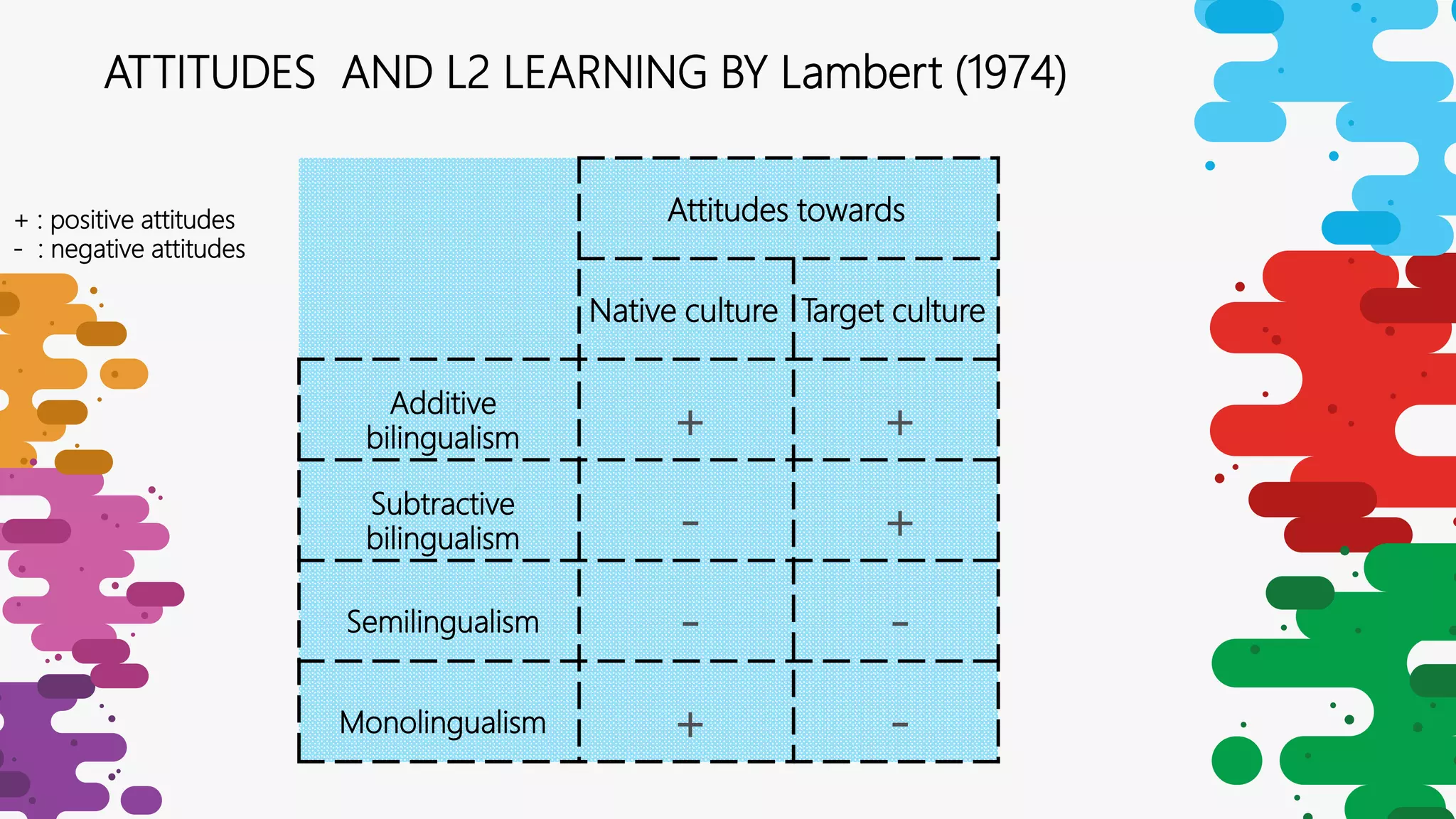
The document discusses the impact of social factors on second language acquisition (SLA), emphasizing that attitudes, social class, gender, and ethnic identity significantly affect language proficiency and learning outcomes. It outlines various models explaining SLA, including the acculturation model and socio-educational model, while highlighting the importance of interaction and comprehensible input in the learning process. Additionally, it concludes that social factors indirectly influence SLA through learners' attitudes and preferences, affecting the variety and quality of language exposure.