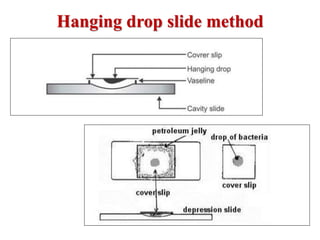
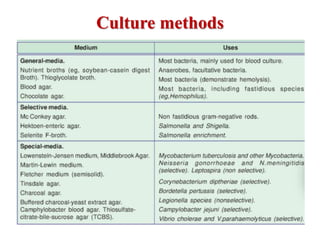
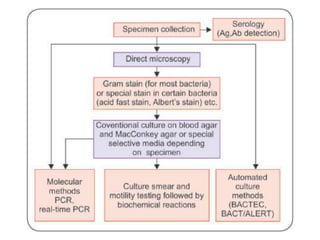
Laboratory methods for identifying microorganisms include direct microscopic examination of stained and unstained samples, culturing techniques to grow bacteria, biochemical tests to characterize bacterial properties, and serological methods using antigen-antibody reactions. Specimen collection, handling, transportation and processing require strict adherence to safety protocols and procedures to avoid contamination and ensure accurate results. Microscopic examination, culturing and biochemical profiling are used to classify unknown bacteria, while serological tests can identify pathogens that are difficult to culture or dangerous to handle.