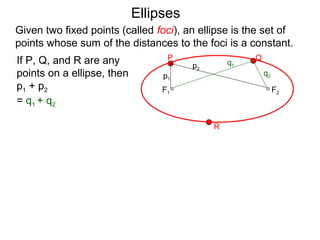
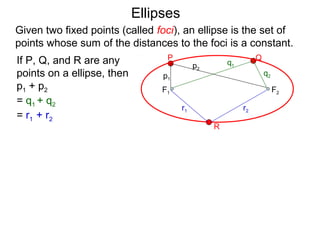
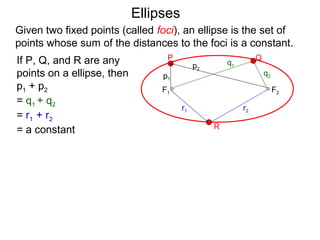
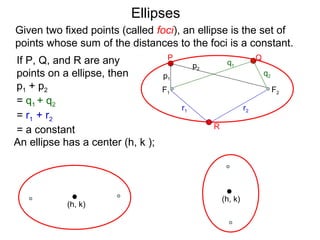
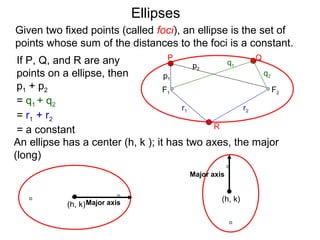
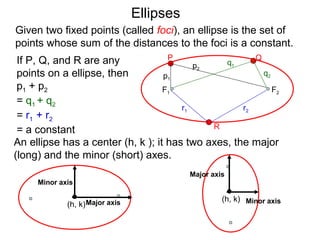
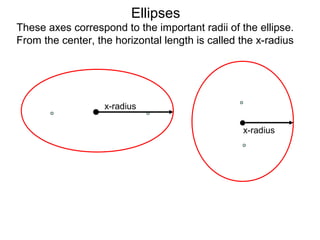
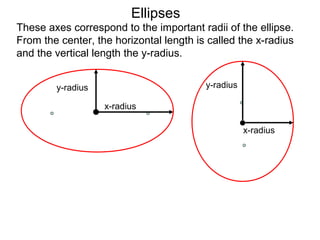
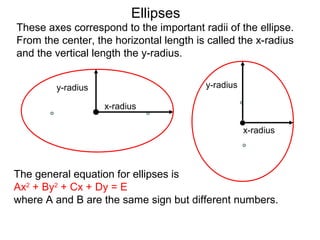
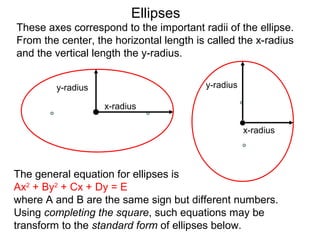
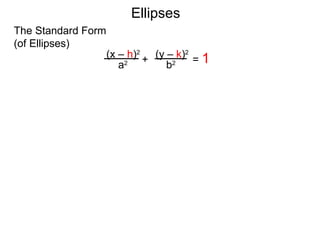
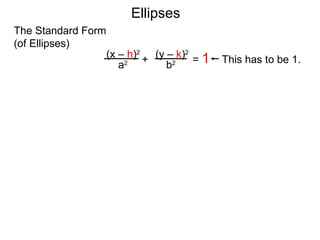
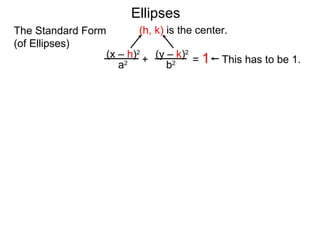
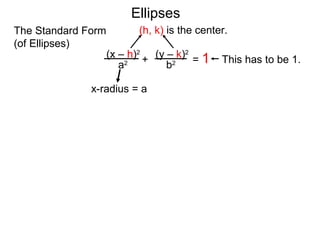
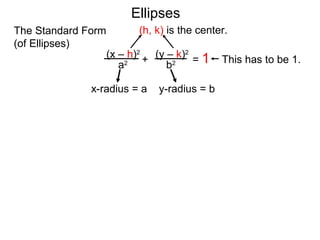
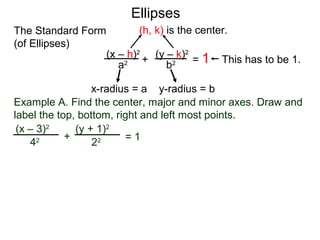
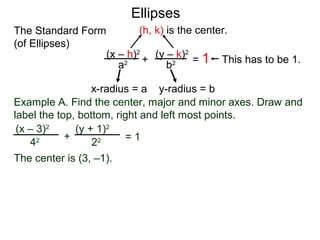
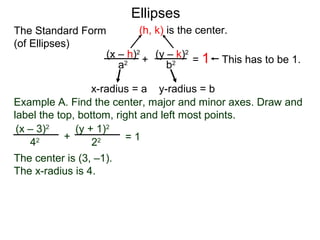
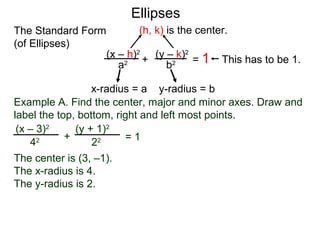
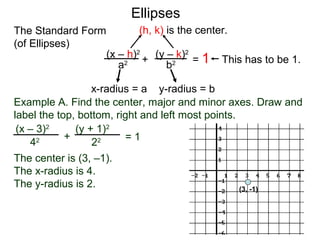
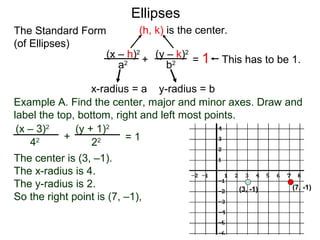
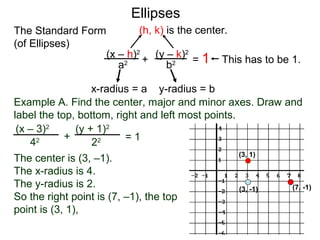
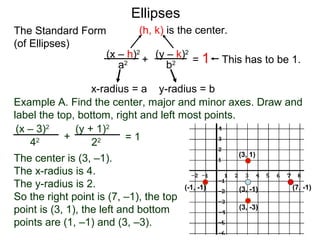
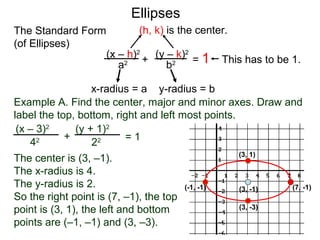
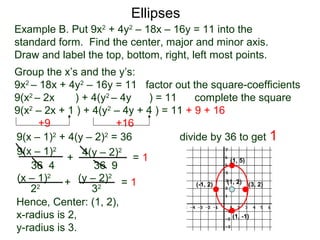
The document defines and describes ellipses. It states that an ellipse is the set of points whose sum of the distances to two fixed foci is a constant. An ellipse has a center, major axis, and minor axis. The standard form of the ellipse equation is given as (x-h)2/a2 + (y-k)2/b2 = 1, where (h,k) is the center, a is the x-radius, and b is the y-radius. An example problem demonstrates how to identify these properties from a given ellipse equation and sketch the ellipse.