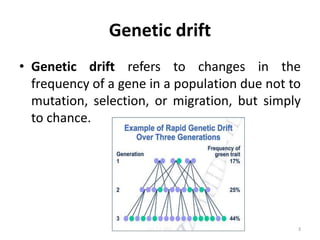
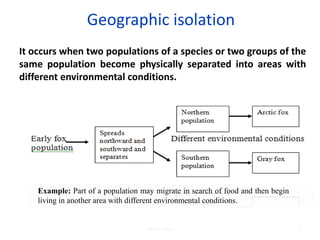
Biological diversity is shaped by biological evolution through processes like natural selection, genetic drift, migration, and geographic and reproductive isolation. Natural selection leads to increases in heritable traits that aid survival and reproduction. Genetic drift causes changes in gene frequencies by chance rather than selection. Geographic isolation occurs when populations become physically separated, and over time this can lead to reproductive isolation and speciation as the populations evolve independently. Extinction also influences biodiversity by removing species. Factors like habitat diversity, moderate disturbance, and evolution tend to increase diversity, while stress, limited resources, and extreme disturbance decrease it.