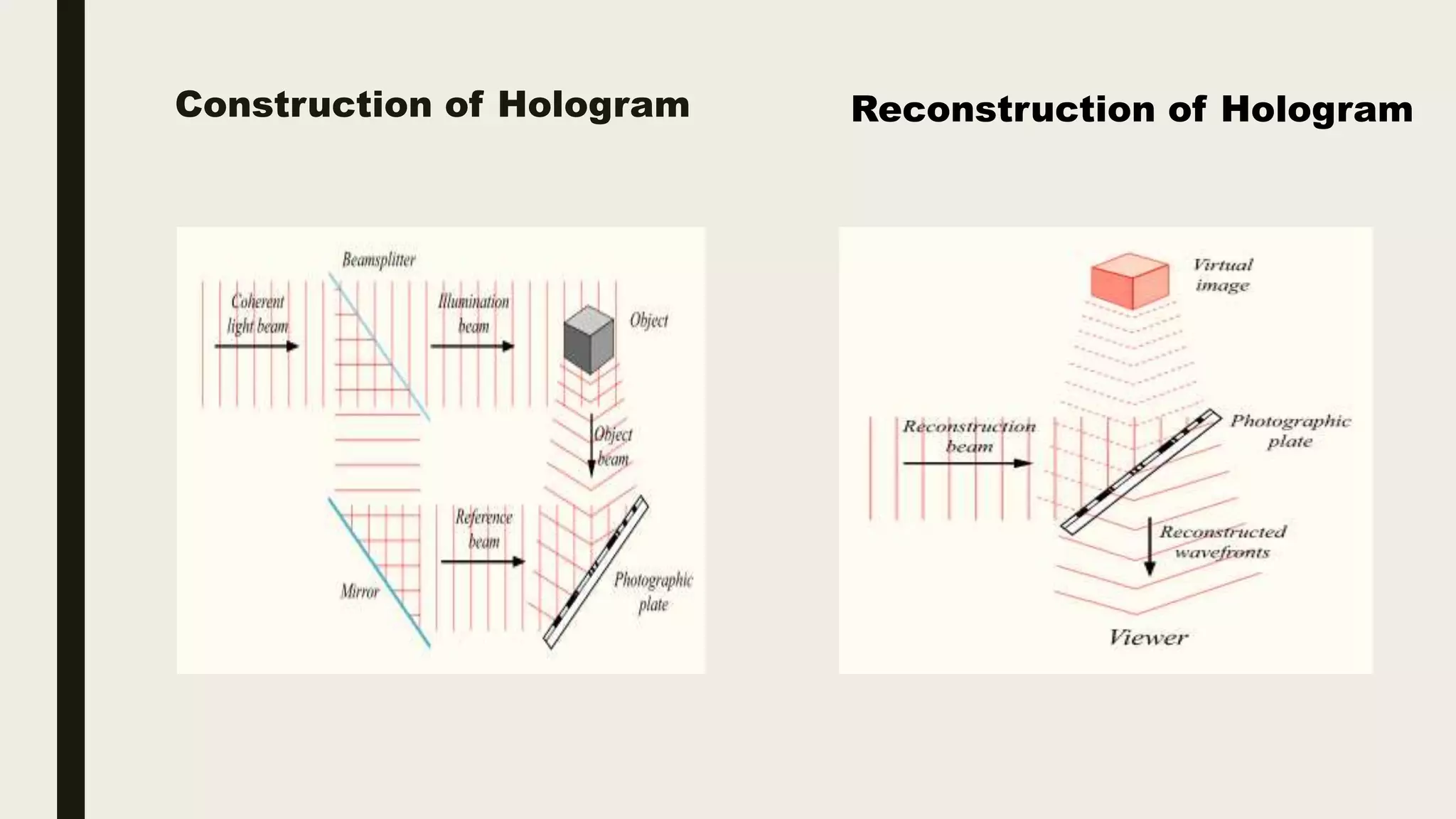
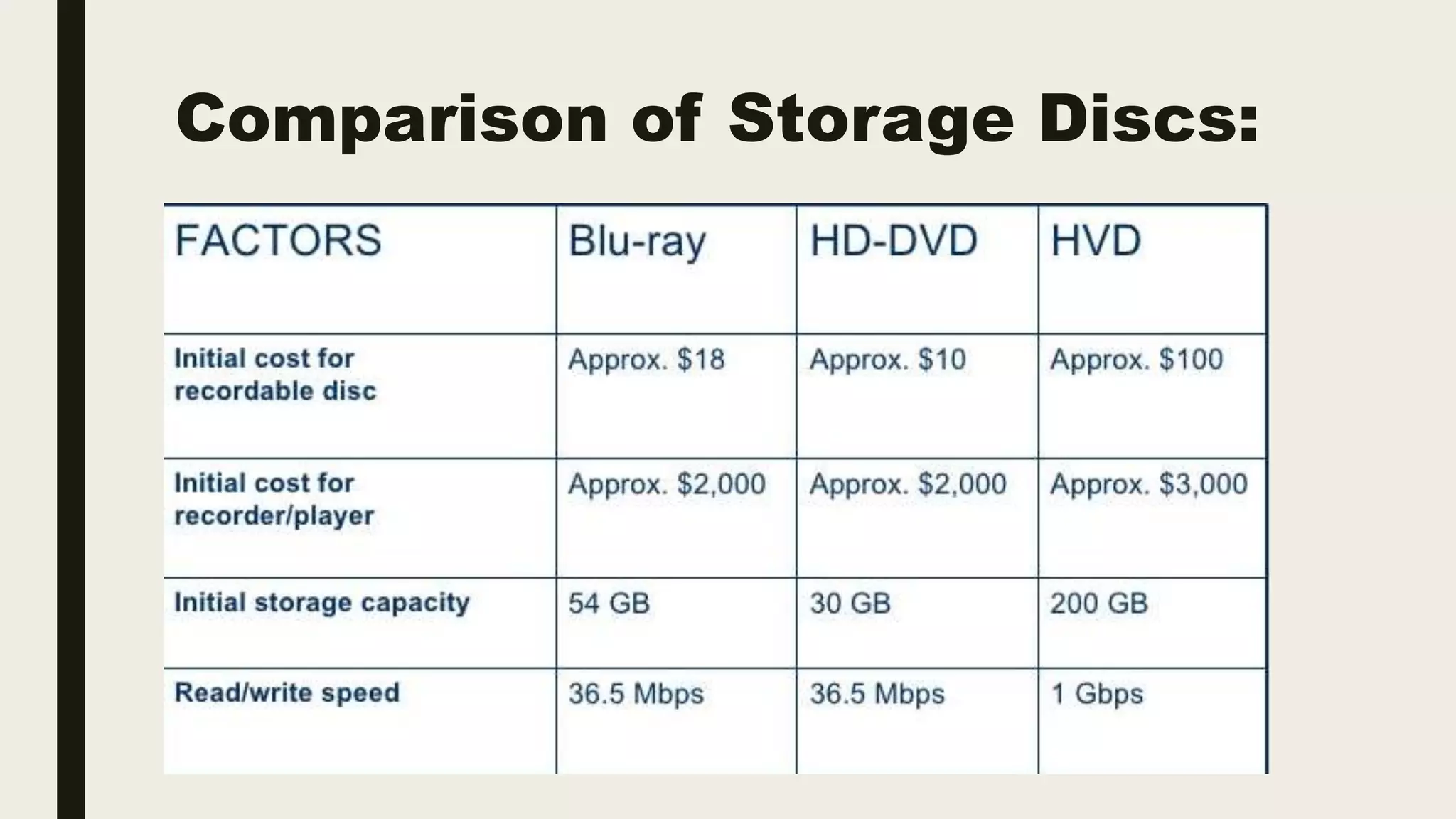
Holographic data storage (HDS) is a technology that allows high-capacity data storage using holograms to represent information in three dimensions, offering significant advantages in data density and retrieval speed compared to traditional methods. HDS utilizes laser technology and various multiplexing methods to store and access data efficiently, making it suitable for applications like data mining and petaflop computing. Despite its potential, challenges such as high development costs and market competition from existing technologies may hinder its widespread adoption.