4.intestine2
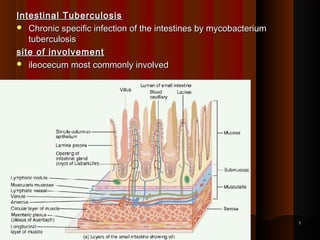
- 1. Intestinal TuberculosisIntestinal Tuberculosis Chronic specific infection of the intestines by mycobacteriumChronic specific infection of the intestines by mycobacterium tuberculosistuberculosis site of involvementsite of involvement ileocecum most commonly involvedileocecum most commonly involved 11
- 2. Mode of transmissionMode of transmission Ingestion of infected sputum (M. Bovis)Ingestion of infected sputum (M. Bovis) Ingestion of contaminated milk (M. Tuberculosis)Ingestion of contaminated milk (M. Tuberculosis) Direct spread from adjacent structureDirect spread from adjacent structure Haematogenous spreadHaematogenous spread Lymphatic spreadLymphatic spread 22
- 3. Primary infectionPrimary infection Primary – ingestion of organism in unsensitised host.Primary – ingestion of organism in unsensitised host. Can cause severe ulcero-inflammatory disease with perforationCan cause severe ulcero-inflammatory disease with perforation Secondary infectionSecondary infection Swallowing ofSwallowing of infectedinfected sputum containing large no of tubercle bacillisputum containing large no of tubercle bacilli in cases of open pulmonary tuberculosisin cases of open pulmonary tuberculosis The local lesion is prominent & the lymph nodes are less commonlyThe local lesion is prominent & the lymph nodes are less commonly affectedaffected 33
- 4. PathogesnesisPathogesnesis Most active inflammation in submucosaMost active inflammation in submucosa Bacill in depth of mucosal glandsBacill in depth of mucosal glands Inflammatory reactionInflammatory reaction Phagocytes carry bacilli to Peyers PatchesPhagocytes carry bacilli to Peyers Patches Formation of tubercleFormation of tubercle Tubercles undergo necrosisTubercles undergo necrosis Submucosal tubercles enlargeSubmucosal tubercles enlarge Endarteritis & edema, Sloughing, Ulcer formation (Endarteritis & edema, Sloughing, Ulcer formation (Annular)Annular) 44
- 5. Accumulation of collagenous tissue, Thickening & StenosisAccumulation of collagenous tissue, Thickening & Stenosis Inflammatory process in submucosa penetrates to serosaInflammatory process in submucosa penetrates to serosa Tubercles on serosal surfaceTubercles on serosal surface Bacilli reach lymphaticsBacilli reach lymphatics Bacilli via lymphaticsBacilli via lymphatics 55 Lymphatic obstruction of mesentery and bowel → Thick fixed mass Regional lymph nodes • Hyperplasia • Caseation necrosis • Calcification
- 6. gross appearancegross appearance ulcerative lesionsulcerative lesions multiple superficial lesions confined to epithelial surfacemultiple superficial lesions confined to epithelial surface Mostly small intestineMostly small intestine hypertrophic lesionshypertrophic lesions scarring, bowel wall thickening, fibrosis strictures, pseudotumoral massscarring, bowel wall thickening, fibrosis strictures, pseudotumoral mass Mostly ileocaecalMostly ileocaecal Ulcerohypertrophic lesionsUlcerohypertrophic lesions
- 7. 77 Circumferential ulceration is characteristic ofCircumferential ulceration is characteristic of intestinal tuberculosis.intestinal tuberculosis.
- 8. Histological featuresHistological features distinguishing lesion -- caseating granulomas; muscularis usuallydistinguishing lesion -- caseating granulomas; muscularis usually sparedspared common in Payer’s patches.common in Payer’s patches.
- 9. T.B. Bacilli, Z.N. stain
- 10. ComplicationsComplications Sub acute intestinal ObstructionSub acute intestinal Obstruction AscitesAscites Chronic diarrheoaChronic diarrheoa Tuberculous MeningitisTuberculous Meningitis Tuberculosis of KidneyTuberculosis of Kidney Cold abscessCold abscess 1010
- 11. Pathologically GI TB is characterized by inflammation and fibrosis ofPathologically GI TB is characterized by inflammation and fibrosis of the bowel wall and the regional lymph nodes.the bowel wall and the regional lymph nodes. Mucosal ulceration results from necrosis of Peyer patches, lymphMucosal ulceration results from necrosis of Peyer patches, lymph follicles, and vascular thrombosis. At this stage of the disease, thefollicles, and vascular thrombosis. At this stage of the disease, the changes are reversible and healing without scarring is possible.changes are reversible and healing without scarring is possible. As the disease progresses, the ulceration becomes confluent, andAs the disease progresses, the ulceration becomes confluent, and extensive fibrosis leads to bowel wall thickening, fibrosis, andextensive fibrosis leads to bowel wall thickening, fibrosis, and pseudotumoral mass lesions.pseudotumoral mass lesions. Strictures and fistulae formation may occur.Strictures and fistulae formation may occur. The serosal surface may show nodular masses of tubercles. TheThe serosal surface may show nodular masses of tubercles. The mucosa is inflamed with hyperemia and edema similar to thatmucosa is inflamed with hyperemia and edema similar to that observed in Crohn disease.observed in Crohn disease. Caseation may not always be seen in the granuloma, especially inCaseation may not always be seen in the granuloma, especially in the mucosa, but it is almost always seen in the regional lymph nodethe mucosa, but it is almost always seen in the regional lymph node 1111
- 12. 1212
- 13. 1313
- 14. Intestinal PolypsIntestinal Polyps AA polyppolyp is an abnormal growth of tissue projecting from a mucousis an abnormal growth of tissue projecting from a mucous membrane.membrane. If it is attached to the surface by a narrow elongated stalk it is saidIf it is attached to the surface by a narrow elongated stalk it is said to be pedunculated.to be pedunculated. If no stalk is present it is said to be sessile.If no stalk is present it is said to be sessile. Polyposis signifies the presence of multiple polypsPolyposis signifies the presence of multiple polyps 1414
- 15. 1515
- 16. Classification – types of intestinal polypsClassification – types of intestinal polyps A. Non-neoplastic polypsA. Non-neoplastic polyps Hyperplastic polypHyperplastic polyp Inflammatory polyp - These are polyps which are associated withInflammatory polyp - These are polyps which are associated with inflammatory conditions such as IBDinflammatory conditions such as IBD Hamartomatous polyp – They are growths, like tumours found inHamartomatous polyp – They are growths, like tumours found in organs as a result of faulty development.organs as a result of faulty development. Lymphoid polypLymphoid polyp 1616
- 17. B. Neoplastic PolypsB. Neoplastic Polyps Benign tumour – AdenomaBenign tumour – Adenoma tubular adenoma, tubulovillous adenoma & villous adenoma of colontubular adenoma, tubulovillous adenoma & villous adenoma of colon Malignant tumour – polypoid carcinomaMalignant tumour – polypoid carcinoma C. Familial polyposis syndromeC. Familial polyposis syndrome 1717
- 18. Tumours of Small intestineTumours of Small intestine All types are uncommon. Simple epithelial tumours are particularly rareAll types are uncommon. Simple epithelial tumours are particularly rare A. Epithelila tumoursA. Epithelila tumours Benign Adenomas – single or multiple ployps. Multiple adenomaBenign Adenomas – single or multiple ployps. Multiple adenoma may occur in familial multiple polyposismay occur in familial multiple polyposis Malignant – AdenocarcinomaMalignant – Adenocarcinoma B. Connective tissue tumoursB. Connective tissue tumours Benign (most common) leiomyoma, fibroma , neurofibromaBenign (most common) leiomyoma, fibroma , neurofibroma Malignant – lymphoma (primary or secondary), leiomyomosarcomaMalignant – lymphoma (primary or secondary), leiomyomosarcoma C. Carcinoid tumour of neuroendocrine cells – potentially malignantC. Carcinoid tumour of neuroendocrine cells – potentially malignant 1818
- 19. Tumours of large intestineTumours of large intestine Almost all the tumours are of epithelial originAlmost all the tumours are of epithelial origin A. Epithelial tumours (common )A. Epithelial tumours (common ) BenignBenign Adenoma or neoplastic polypsAdenoma or neoplastic polyps MalignantMalignant Carcinoma – colorectal carcinoma is the 2Carcinoma – colorectal carcinoma is the 2ndnd most common visceralmost common visceral cancercancer B. Connective tissue tumours (rare)B. Connective tissue tumours (rare) Beningn – leiomyomaBeningn – leiomyoma Malignant – malignant spindle cell (mesenchymal) tumors,Malignant – malignant spindle cell (mesenchymal) tumors, malignant lymphomamalignant lymphoma Carcinoid tumurs – may arise anywhere in the colon especially theCarcinoid tumurs – may arise anywhere in the colon especially the rectumrectum 1919
- 20. Adenoma / Beging Neoplastic polypsAdenoma / Beging Neoplastic polyps Derived from glandular epitheliumDerived from glandular epithelium 4 fold greater risk of colorectal carcinoma in any person with adenomas4 fold greater risk of colorectal carcinoma in any person with adenomas Predictors of cancer riskPredictors of cancer risk Size – greater than 2.5 cm – high riskSize – greater than 2.5 cm – high risk Villous component more – higher the riskVillous component more – higher the risk Dysplasia of neoplastic cells – more dysplasia more riskDysplasia of neoplastic cells – more dysplasia more risk
- 21. 3 types3 types Tubular Adenoma - 75%Tubular Adenoma - 75% Most common (rectum & sigmoid colon)Most common (rectum & sigmoid colon) Singe or multipleSinge or multiple Pedunculated, tubule shaped glandsPedunculated, tubule shaped glands Head of the polyp has neoplastic epithelium forming well formedHead of the polyp has neoplastic epithelium forming well formed tubules or glandstubules or glands Low malignant potentialLow malignant potential Core of the stalk is fibrovascularCore of the stalk is fibrovascular 2121
- 22. 2222 tubular adenoma – dysplastic epithelium (dark purple) on left of image; normal epithelium (blue) on right
- 23. 2. Villous adenoma – 10 %2. Villous adenoma – 10 % Commonly found in rectumCommonly found in rectum Most are broad & sessile,Most are broad & sessile, Velvety red, finger like epi projectionsVelvety red, finger like epi projections It consists of frond like papillary projections of adenomatousIt consists of frond like papillary projections of adenomatous epitheliumepithelium Highest potential for malignancy transformationHighest potential for malignancy transformation 2323
- 24. 2424
- 25. 2525
- 26. 3. tubulovillous adenoma – 15 %3. tubulovillous adenoma – 15 % Raised, 1-4 cm redRaised, 1-4 cm red Pedunculated, surface villous patternPedunculated, surface villous pattern Histology tubular & villousHistology tubular & villous 2626
