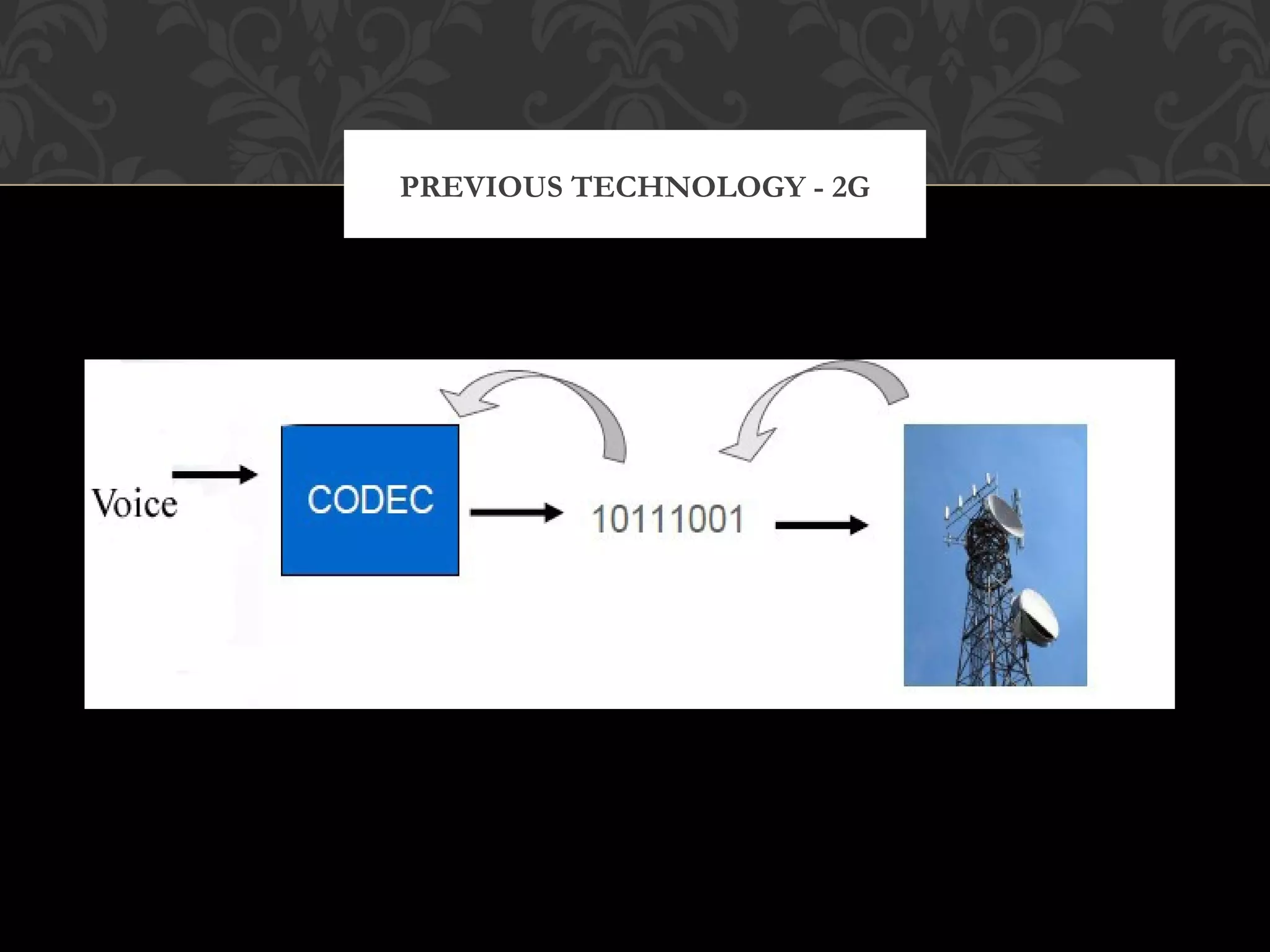
4G networks are optimized for data and aim to provide speeds of 100Mbps for mobile users and 1Gbps for stationary users. 4G allows for lower powered radio signals, digital error checking, and the introduction of digital data services like SMS and email. However, 3G networks still face issues like high license fees and expensive phones. 4G is expected to offer faster, more reliable connections at lower costs using technologies like OFDM and potentially incorporating IEEE 802.11n standards.