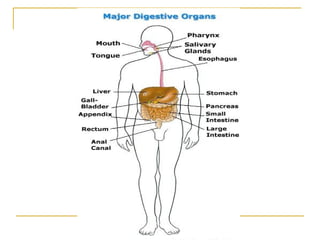
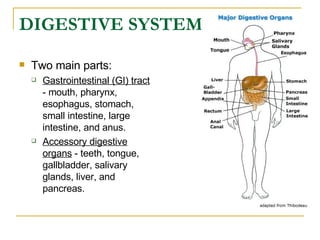
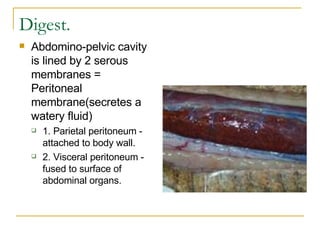
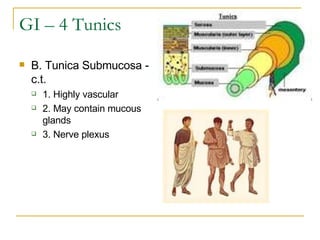
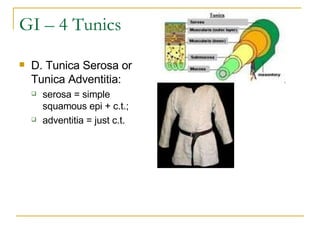
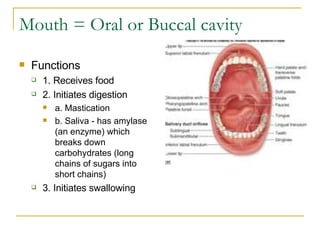
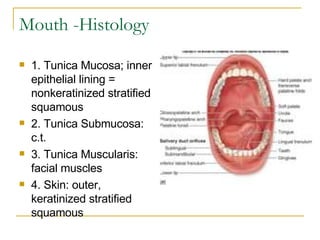
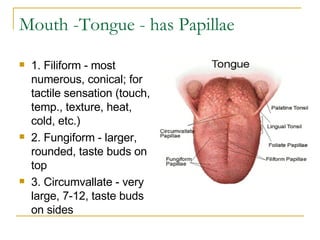
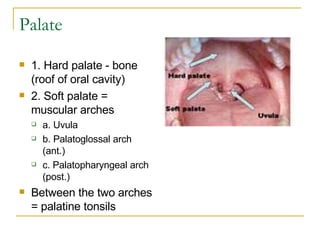
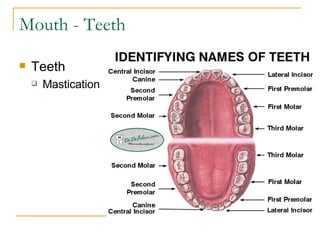
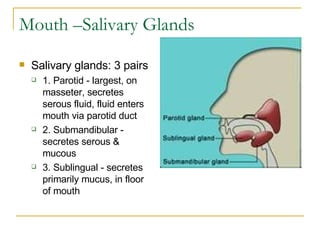
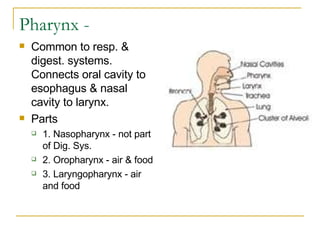
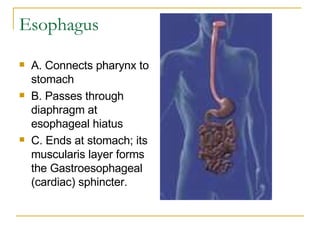
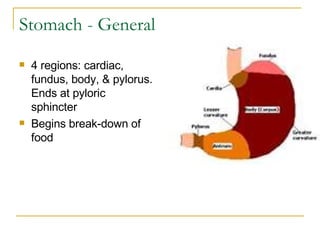
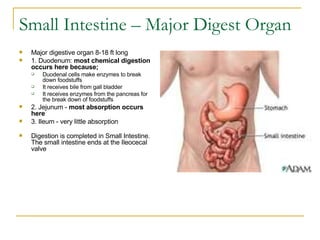
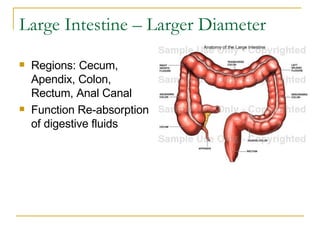
The digestive system has two main parts: the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and accessory organs. The GI tract includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus. Accessory organs include the teeth, tongue, liver, gallbladder and pancreas. Food enters the mouth where it is broken down by chewing and saliva before passing through the esophagus into the stomach for further breakdown. Digestion is completed in the small intestine where nutrients are absorbed. Undigested material then passes into the large intestine to be compacted and expelled as waste.