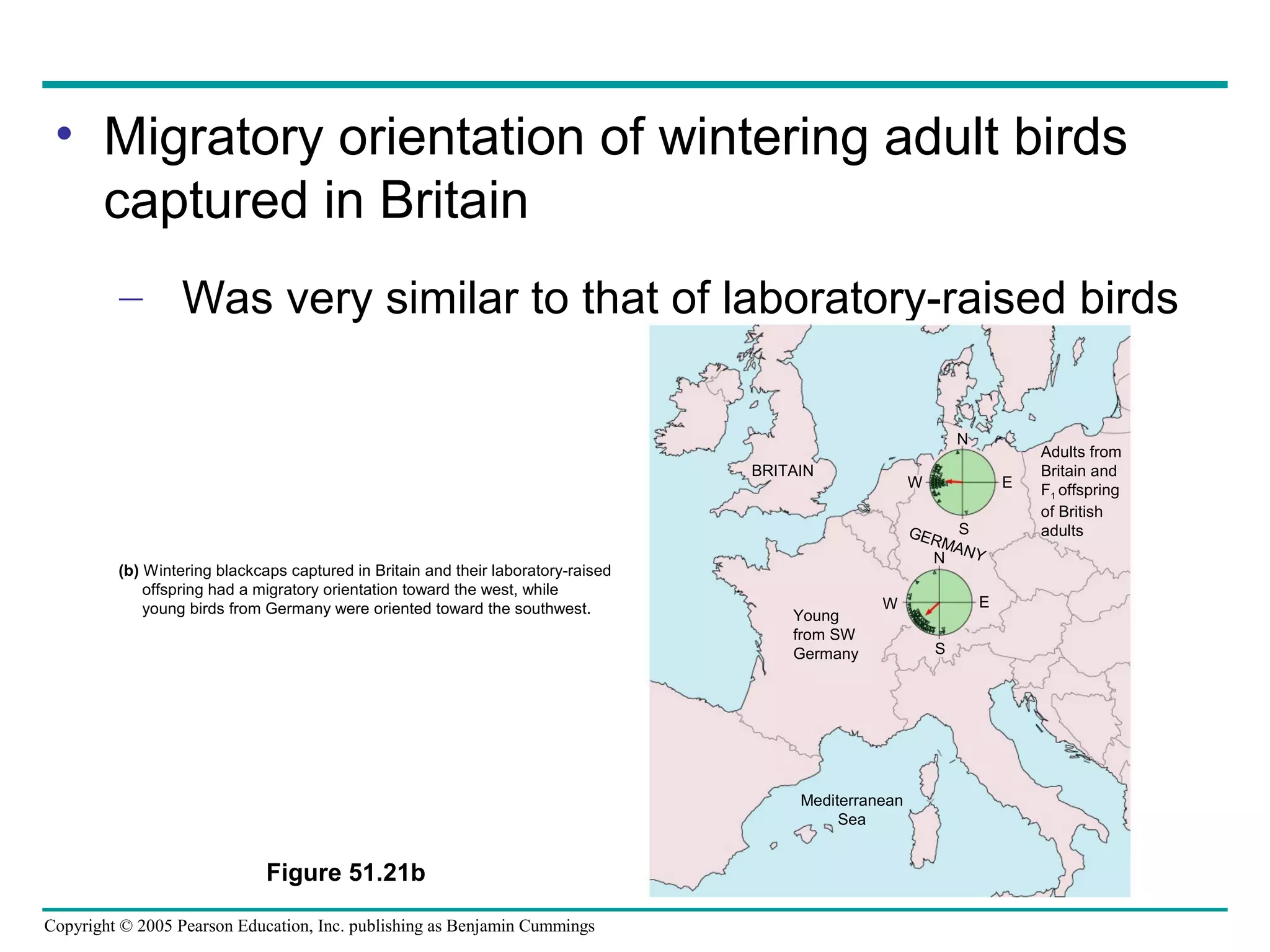
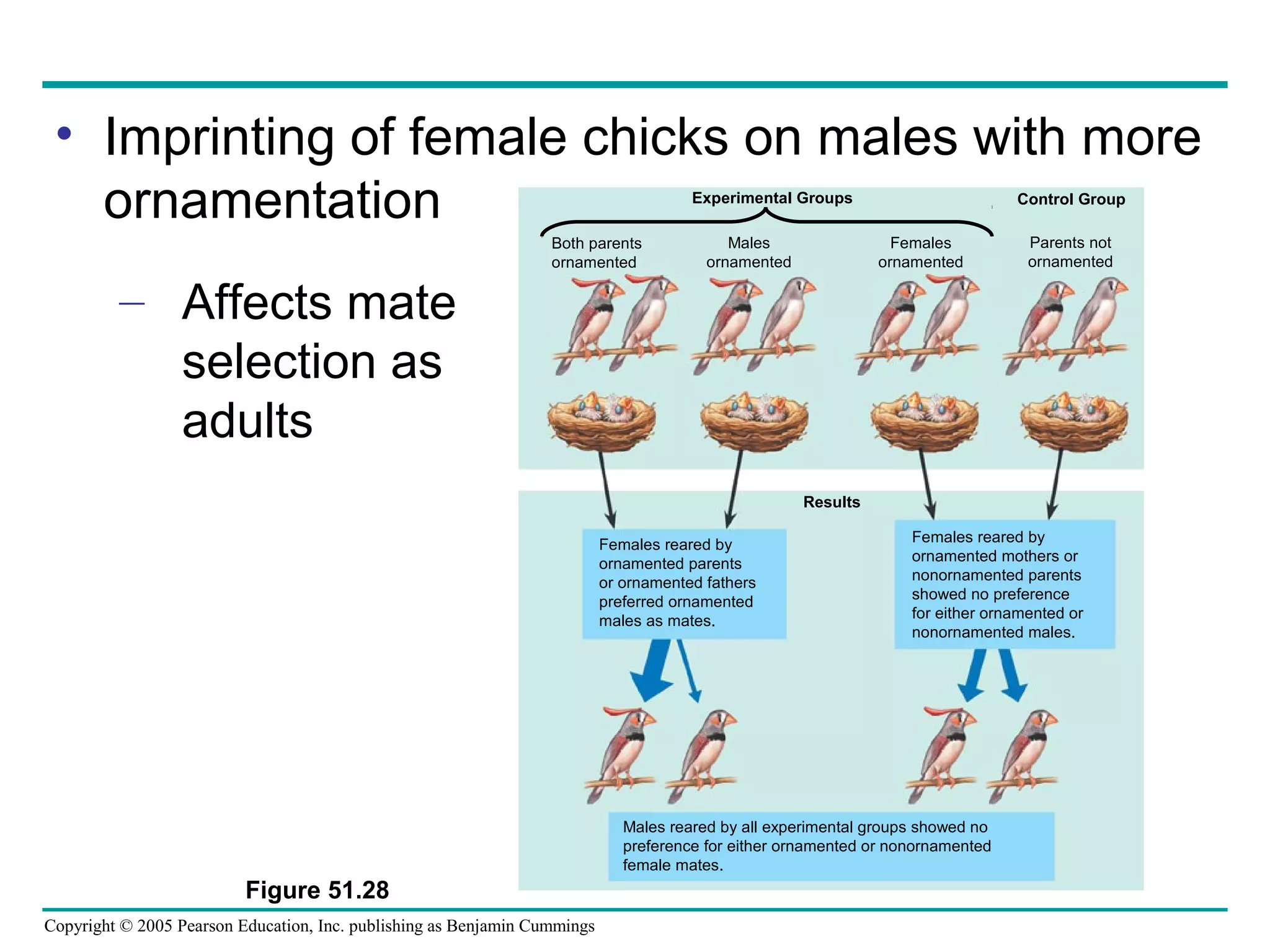
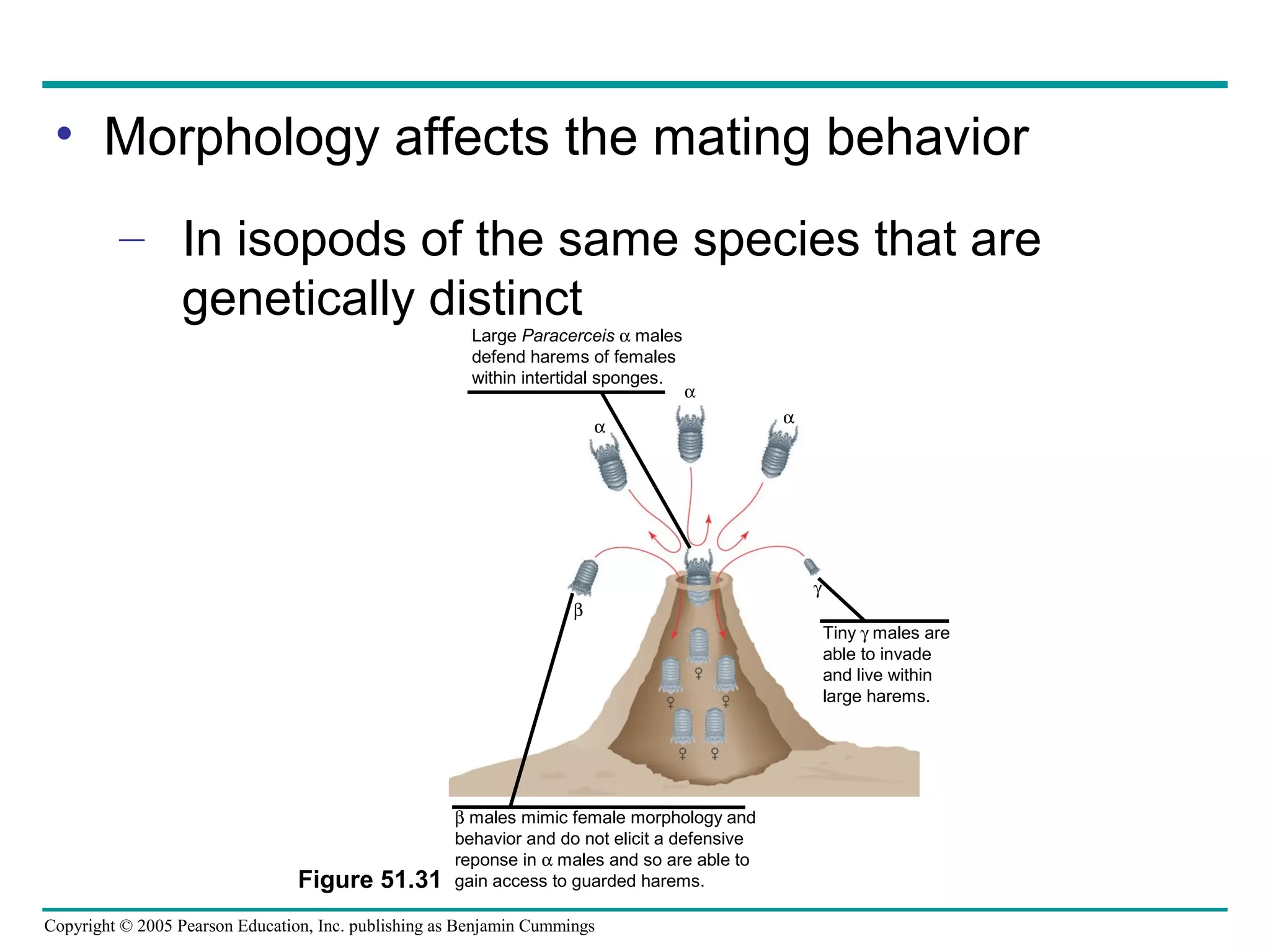
This document discusses behavioral ecology and how it studies animal behavior. It covers some key topics:
1) Behavioral ecologists study the proximate (immediate) and ultimate (evolutionary) causes of behavior.
2) Examples of innate behaviors discussed include fixed action patterns in stickleback fish and imprinting in geese.
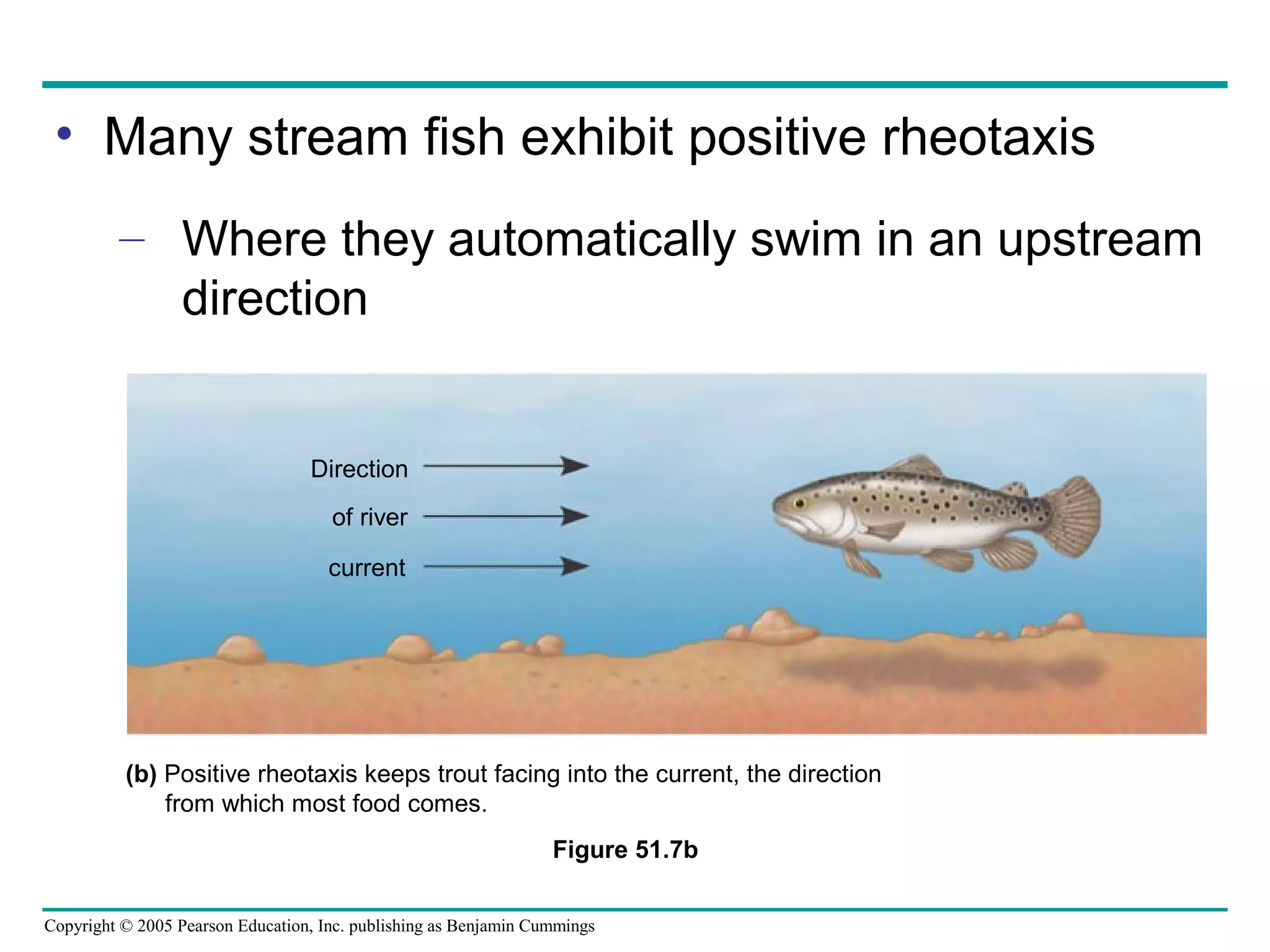
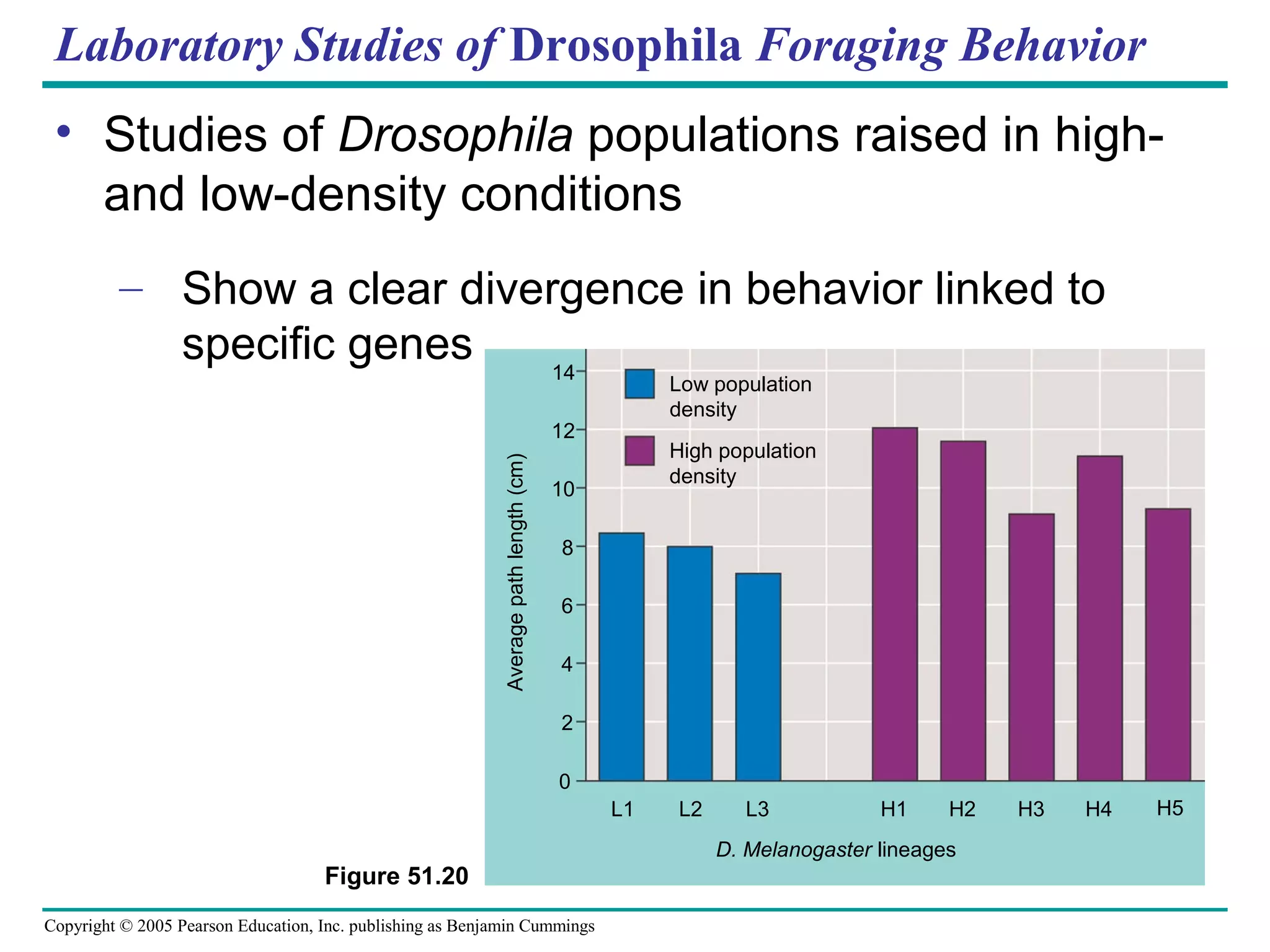
3) Many behaviors have genetic components, such as directed movements like kinesis, taxis, and migration patterns.
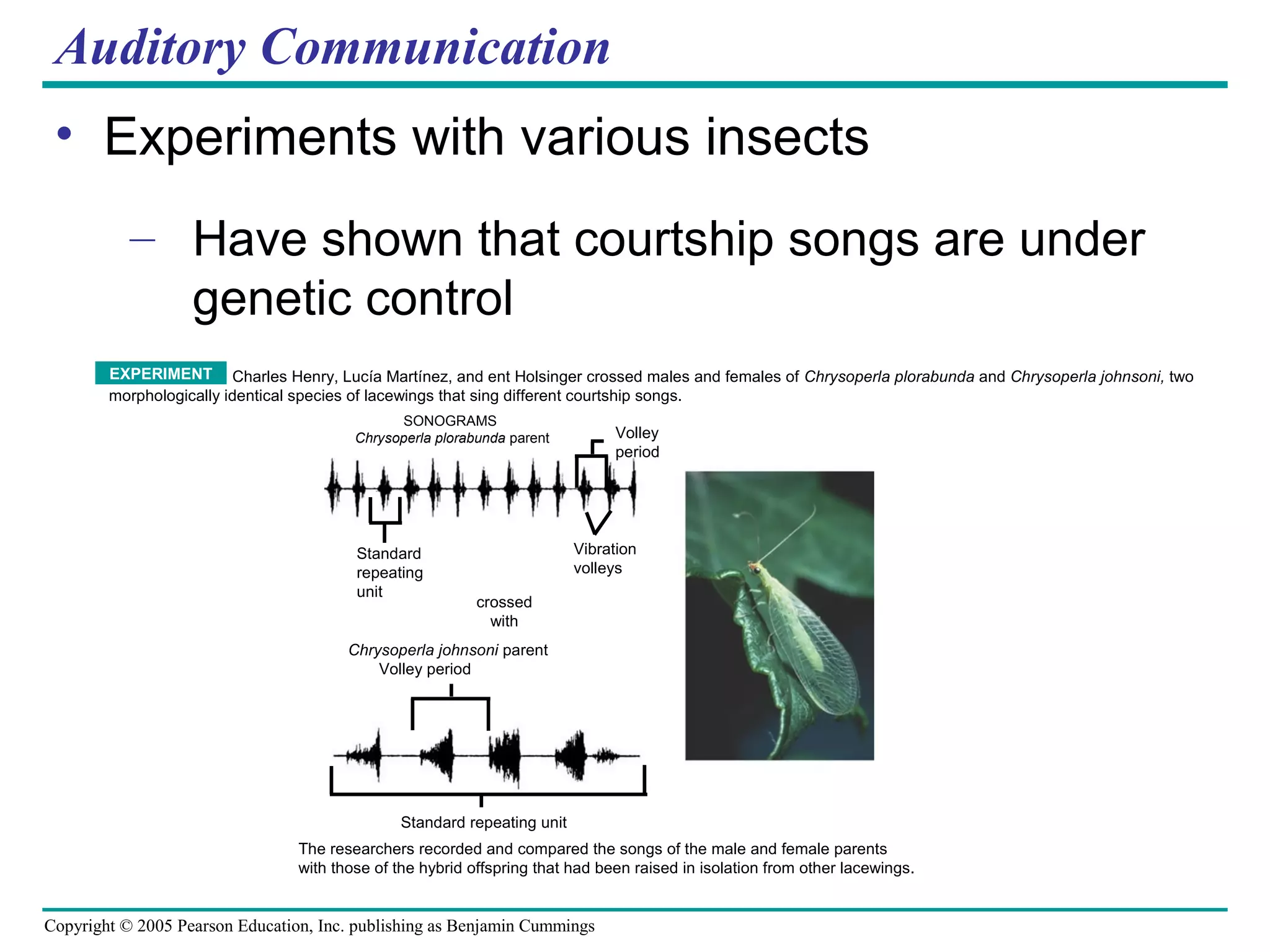
4) Animals communicate using various signals like visual, auditory, chemical and more, which are adapted to their environments.