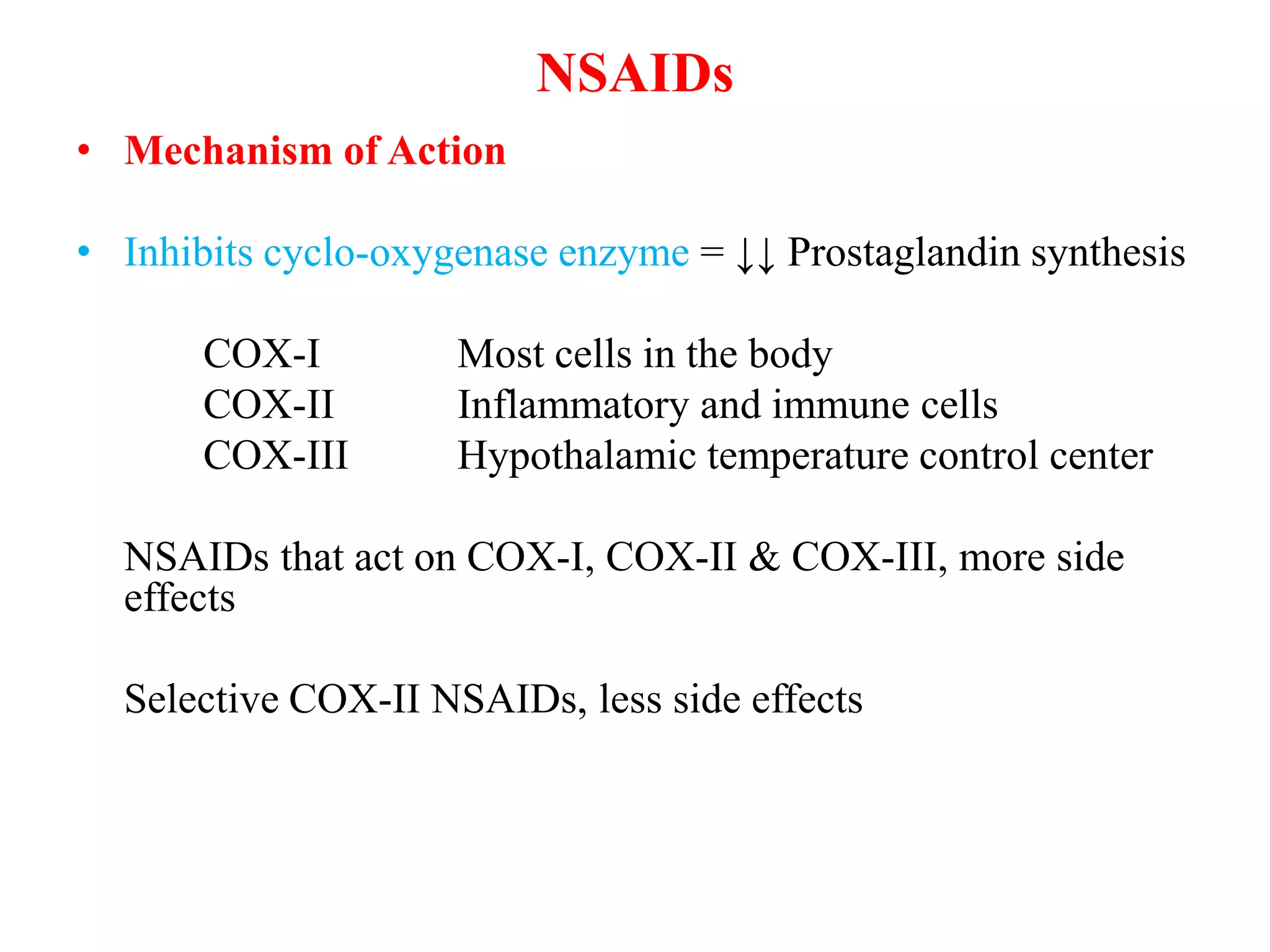
1. NSAIDs work by inhibiting the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, mainly COX-1 and COX-2, which decreases prostaglandin synthesis and produces their pharmacological effects. Selective COX-2 inhibitors have fewer side effects than non-selective NSAIDs.
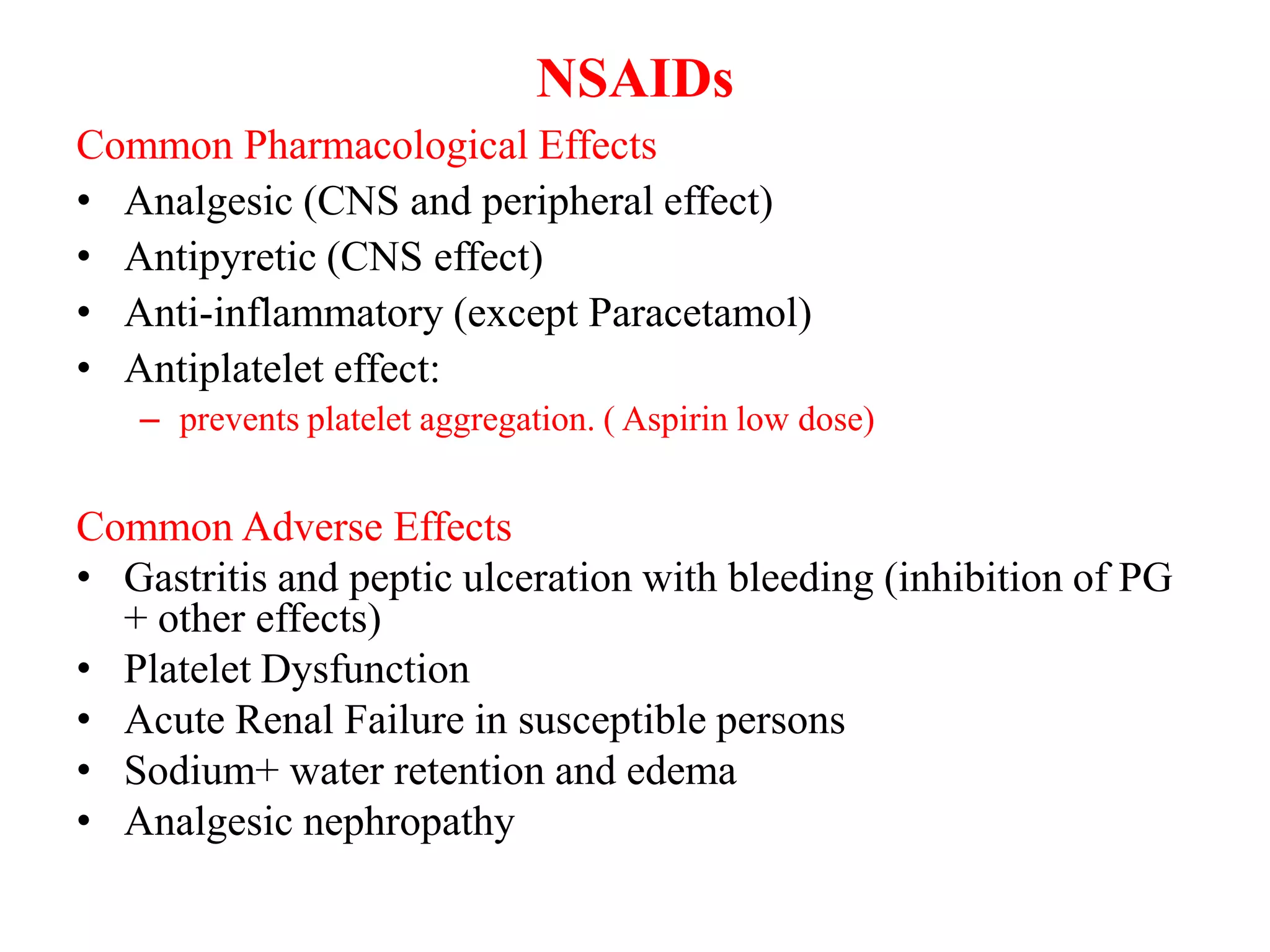
2. NSAIDs have analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory effects. Common side effects include gastric irritation, ulcers, renal impairment, and platelet dysfunction.
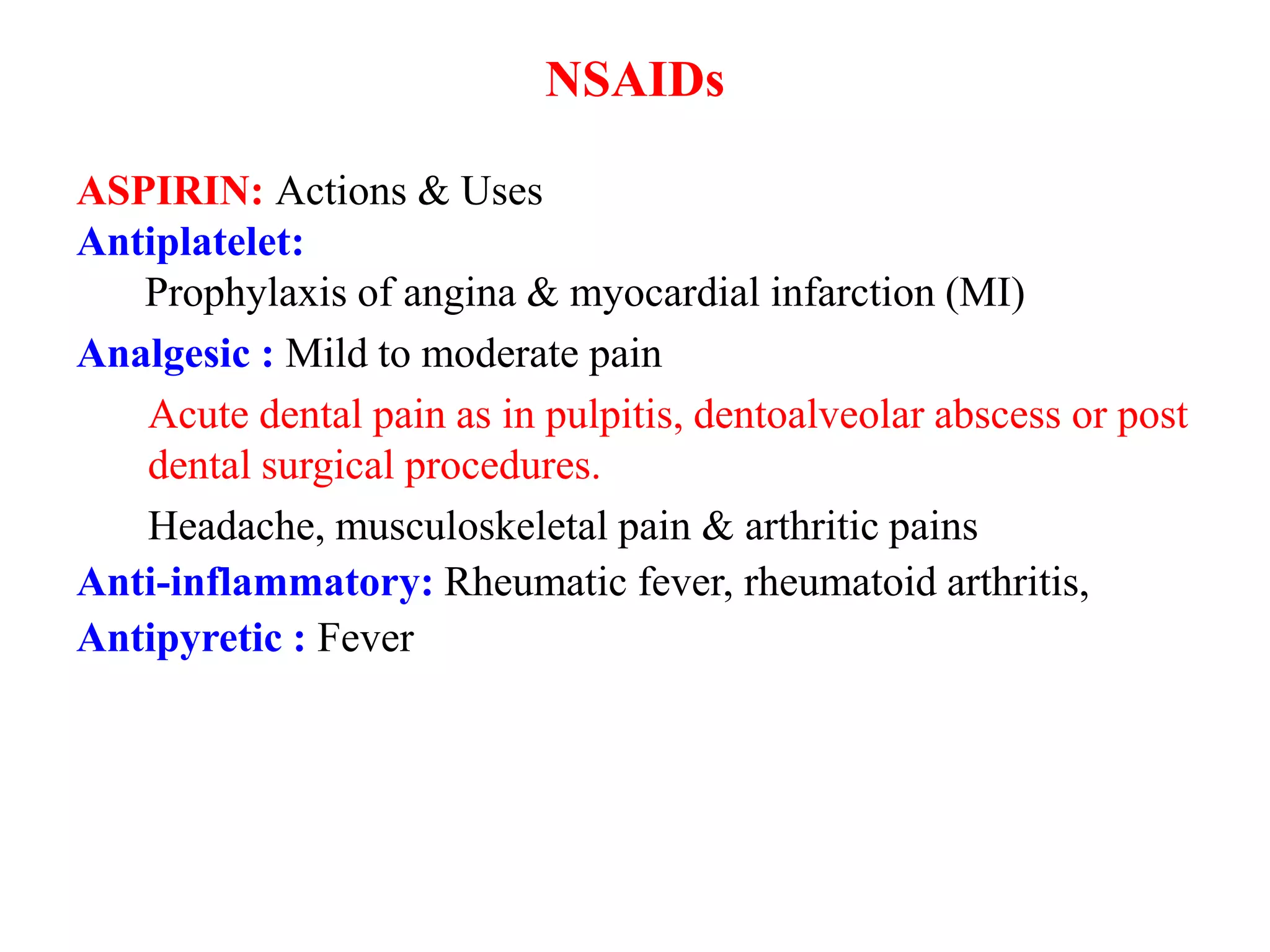
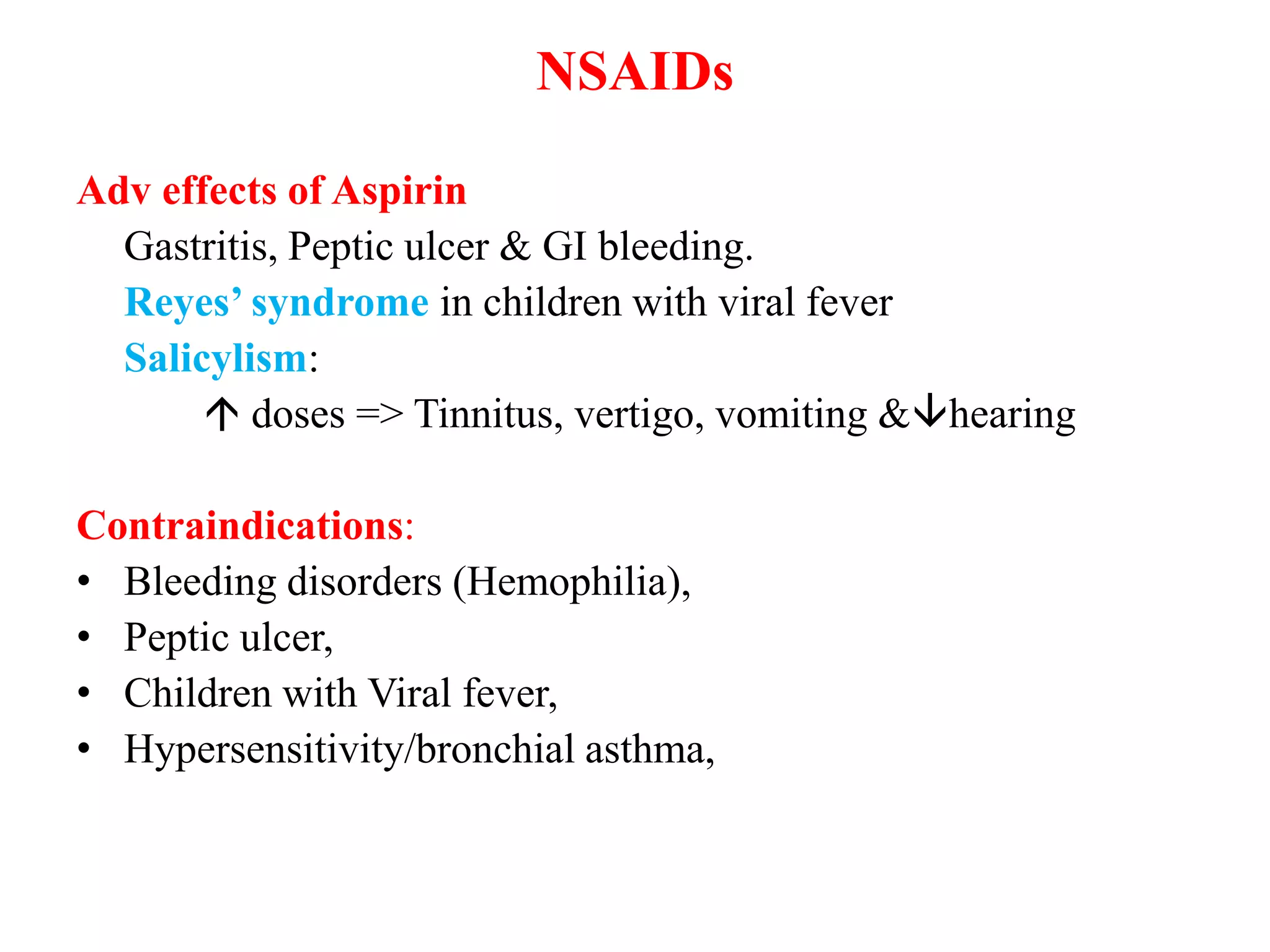
3. Aspirin has antiplatelet effects useful for cardiovascular protection. Indomethacin is potent but non-selective. Paracetamol is safer for those with bleeding risks but less effective at inflammation. COX-