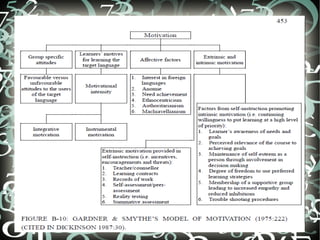
This document discusses several factors that can influence second language learning: motivation, age, gender, ethnicity/cultural background, and intelligence. For motivation, it describes how teachers can intrinsically and extrinsically motivate students. It notes that age affects how quickly adults versus children learn initially, but that starting younger allows for higher proficiency levels. Gender differences in learning strategy use are inconclusive between studies. Cultural background and first language can impact the learning process through issues like linguistic interference. Intelligence is difficult to separate from environment, but seems important for language rule learning.