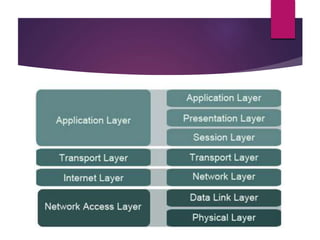
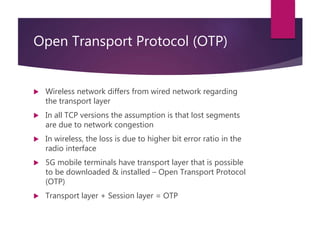
The document presents an overview of 5G wireless technology, detailing its evolution from previous generations and highlighting its key features such as high data rates, enhanced connectivity, and low costs. It describes the architecture, hardware and software components of 5G, emphasizing its potential for massive machine communications and applications in various fields. The conclusion suggests that 5G is designed as an open platform and is expected to be accessible at affordable rates, offering significant improvements over earlier technologies.