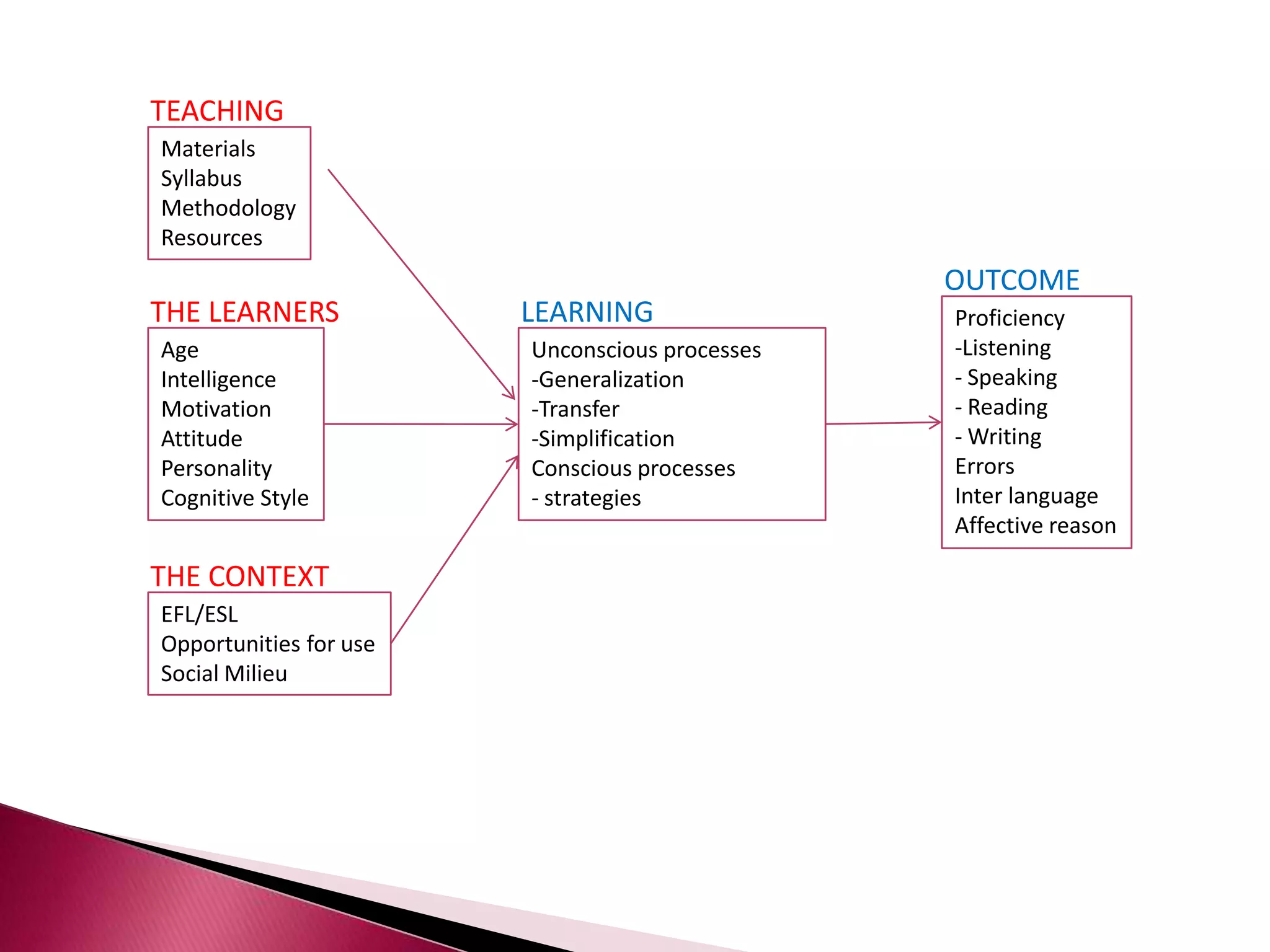
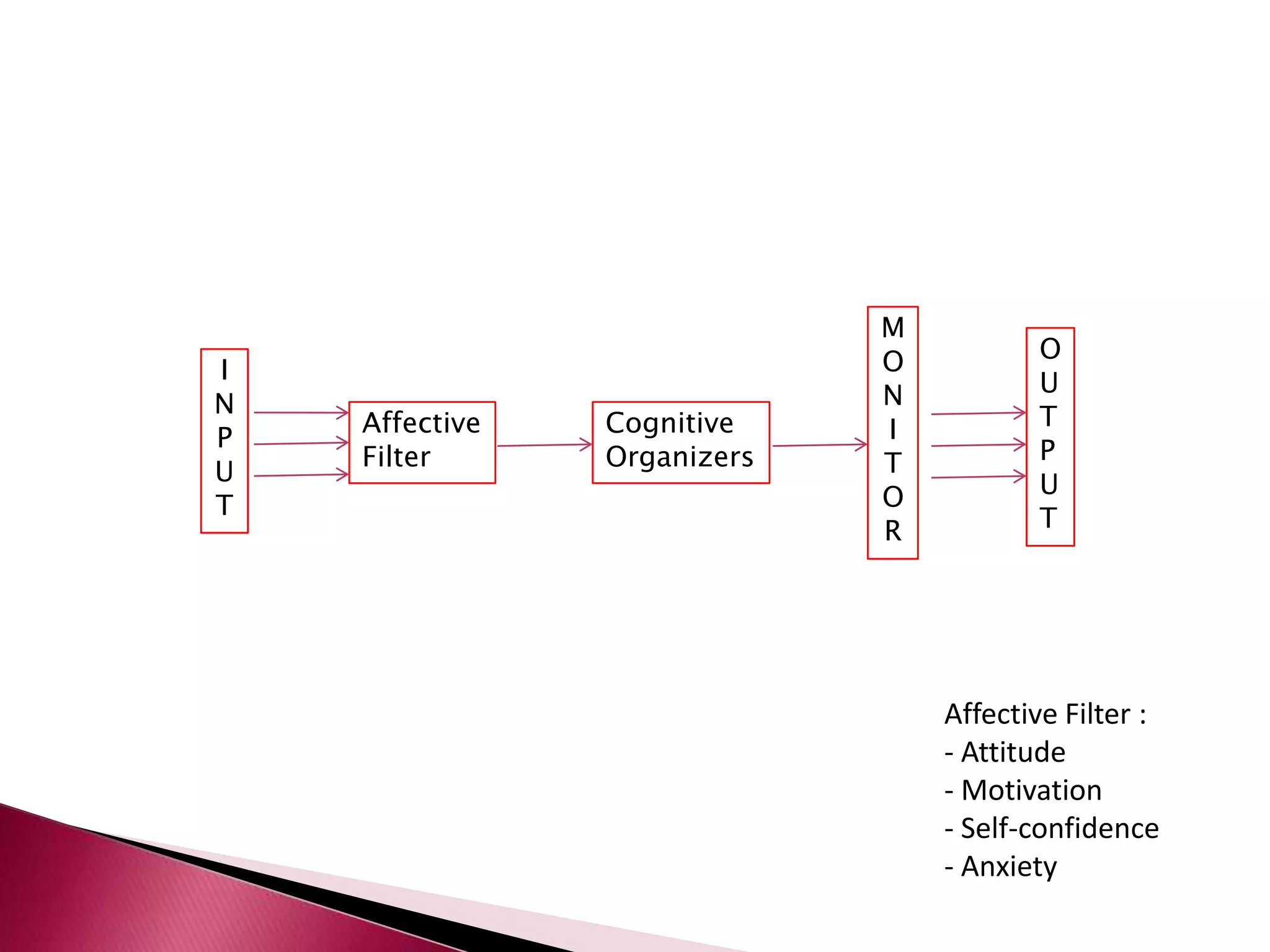
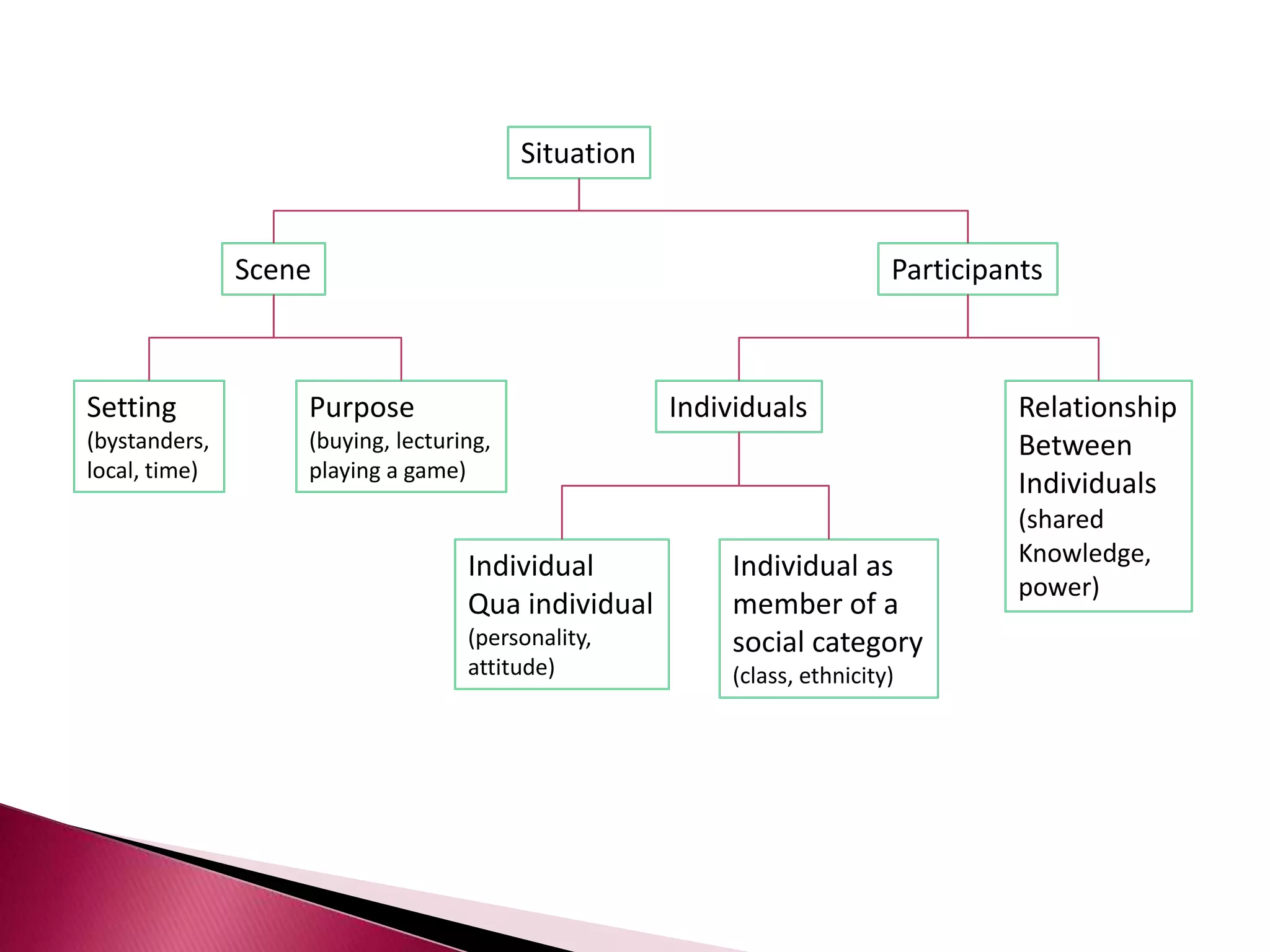
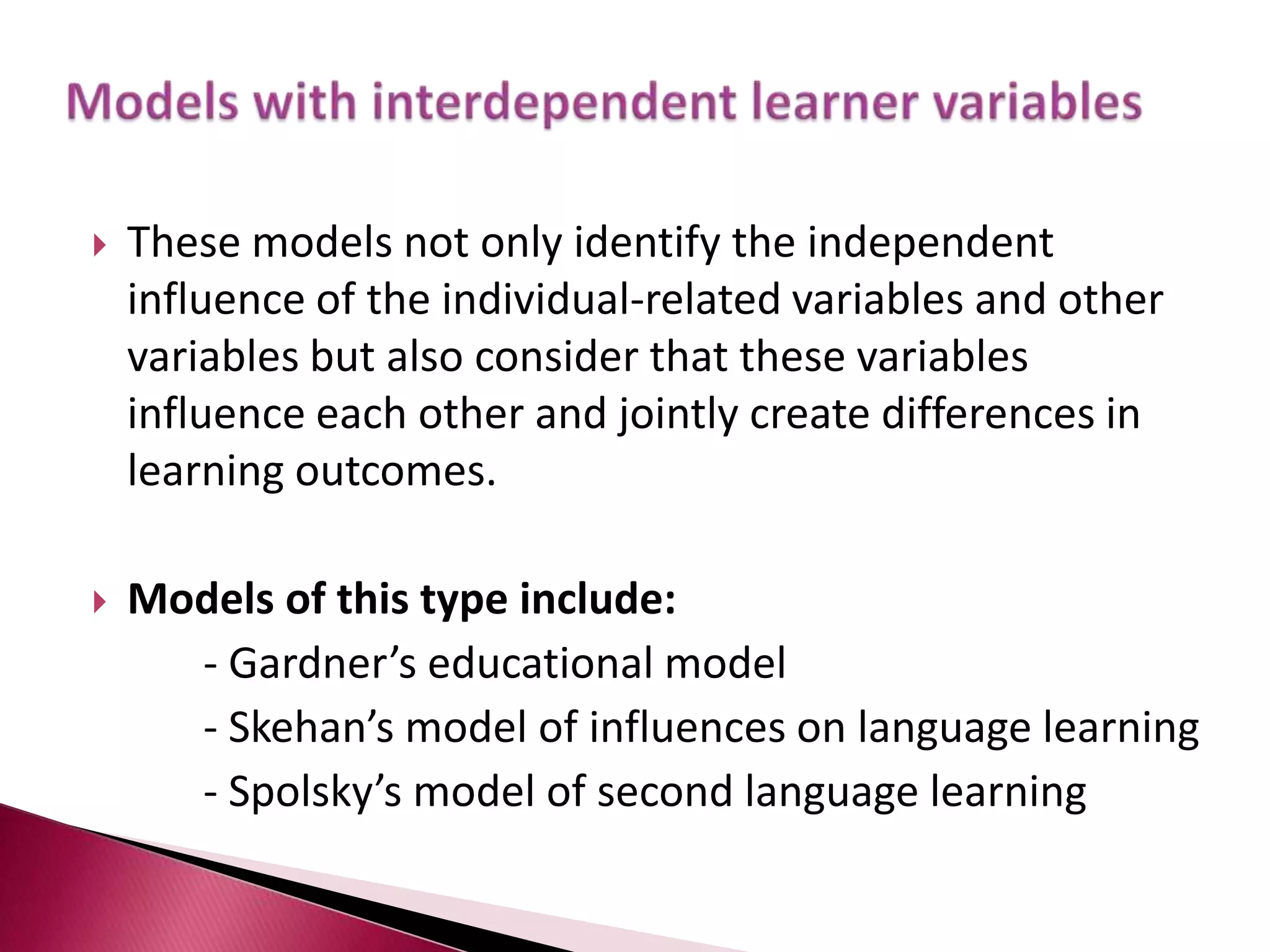
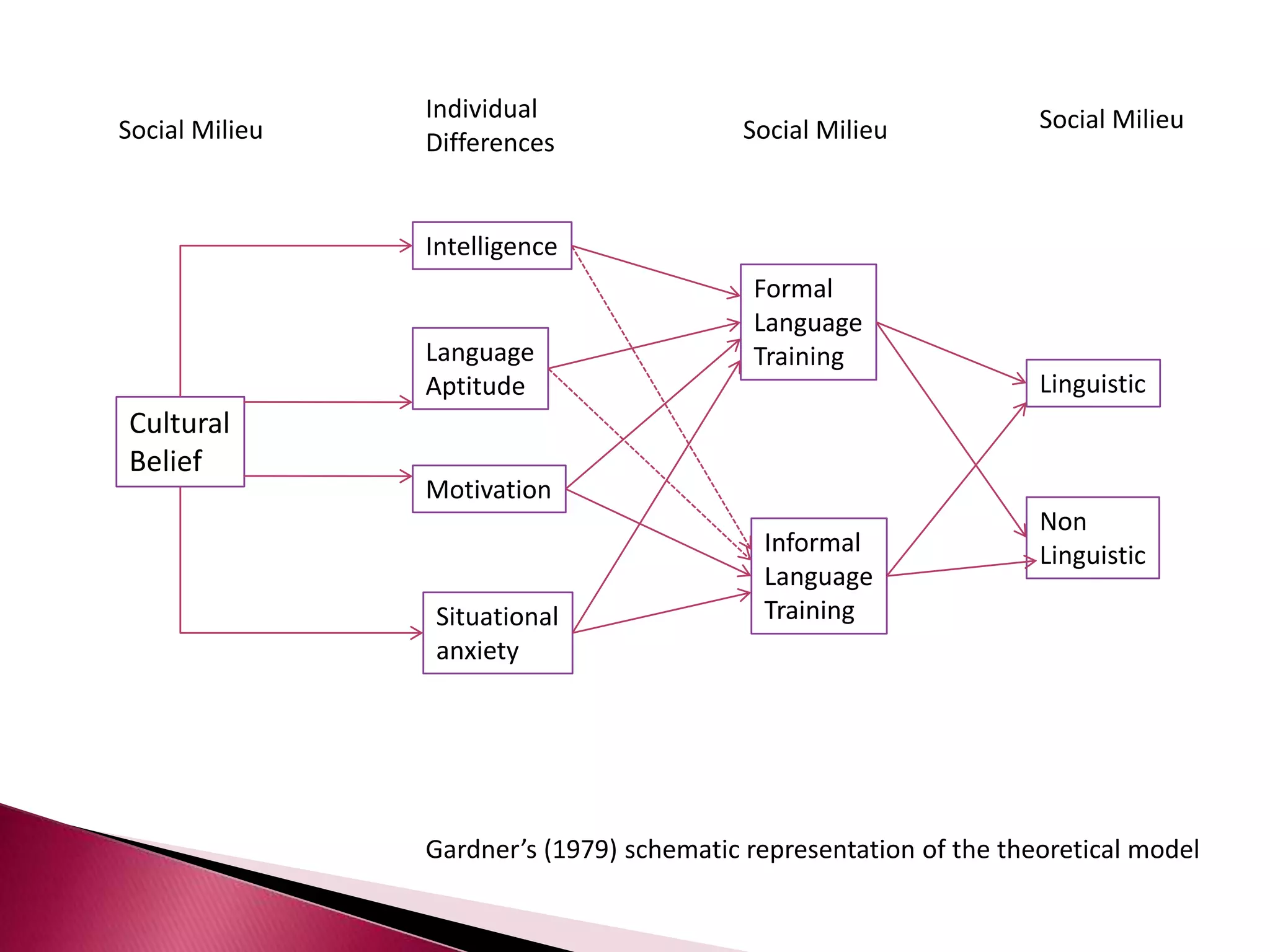
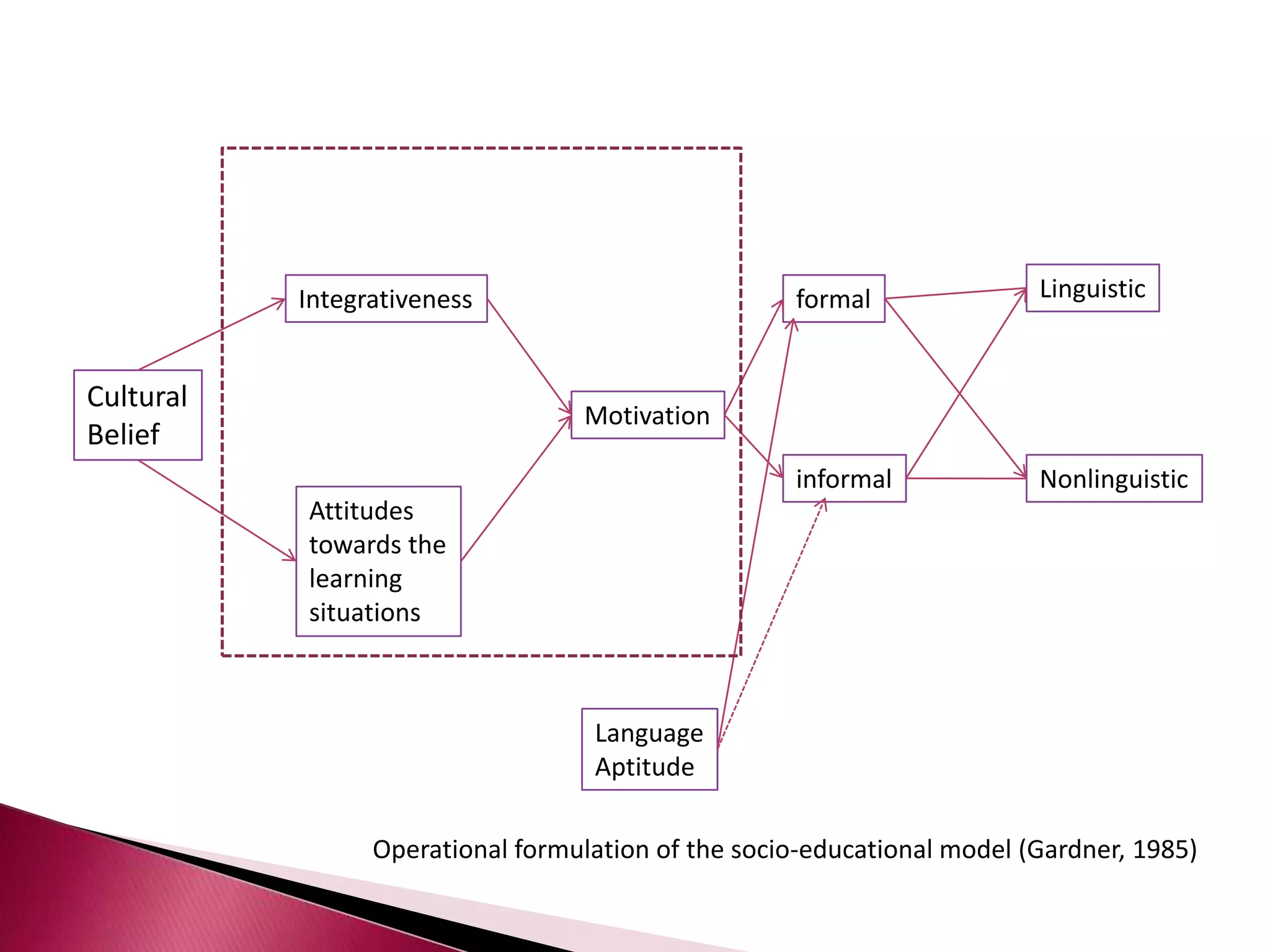
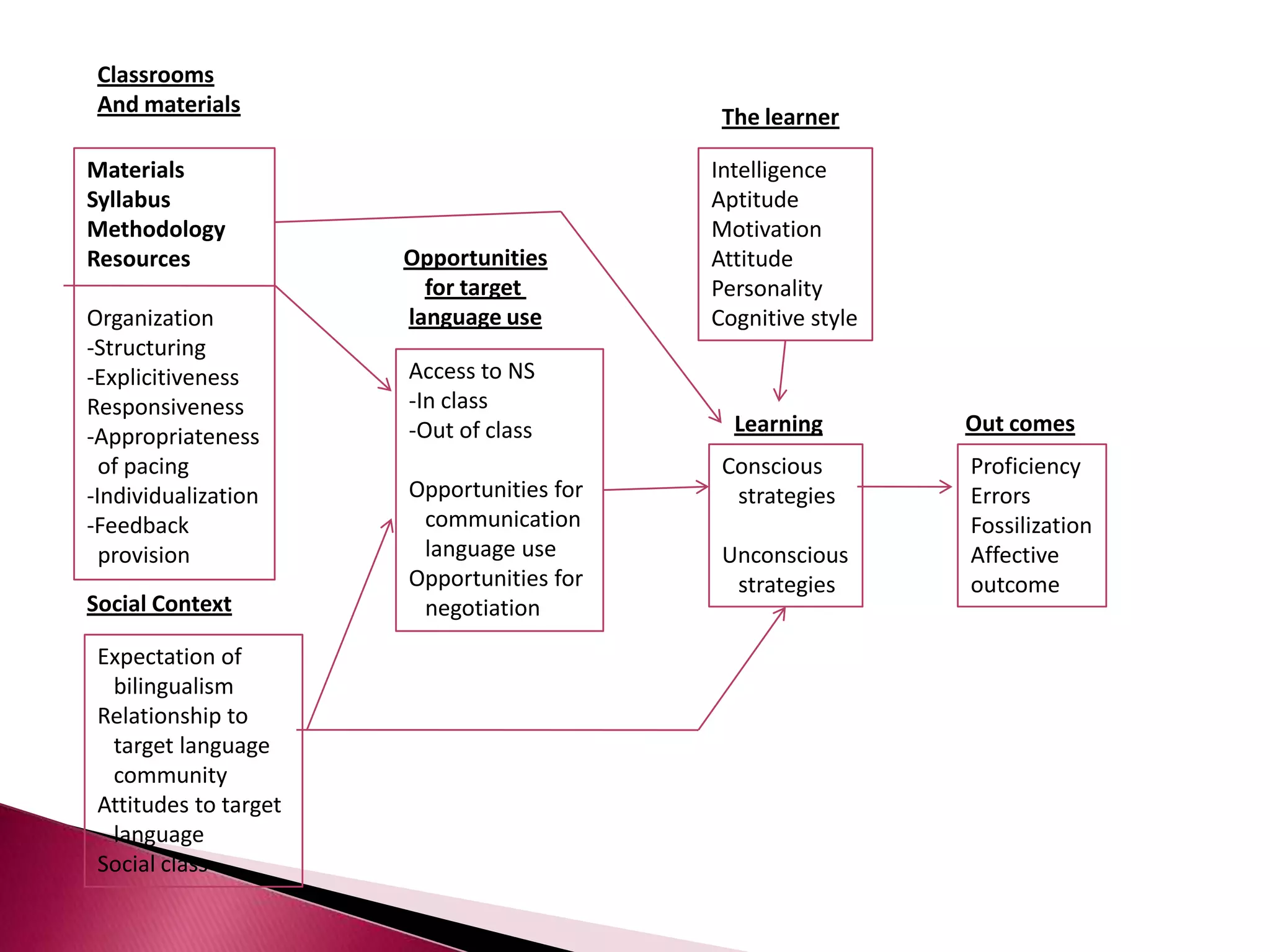
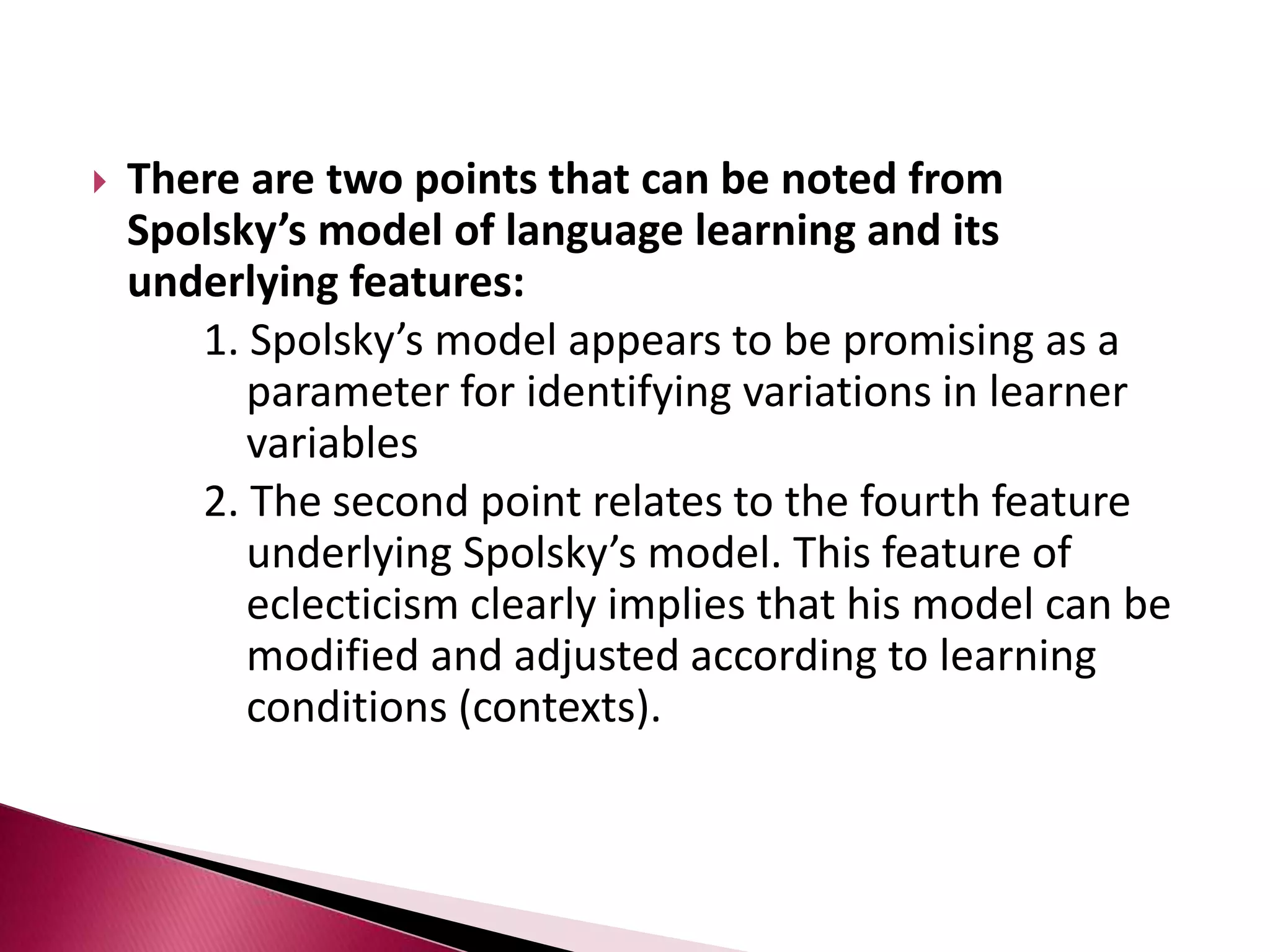
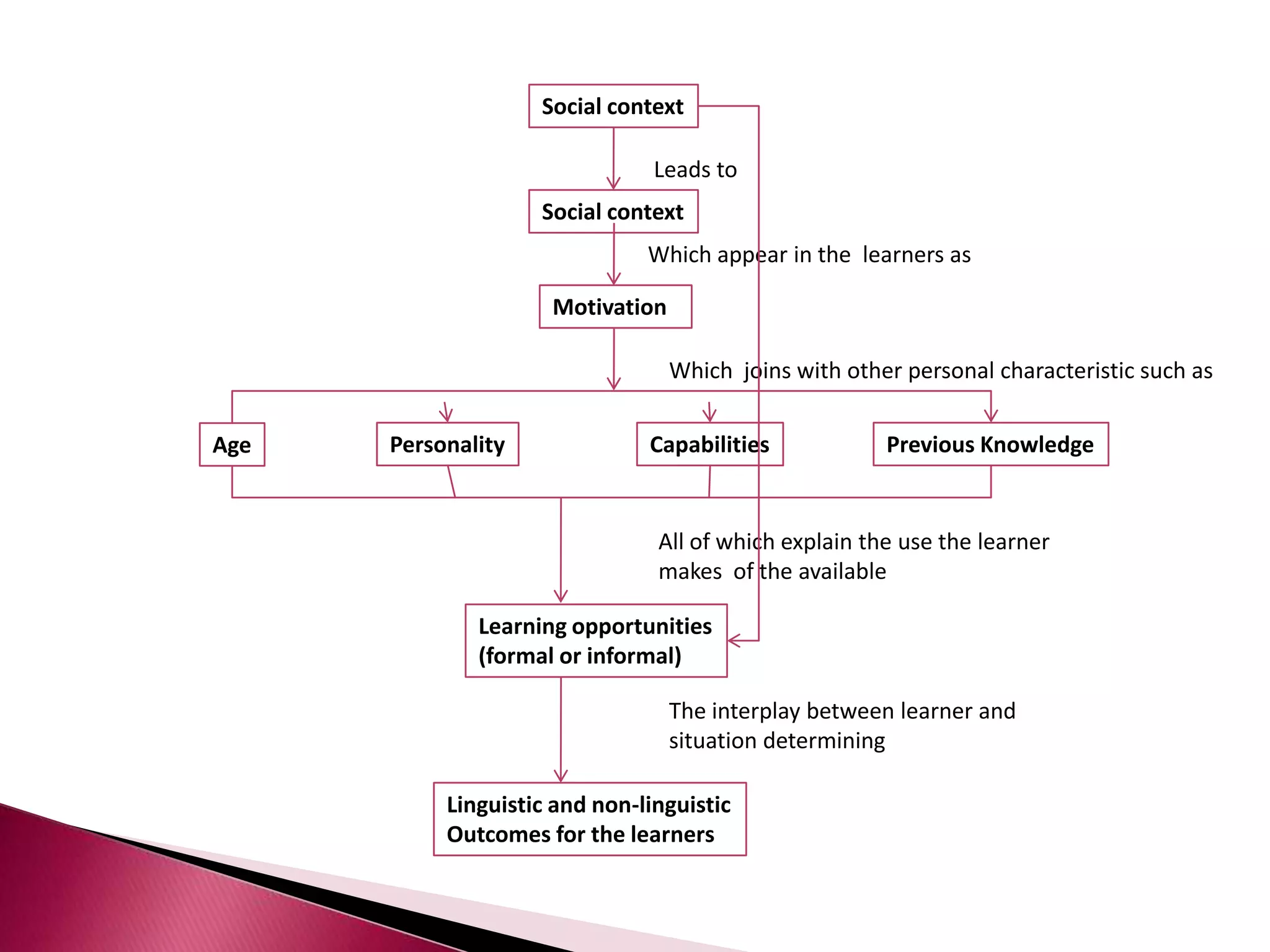
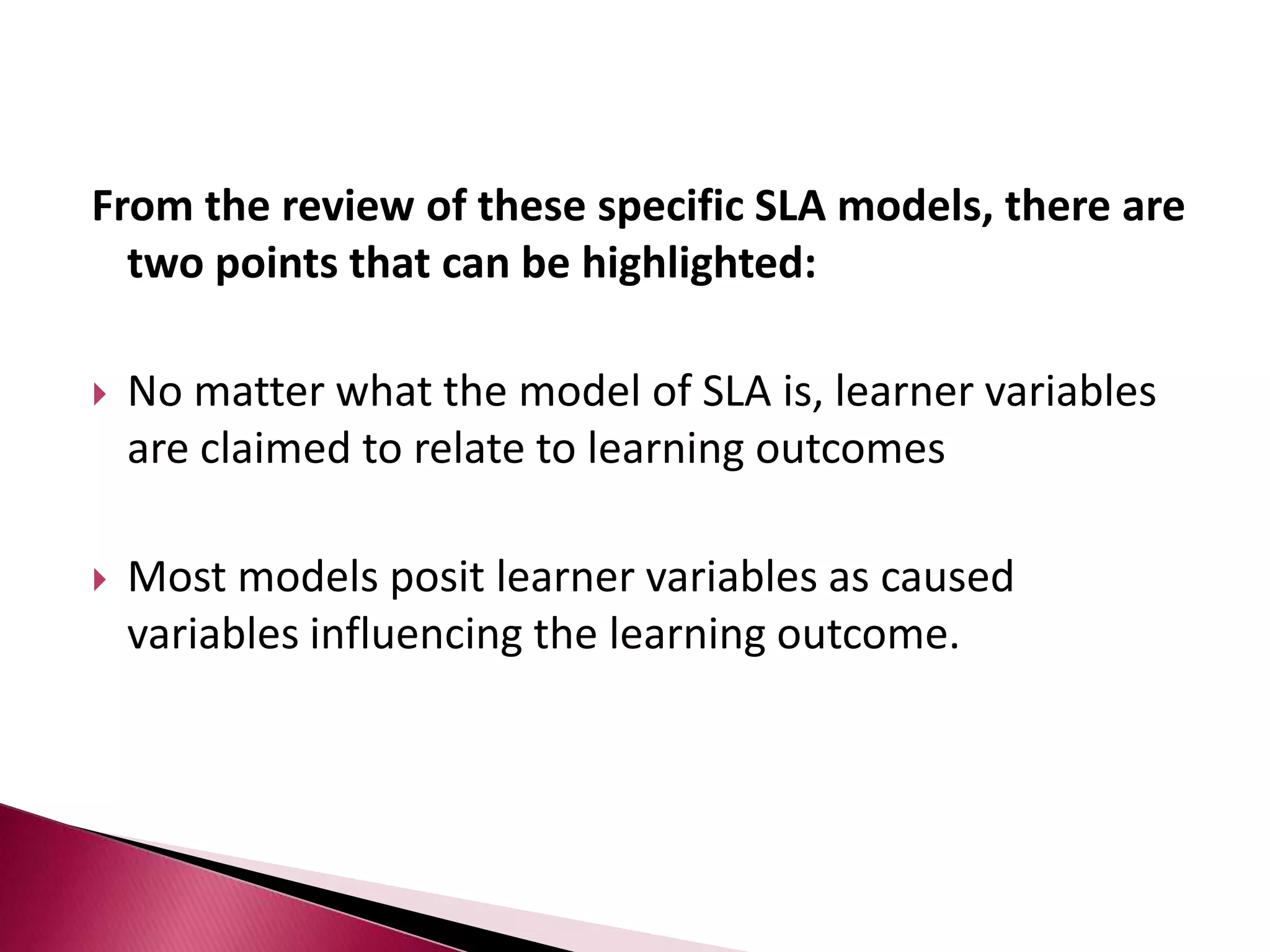
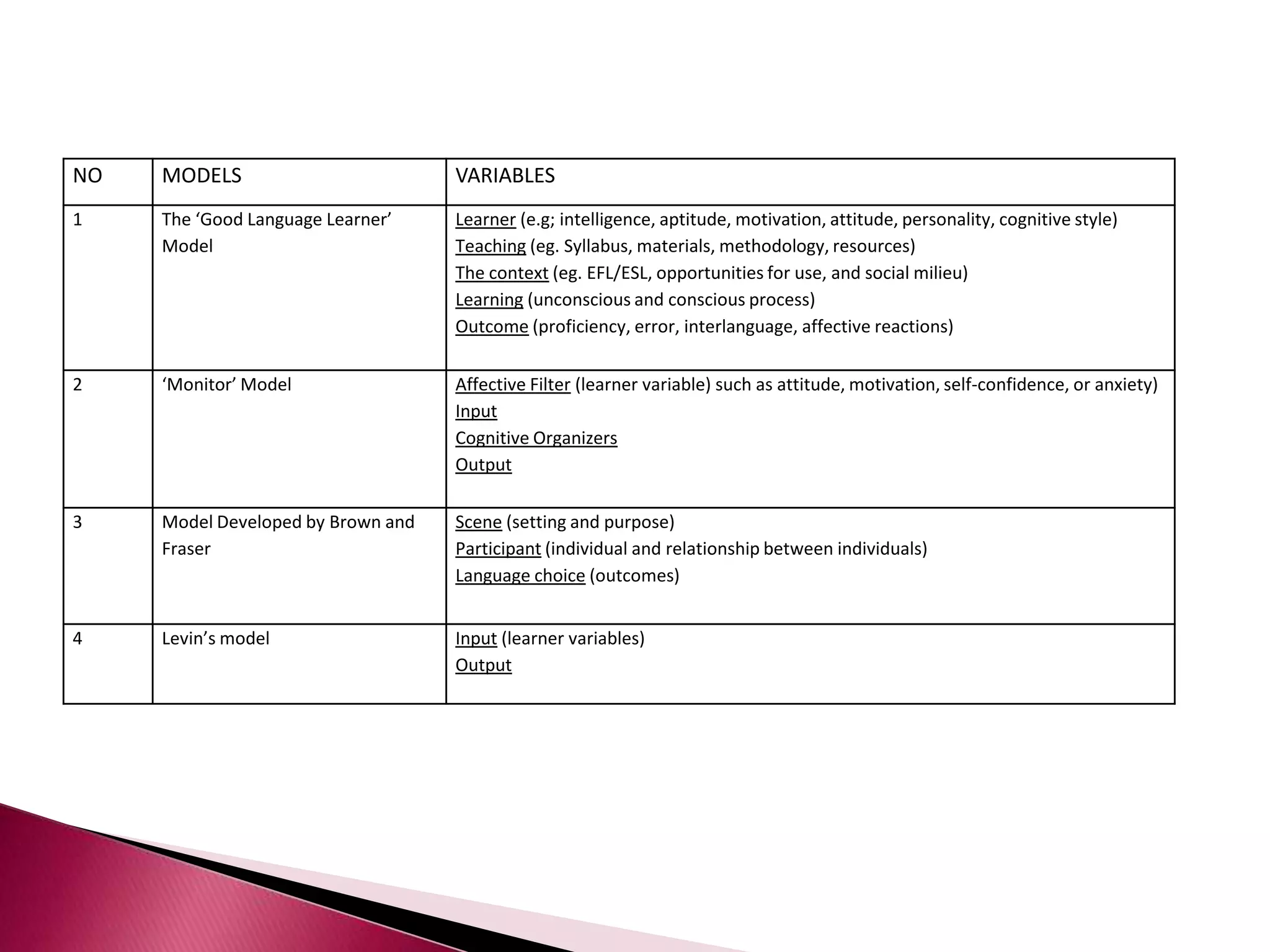
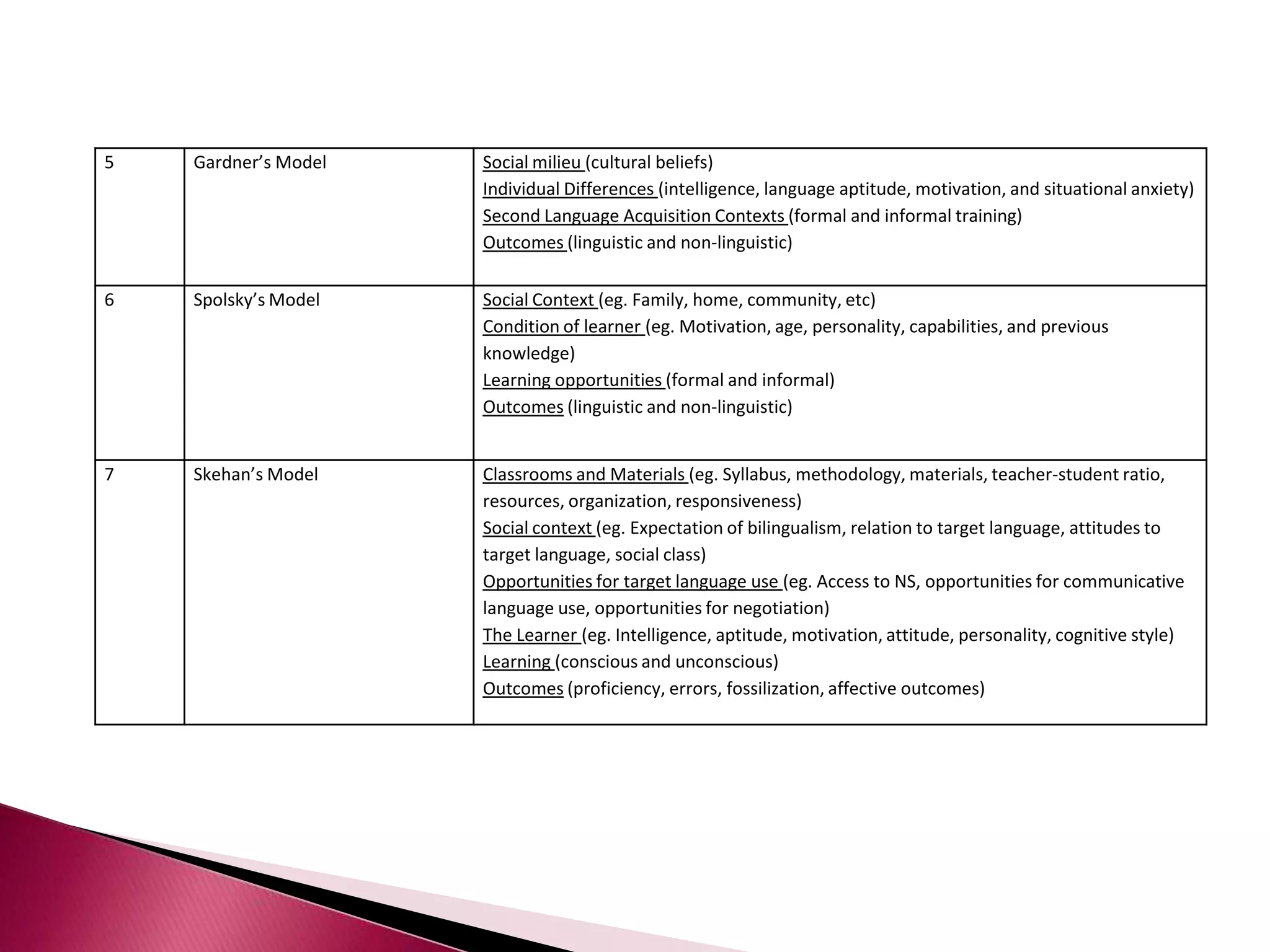
This document discusses several models of second language acquisition and individual difference factors that influence language learning. It summarizes several key models including Krashen's Monitor Model, Brown and Fraser's framework, Gardner's educational model, Skehan's model of language learning influences, and Spolsky's model of second language learning. The document also discusses how individual difference factors like age, attitudes, motivation, intelligence, language aptitude, previous knowledge, familiarity with computers, interactions with native speakers, and language used in the community can impact language learning outcomes, though notes there are often interactions between these different factors.