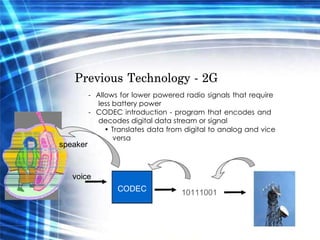
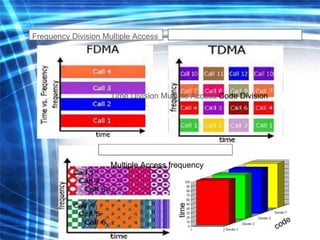
4G technology provides faster wireless internet speeds of up to 100 Mbps, uses multiple standards like Bluetooth and WiFi, and has a lower cost than previous generations. It uses an IP core and OFDM instead of CDMA for signal transmission. 4G networks are expected to be widely available between 2008-2010 and will impact society through increased mobile internet access and economic activity.