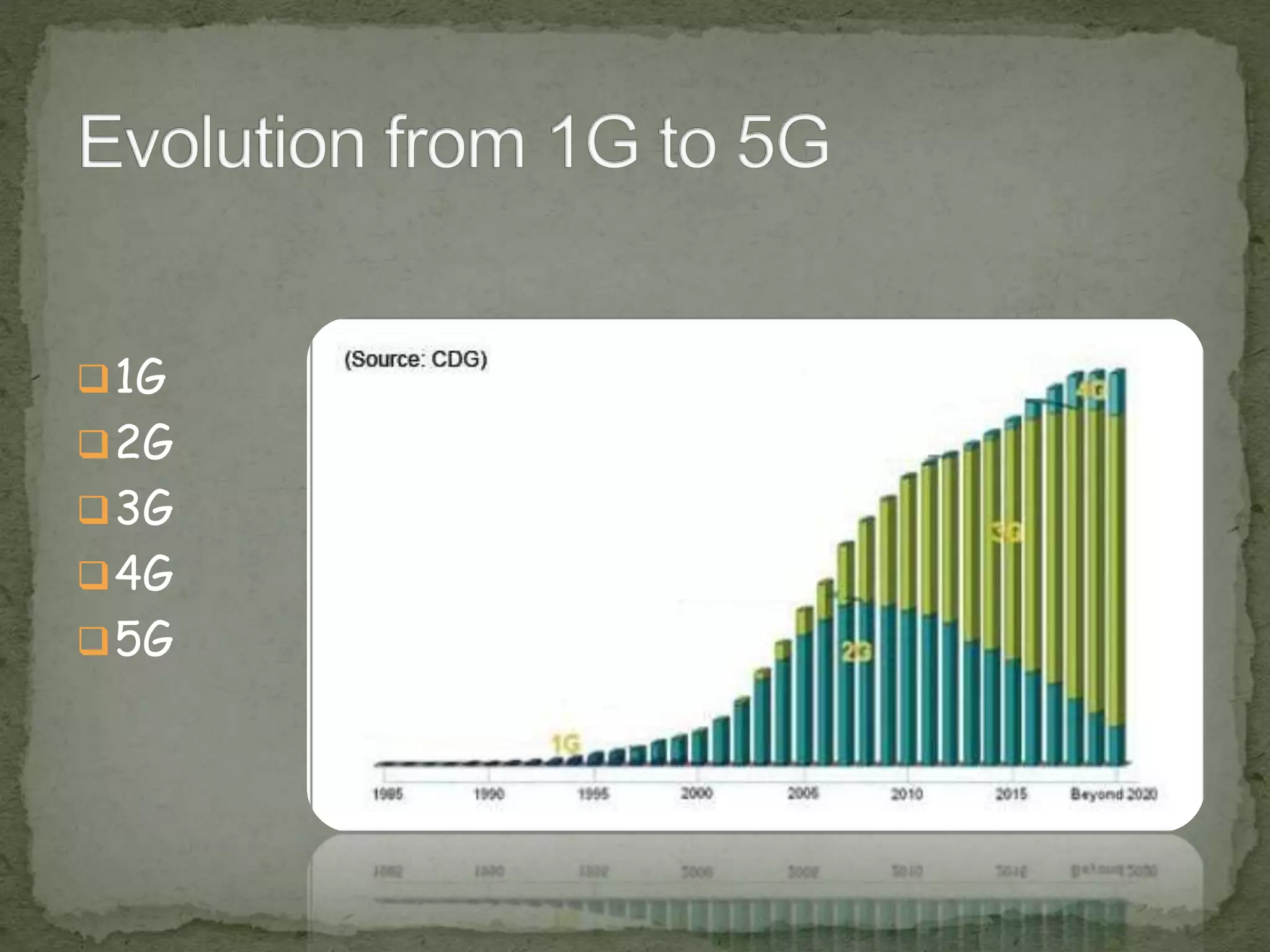
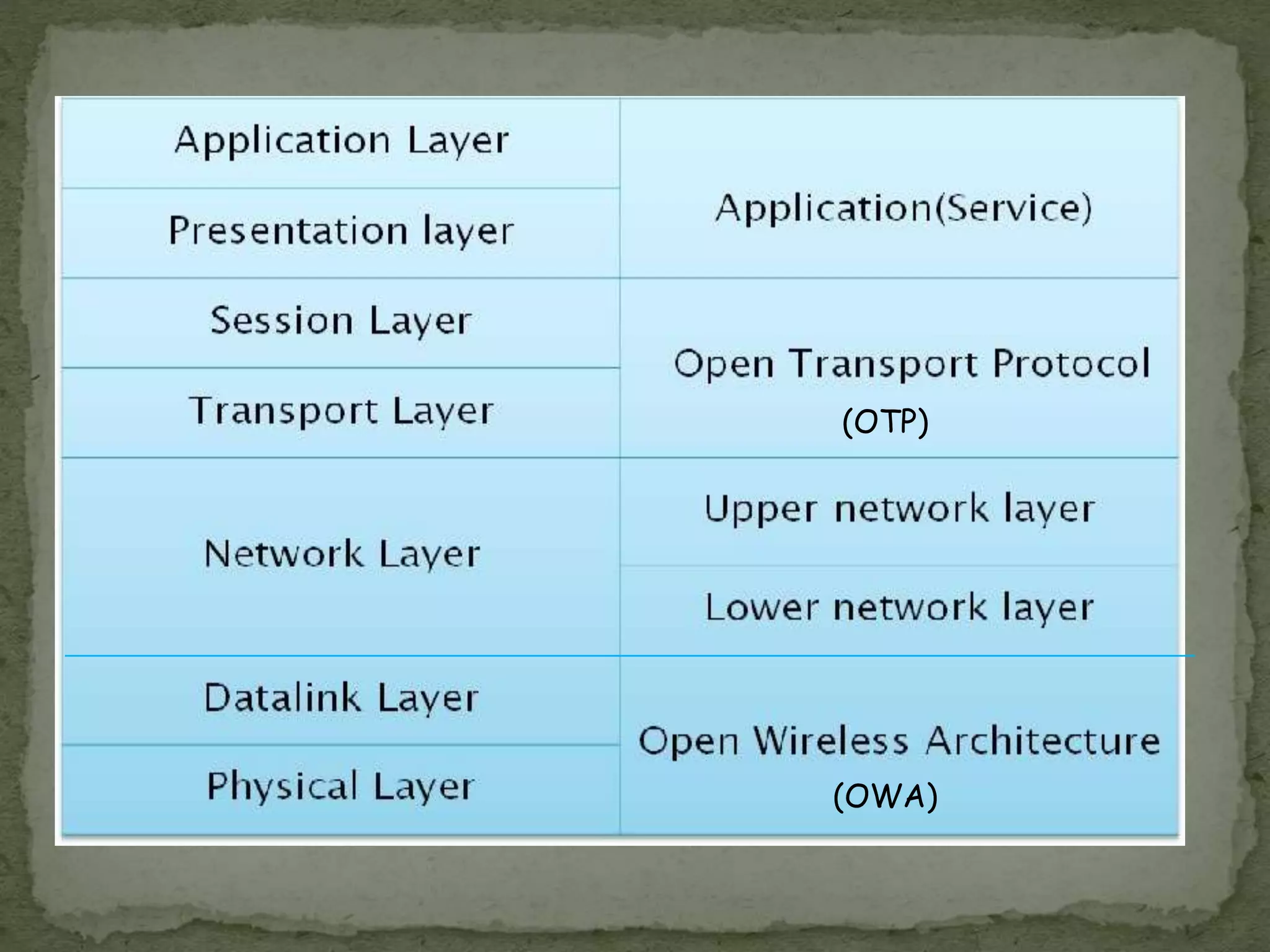
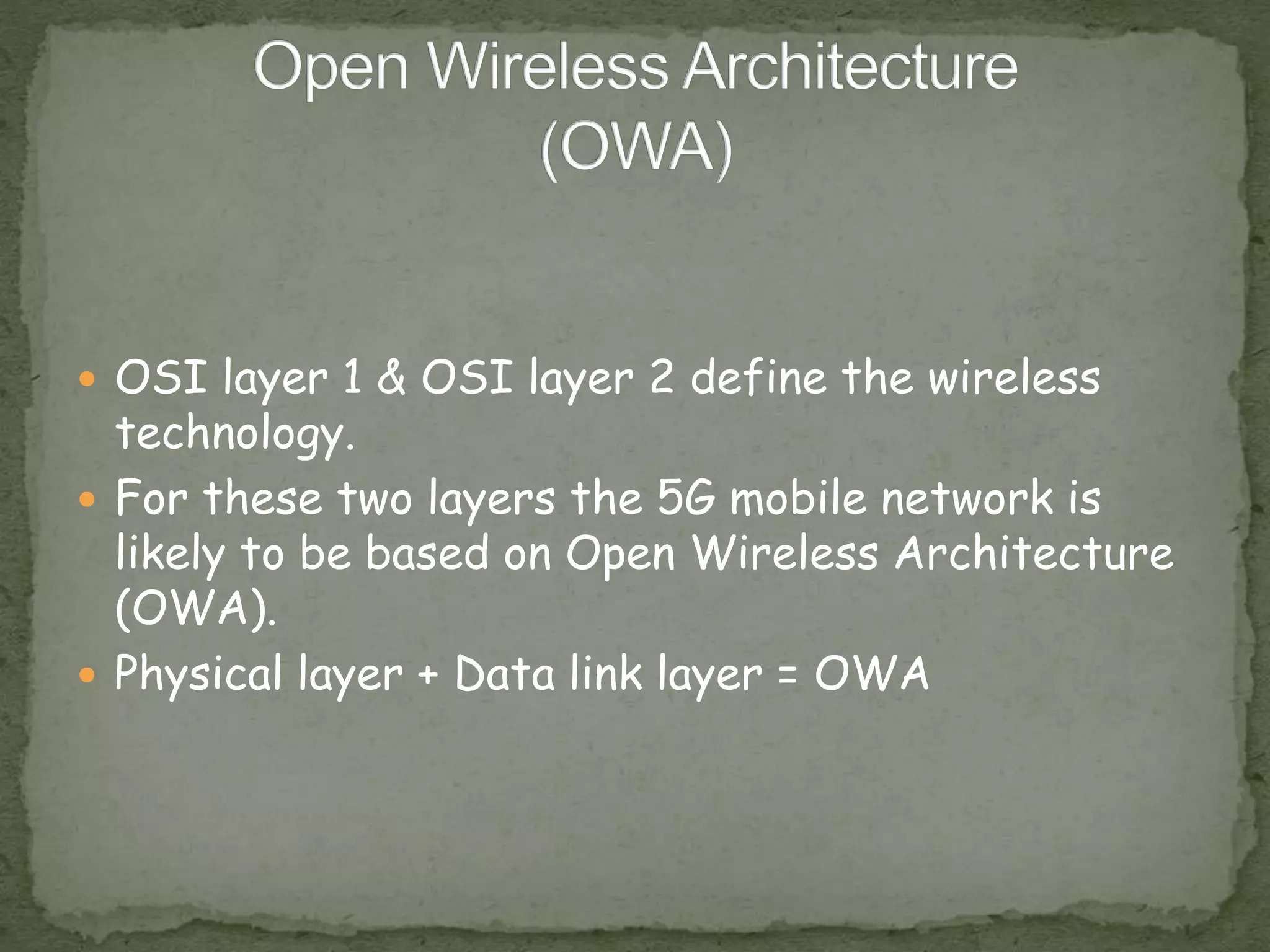
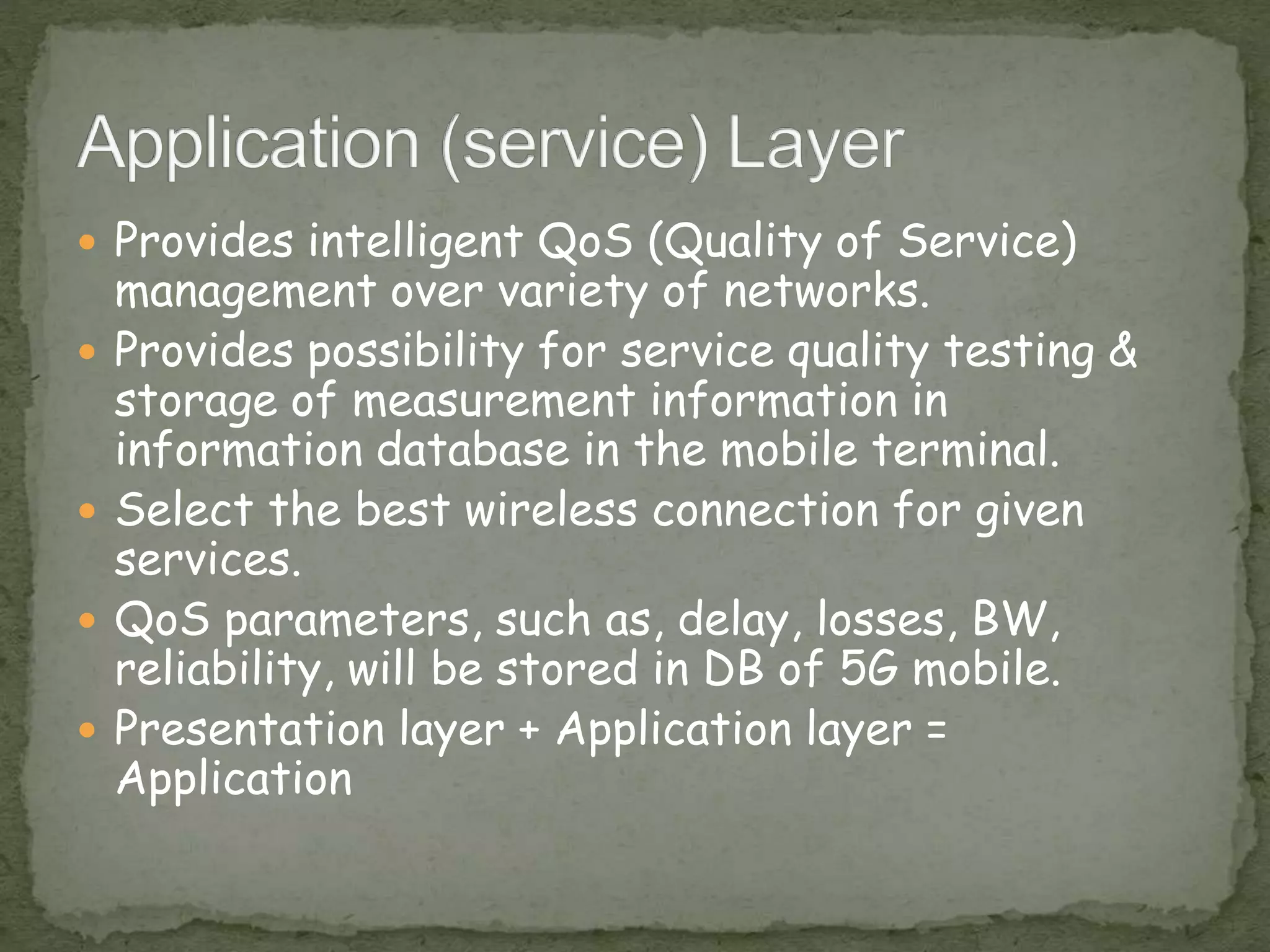
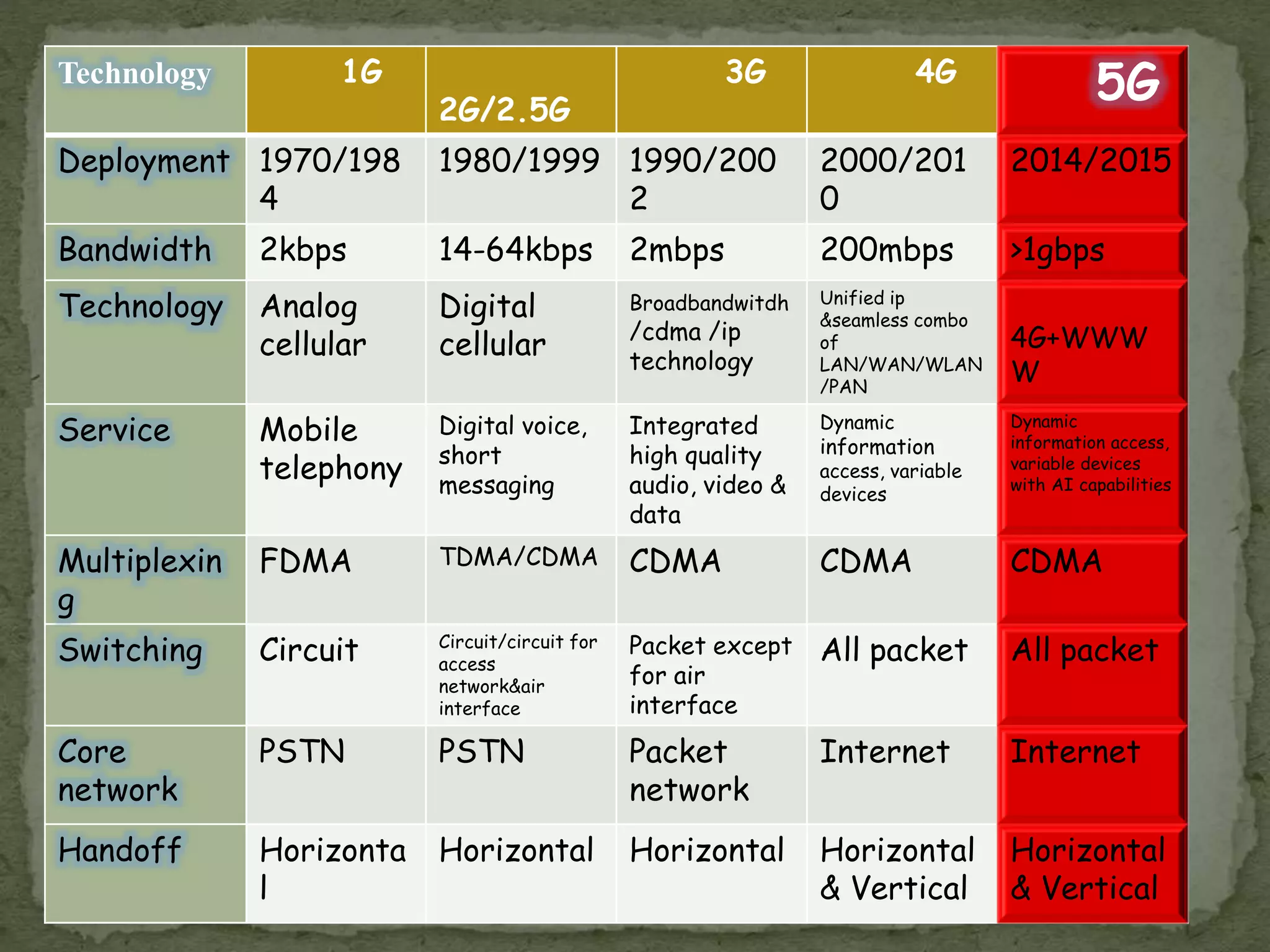
This document provides an overview of 5G technology, including its evolution from earlier generations of wireless technology (1G to 4G), key concepts, architecture, hardware and software components, features, advantages, applications, and conclusions. 5G is expected to offer transmission speeds up to 1 Gbps, support a wide range of devices and applications through highly connected global networks, and provide more advanced capabilities through integration with technologies like artificial intelligence.