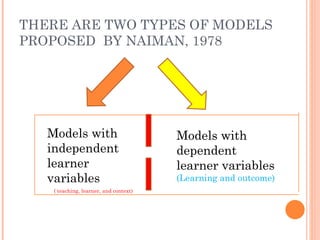
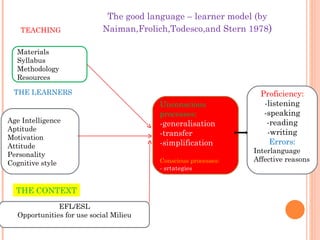
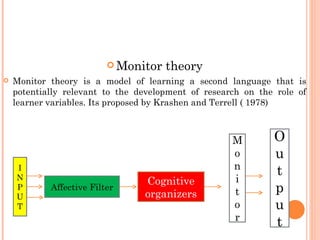
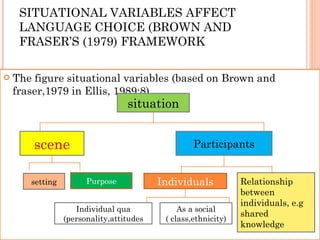
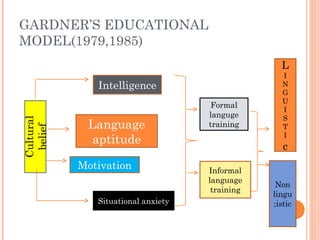
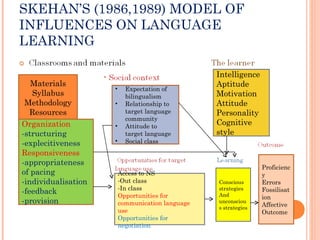
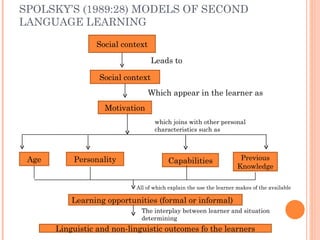
There are two main models of second language learning proposed by Naiman in 1978: models with independent learner variables and models with dependent learner variables. The good language learner model identifies factors such as age, intelligence, aptitude, and motivation that influence the learner. Monitor theory proposes that factors like affective filter, input, and output impact language learning. Situational variables also affect language choice and use according to Brown and Fraser's framework. Later models by scholars like Skehan and Spolsky further explored how individual differences, social and environmental factors influence second language acquisition.