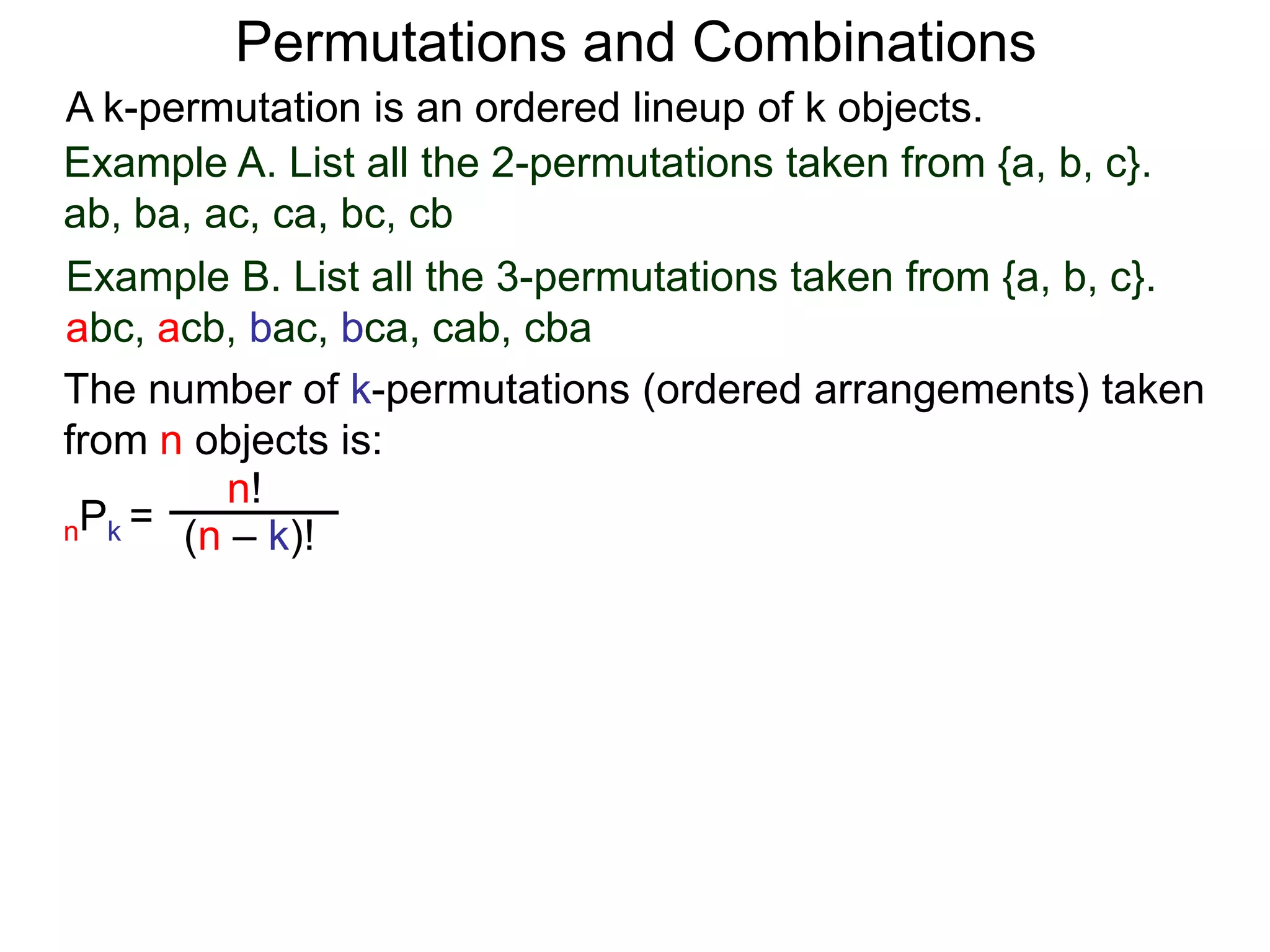
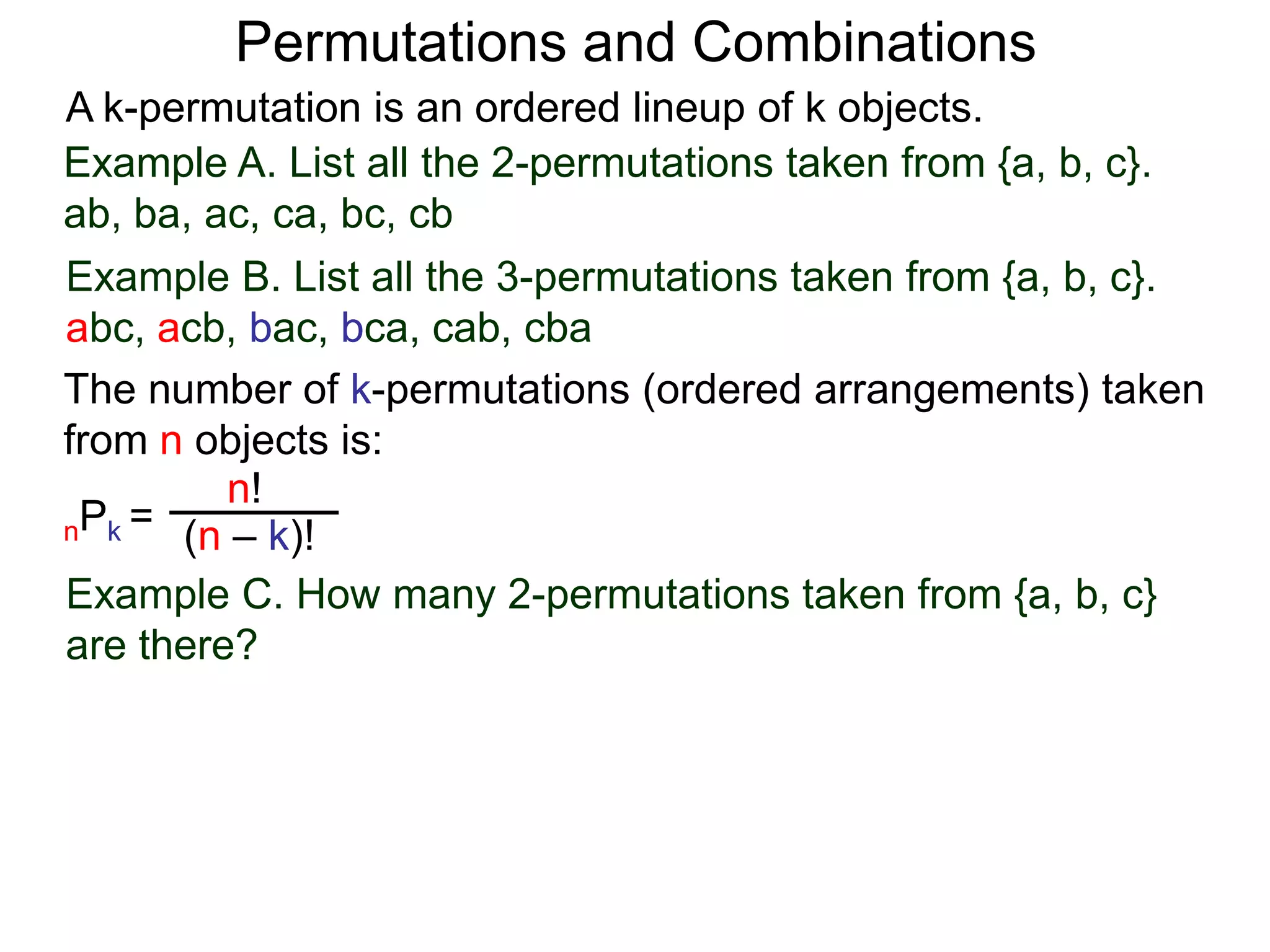
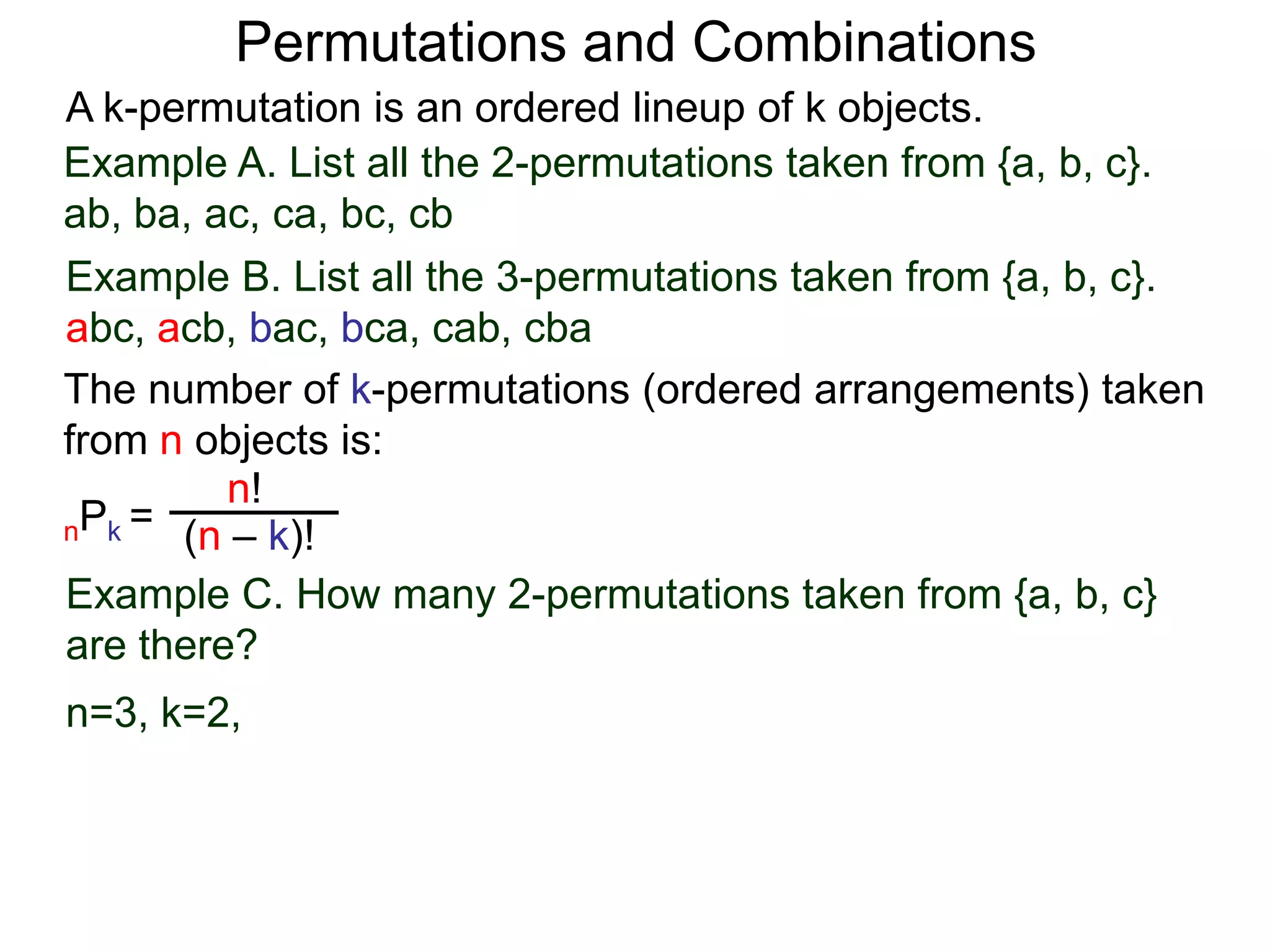
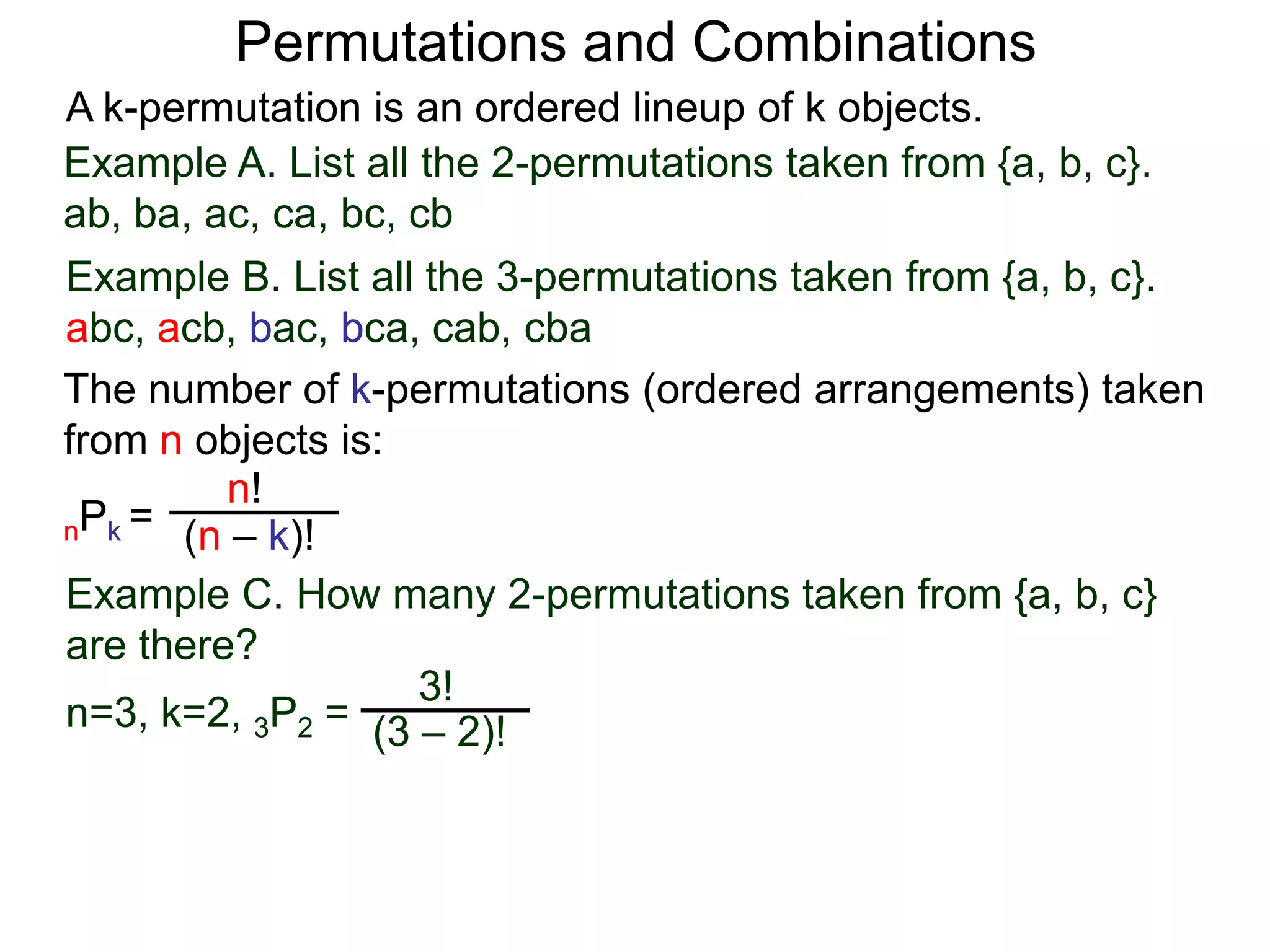
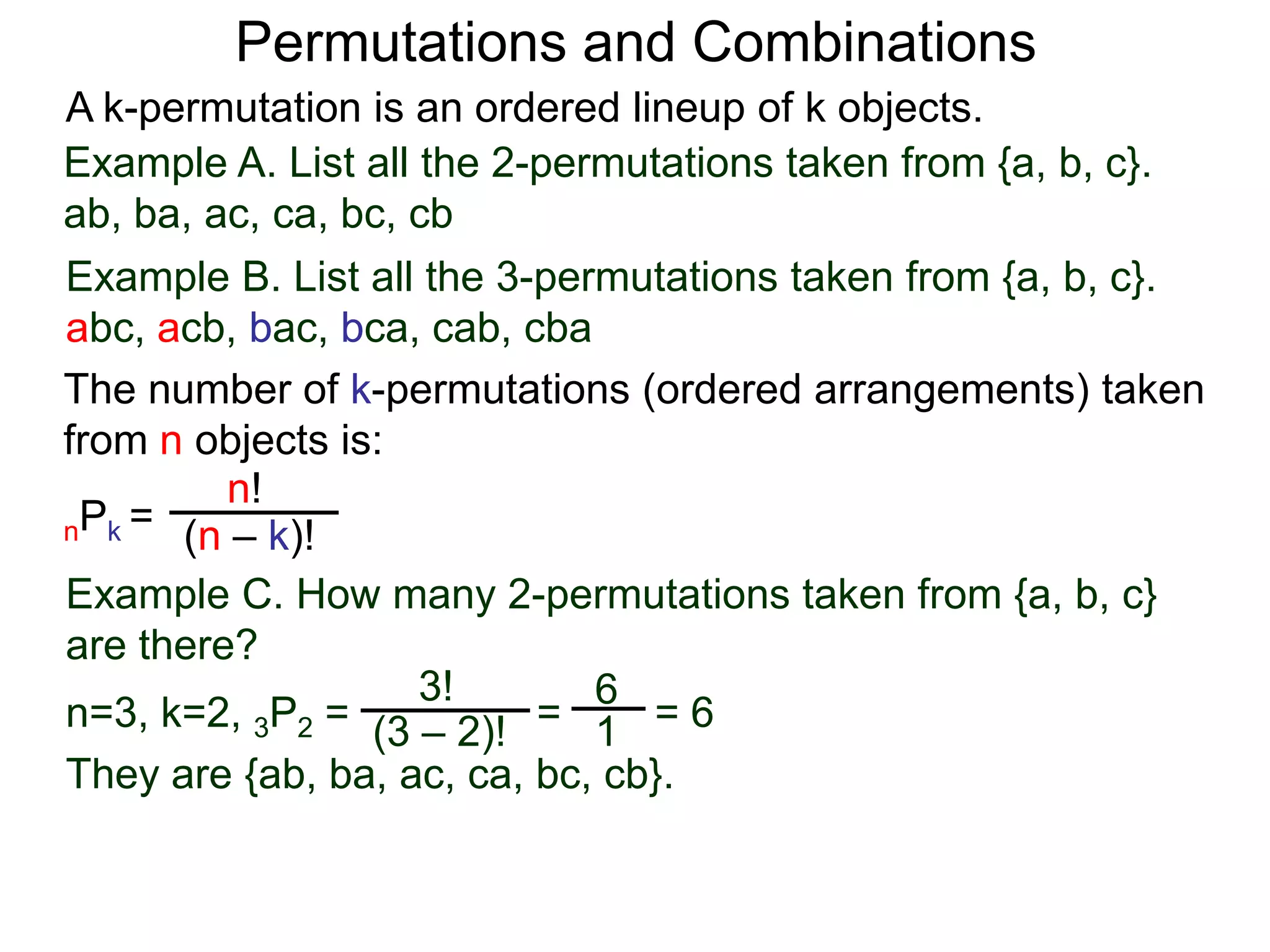
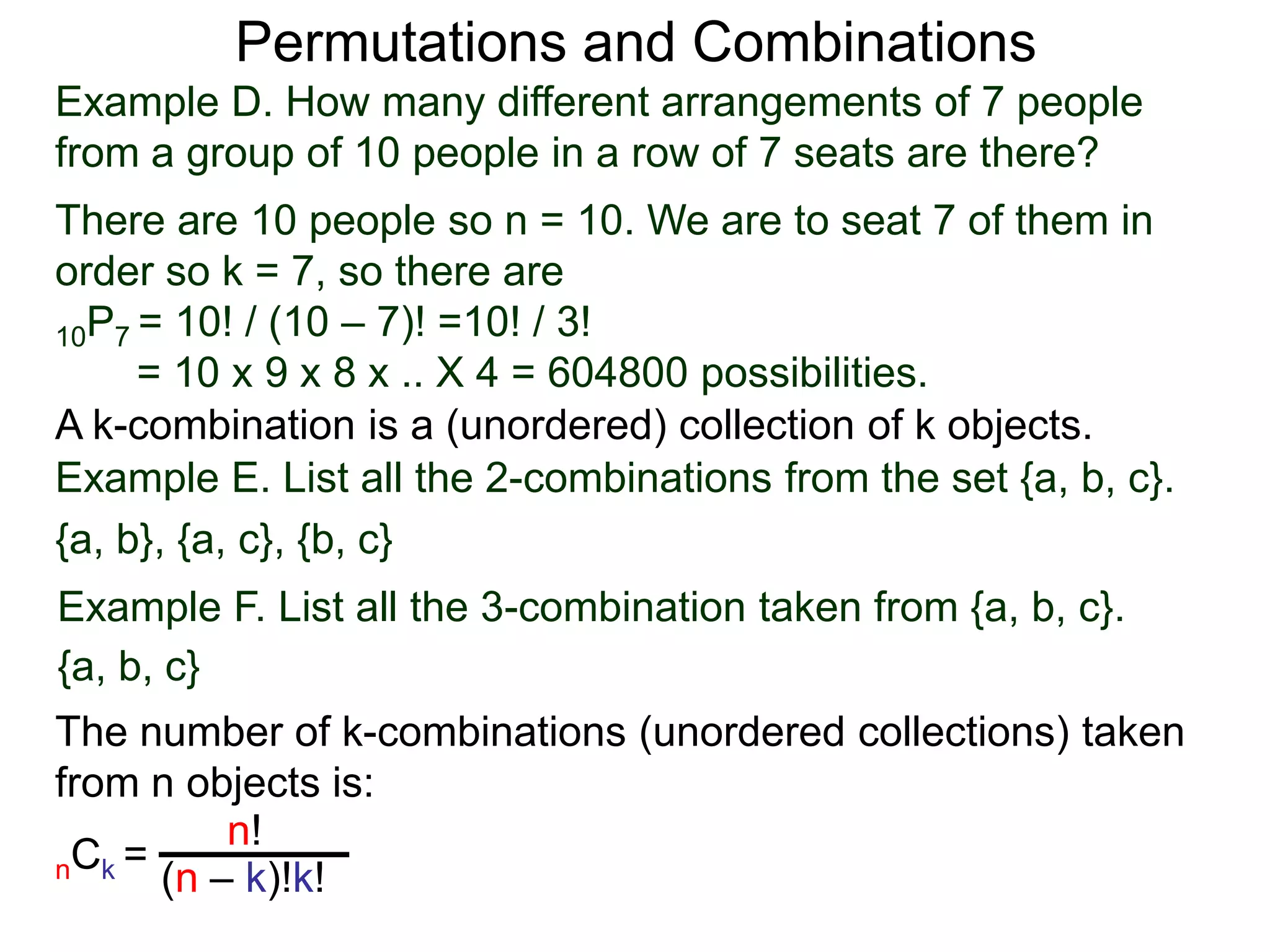
The document defines permutations and combinations. A k-permutation is an ordered lineup of k objects taken from a set of n objects. The number of k-permutations of n objects is nPk = n!/(n-k)!. A k-combination is an unordered collection of k objects from a set of n objects. The number of k-combinations of n objects is nCk = n!/(n-k)!k!. Several examples are provided to illustrate calculating the number of permutations and combinations.