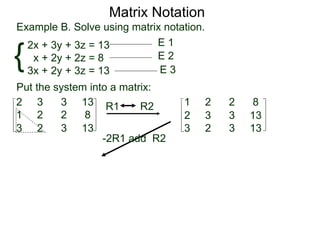
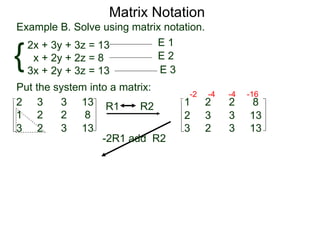
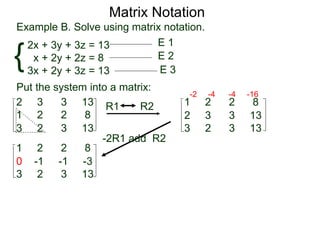
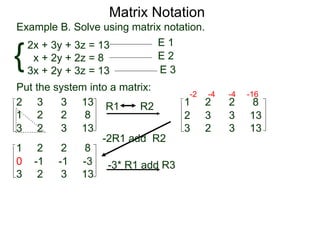
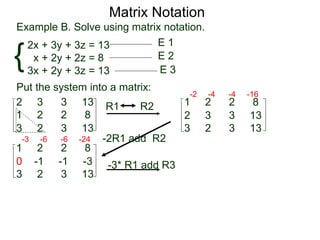
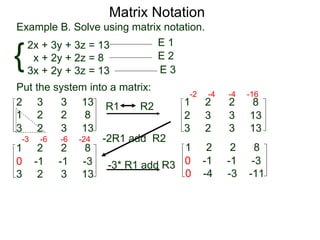
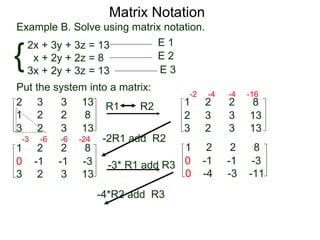
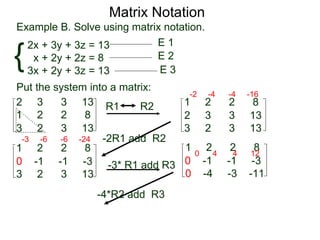
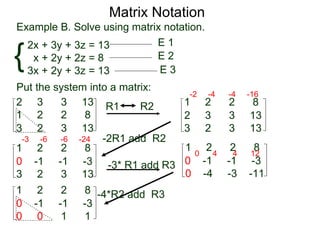
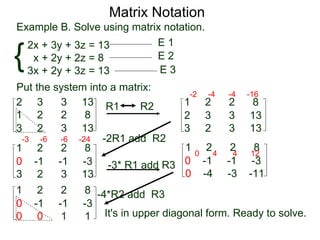
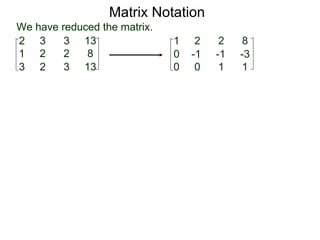
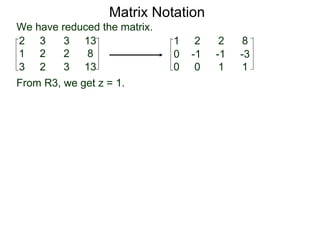
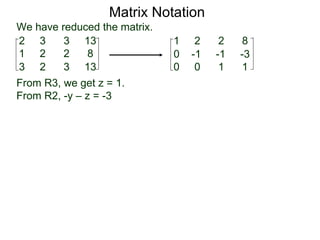
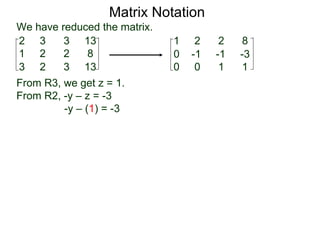
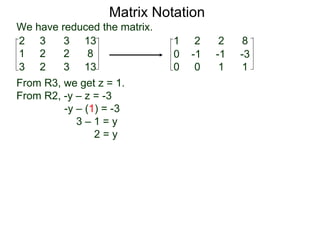
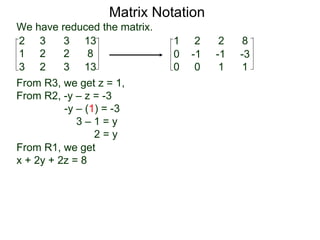
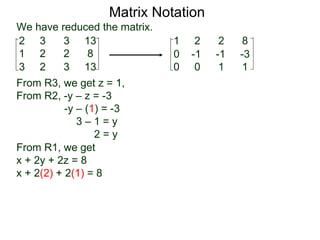
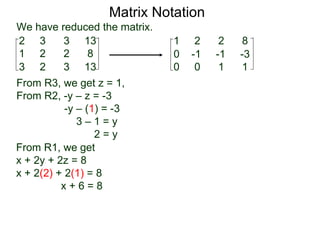
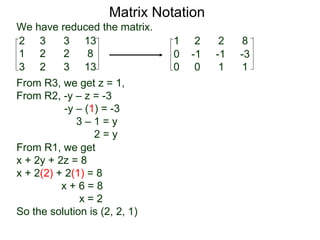
The document discusses matrix notation for representing and solving systems of linear equations. A matrix is defined as a rectangular table of numbers, and systems of linear equations can be represented as matrices with rows corresponding to equations and columns to variables. Three row operations - row switching, row scaling, and adding row multiples - can be performed on matrices while preserving the solution(s) to the corresponding system of equations. The elimination method uses row operations to transform a matrix representing a system into upper triangular form to solve for the variables.