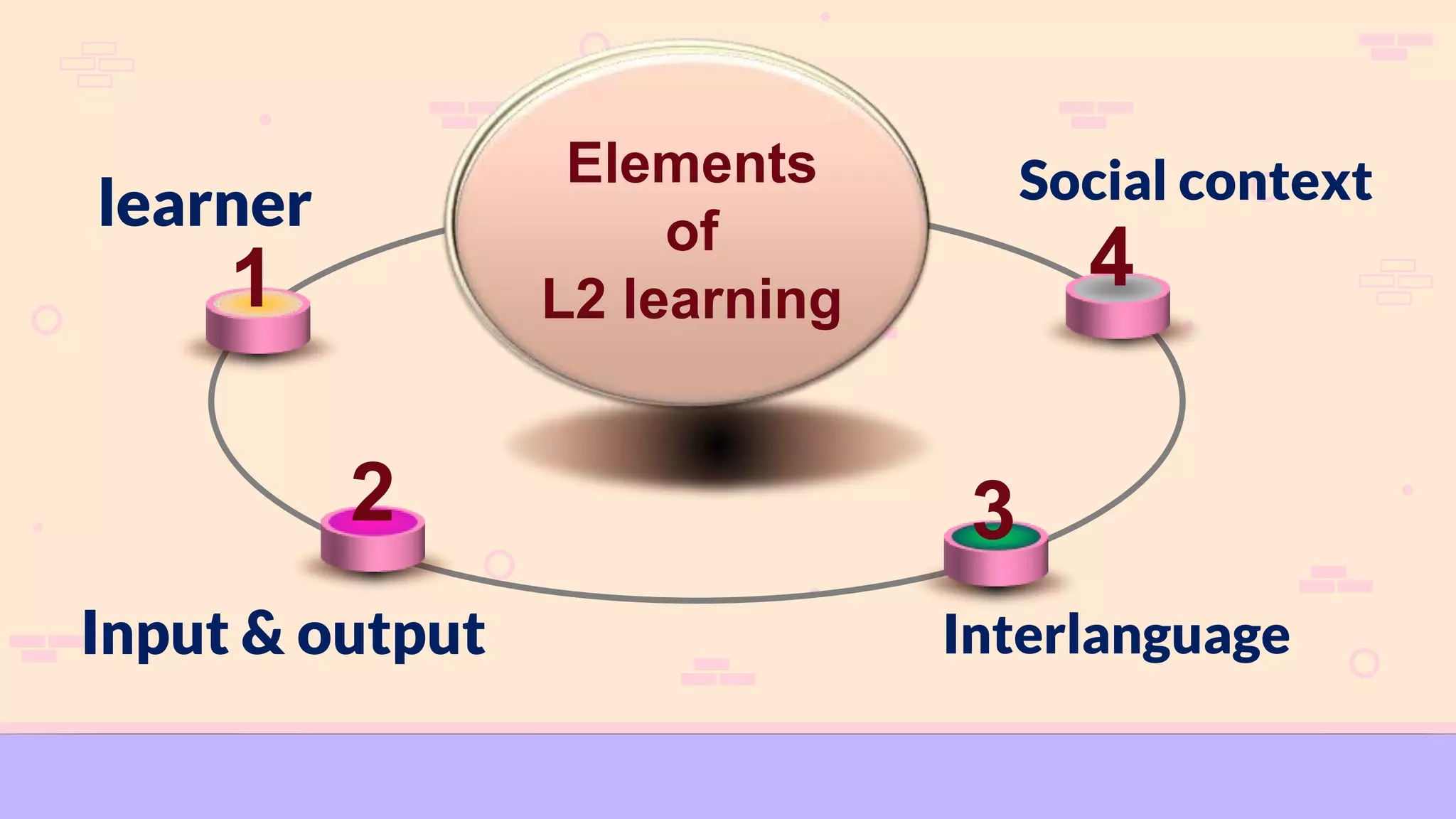
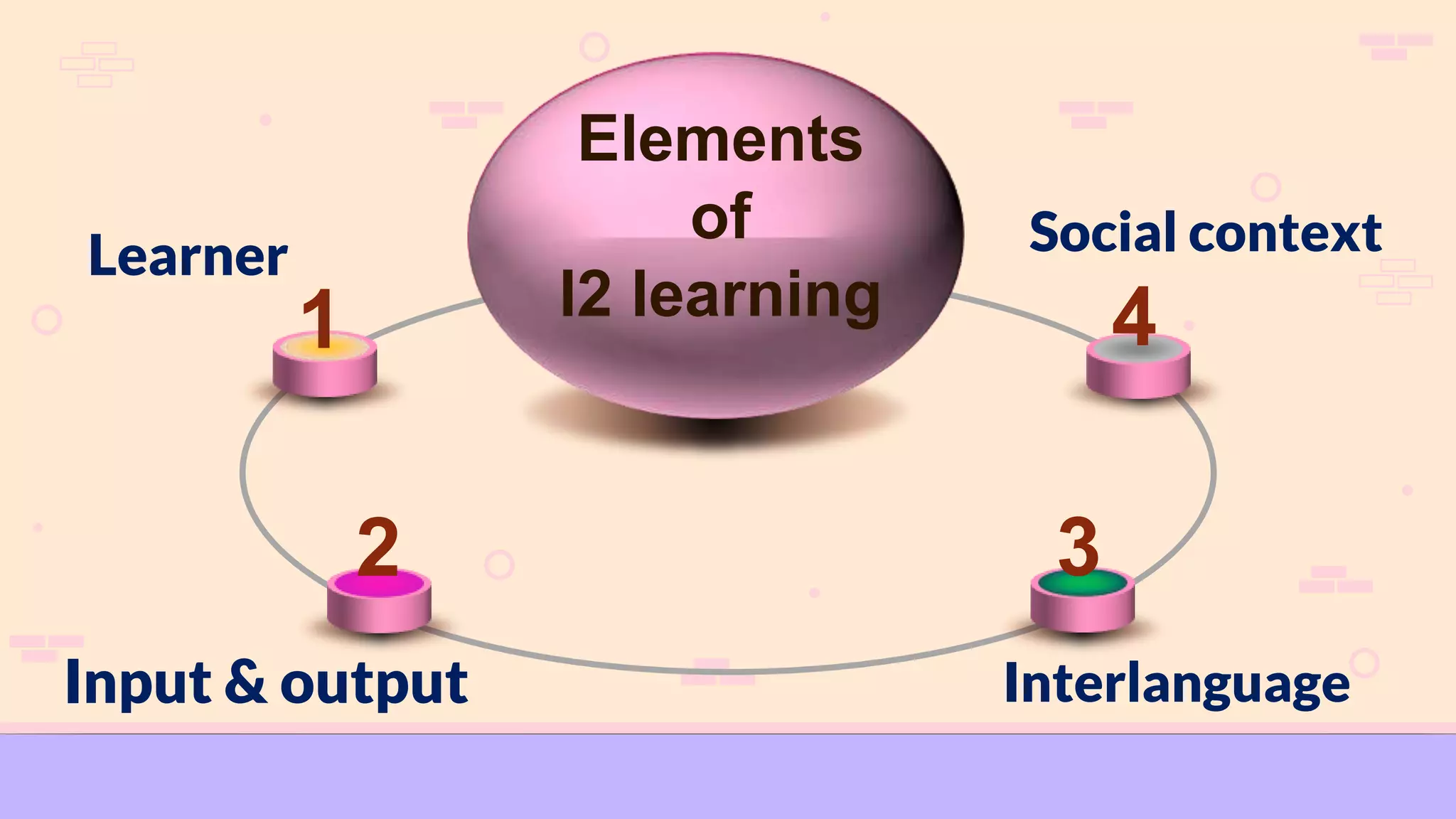
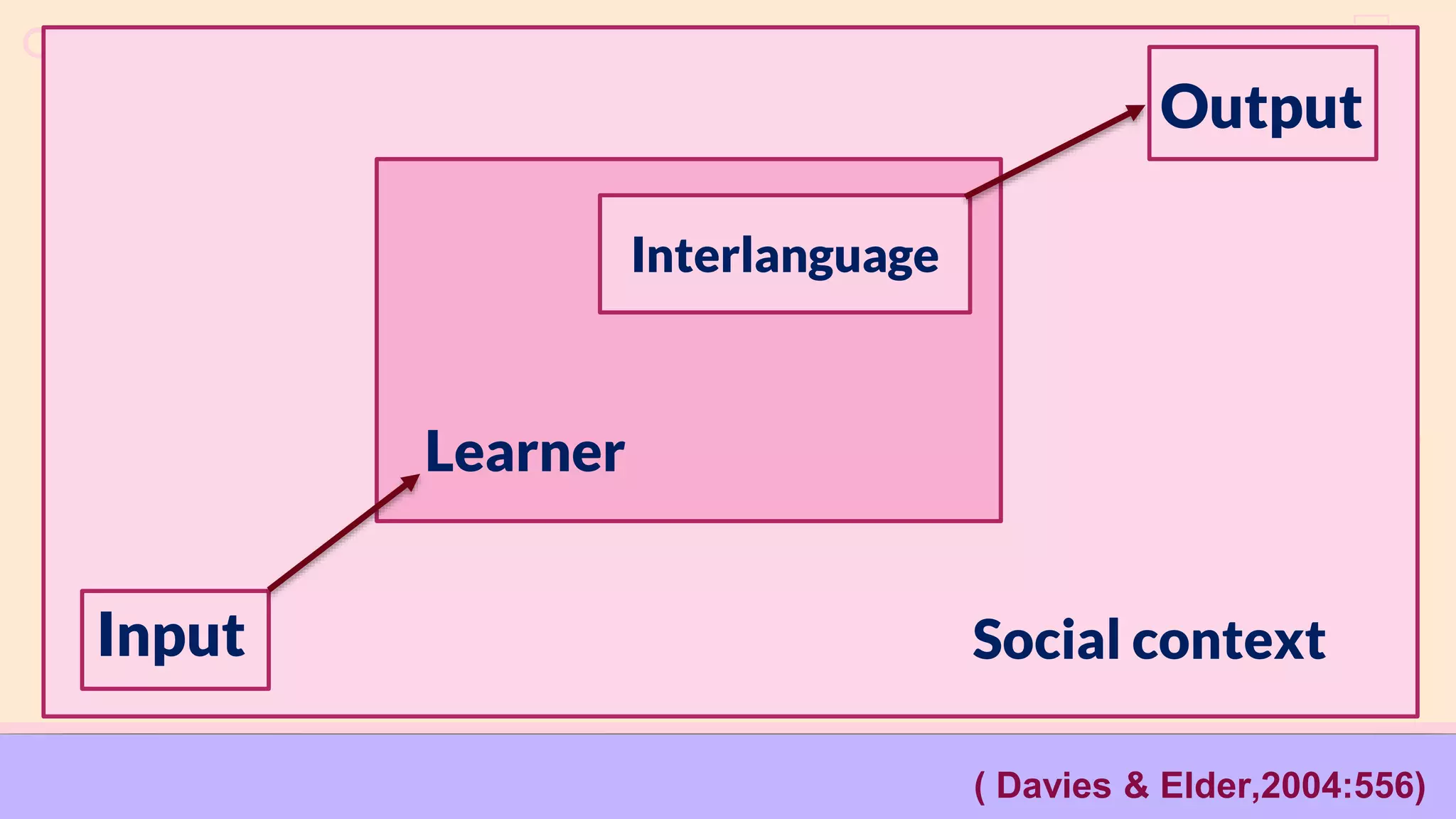
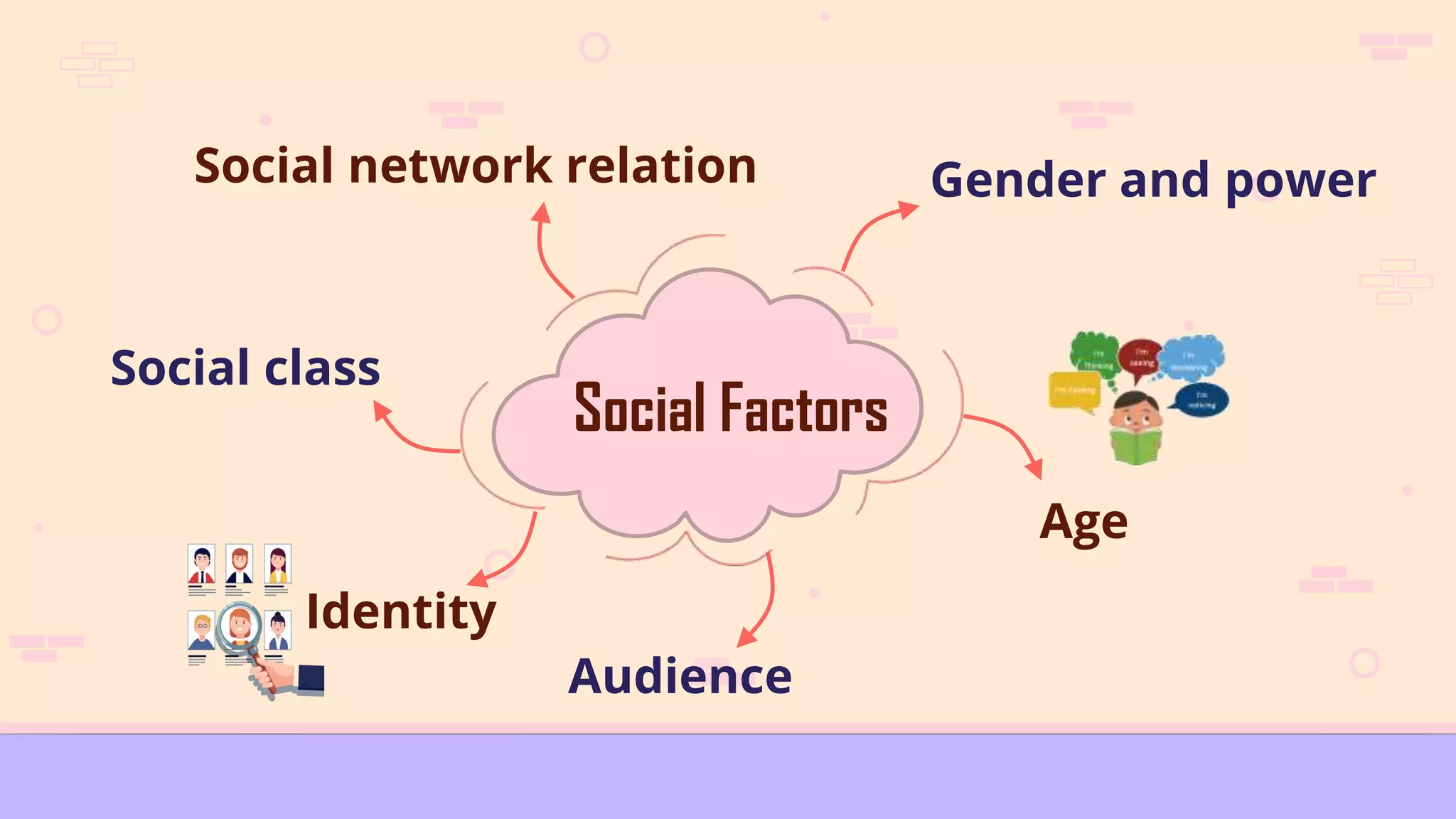
Social influences play an important role in language learning. The document discusses several social factors that can influence language acquisition, including gender, age, social class, ethnicity, and circumstances of learning. Gender differences in particular can impact language proficiency, as women may be more open to new linguistic forms while men tend to rely more on translation strategies. Younger learners are also generally more successful than older learners at acquiring a new language. The social context and relationships within a learning environment shape the input and output learners are exposed to. Together, social factors help determine an individual's developing interlanguage system as they learn between their first and second languages.