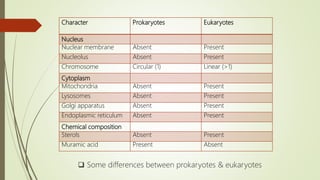
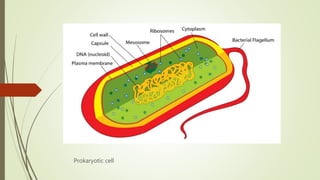
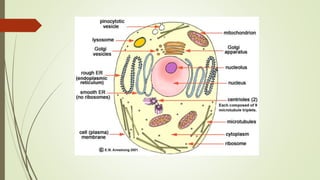
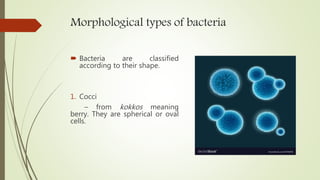
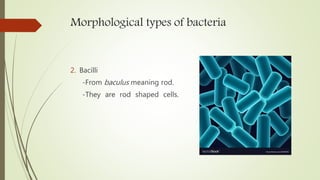
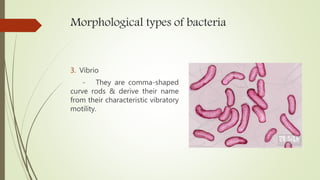
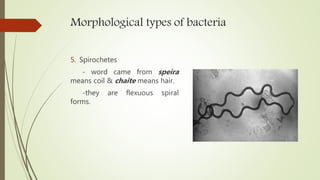
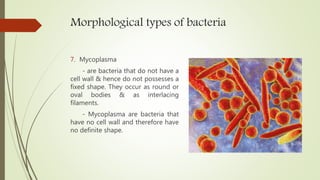
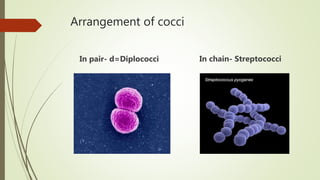
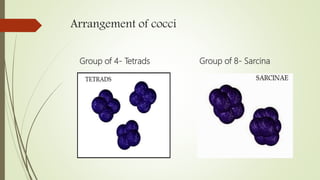
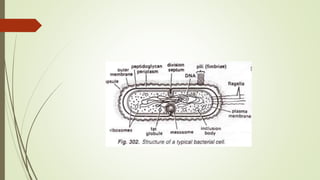
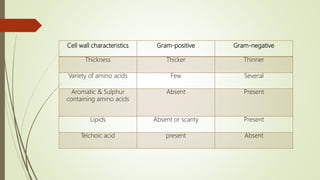
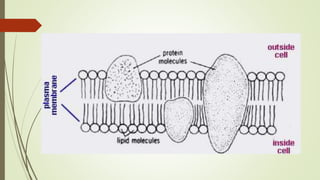
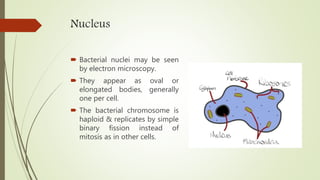
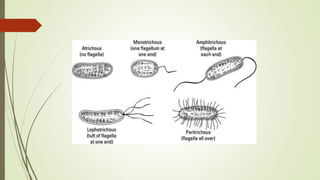
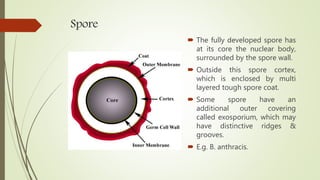
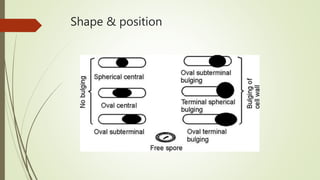
This document discusses the structure and classification of microbes. It begins by defining microorganisms and explaining that they can only be seen under an electron microscope due to their small size. It then outlines the five kingdoms of life - Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. Most of the document focuses on characteristics of the Monera kingdom, which includes bacteria. It describes bacterial cell structures like the cell wall, cytoplasmic membrane, flagella, and endospores. It also discusses different bacterial shapes, arrangements, staining properties and includes examples of some pathogenic bacteria.