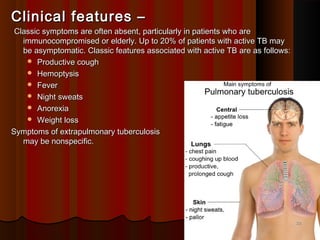
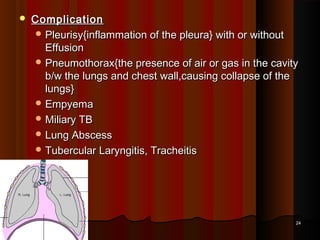
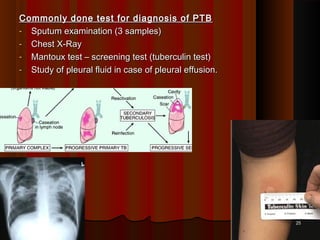
This document discusses pulmonary tuberculosis, which is a chronic granulomatous disease caused by the mycobacterium bacillus. It can be caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis or atypical mycobacteria. Primary infection occurs through inhalation of contaminated droplets and leads to the formation of Ghon's focus in the lungs. This may heal or progress to active disease. Secondary tuberculosis occurs through reactivation of a latent infection or reinfection, and presents as apical lung lesions or cavities. Miliary tuberculosis is a severe form of widespread dissemination through the bloodstream. Clinical features vary but often include non-specific symptoms.

![Pulmonary TuberculosisPulmonary Tuberculosis
• It is a chronic granulomatous disease caused byIt is a chronic granulomatous disease caused by
mycobacterium bacillimycobacterium bacilli
AetiologyAetiology
Mycobacterium tuberculosis [Human Type] CommonestMycobacterium tuberculosis [Human Type] Commonest
Mycobacterium tuberculosis [Bovine Type]Mycobacterium tuberculosis [Bovine Type]
Atypical or Opportunistic Mycobacterium – Myco.Atypical or Opportunistic Mycobacterium – Myco.
Kansasii, Myco. Marium etcKansasii, Myco. Marium etc
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-180804083311/85/3-pulmonary-tuberculosis-tb-2-320.jpg)
![Primary SitesPrimary Sites
Lungs, Intestine, Tonsils[lymph node], Genito-urinaryLungs, Intestine, Tonsils[lymph node], Genito-urinary
Tract, Bones, Meninges, Peritoneum.Tract, Bones, Meninges, Peritoneum.
Organs relative resistant to TBOrgans relative resistant to TB
Cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle, thyroid gland &Cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle, thyroid gland &
Pancreas.Pancreas.
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-180804083311/85/3-pulmonary-tuberculosis-tb-3-320.jpg)
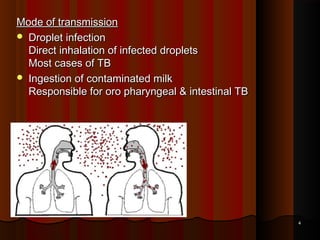

![Primary infectionPrimary infection
Inhalation of contaminated Mycobacterium reach the alveolus afterInhalation of contaminated Mycobacterium reach the alveolus after
escaping the muco-cilliary defense & forms a local lesion calledescaping the muco-cilliary defense & forms a local lesion called
Ghon's focus'Ghon's focus'
Neutrophils come & try to engulf the bacteria & many of them areNeutrophils come & try to engulf the bacteria & many of them are
killed killed
Then Monocytes come (after 24 hrs). They try to engulf theThen Monocytes come (after 24 hrs). They try to engulf the
organisms & many of them are killed in the process. The survivingorganisms & many of them are killed in the process. The surviving
Monocytes carry the organisms via lymphatics to the lymph nodesMonocytes carry the organisms via lymphatics to the lymph nodes
[hilar lymph nodes][hilar lymph nodes]
Ghon's focus + hilar lymph node enlargement are together calledGhon's focus + hilar lymph node enlargement are together called
Primary Ghon's complexPrimary Ghon's complex
66](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-180804083311/85/3-pulmonary-tuberculosis-tb-6-320.jpg)
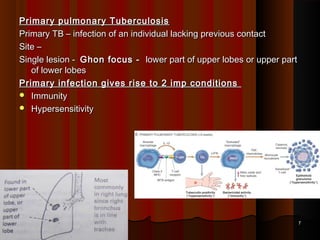
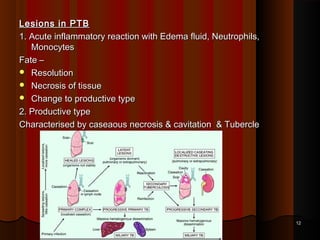
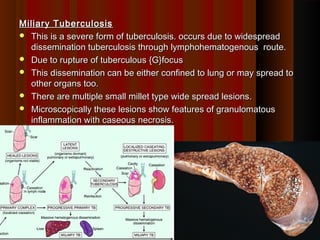
![FatesFates
Healing with scar & calcification (95%) of Ghon’s focusHealing with scar & calcification (95%) of Ghon’s focus
May harbor viable bacilli for years & may reactivteMay harbor viable bacilli for years & may reactivte
Progressive primary TBProgressive primary TB
PTB progress over a period of months or years causing furtherPTB progress over a period of months or years causing further
pulmonary and even distant organ involvement.pulmonary and even distant organ involvement.
Miliary tuberculosisMiliary tuberculosis
No Clinical disease [+ve tuberculin test]No Clinical disease [+ve tuberculin test]
Usual outcome in most casesUsual outcome in most cases
88](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-180804083311/85/3-pulmonary-tuberculosis-tb-8-320.jpg)
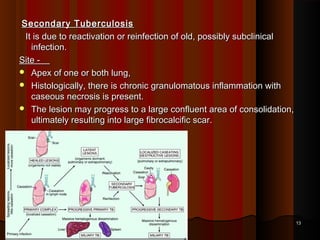
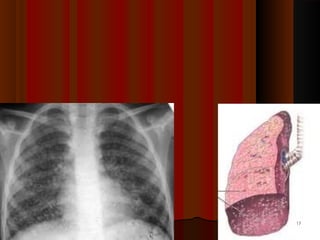
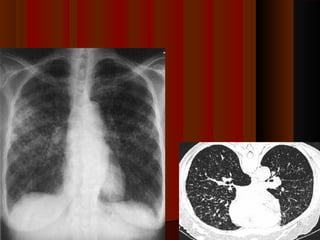
![Post Primary [Secondary TB]Post Primary [Secondary TB]
1. Reactivation [Ghon's complex] common[Endogenous]1. Reactivation [Ghon's complex] common[Endogenous]
2. Reinfection [Exogenous]2. Reinfection [Exogenous]
Neutrophils come very quickly along with antibody rich fluidNeutrophils come very quickly along with antibody rich fluid
Monocytes also make their appearance very quicklyMonocytes also make their appearance very quickly
Many neutrophils die trying to engulf forming pus & caseous materialMany neutrophils die trying to engulf forming pus & caseous material
Lung tissue is damaged producing cavitiesLung tissue is damaged producing cavities
99](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-180804083311/85/3-pulmonary-tuberculosis-tb-9-320.jpg)
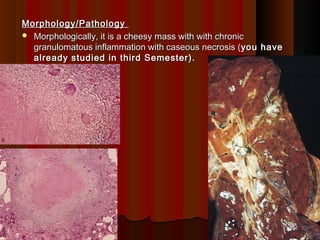
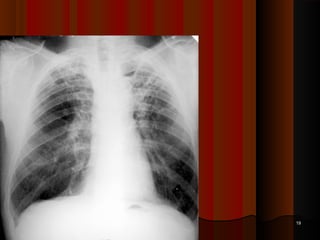
![Post Primary [Secondary TB]cont ….Post Primary [Secondary TB]cont ….
Monocytes are modified to form epitheloid cellsMonocytes are modified to form epitheloid cells
Joins together to form Langhans's giant cellJoins together to form Langhans's giant cell
Lymphocytes surround the periphery & fibroblasts start laying downLymphocytes surround the periphery & fibroblasts start laying down
collagen fibres around the lesioncollagen fibres around the lesion
The structure formed is called tubercle or GranulomaThe structure formed is called tubercle or Granuloma
1010](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-180804083311/85/3-pulmonary-tuberculosis-tb-10-320.jpg)