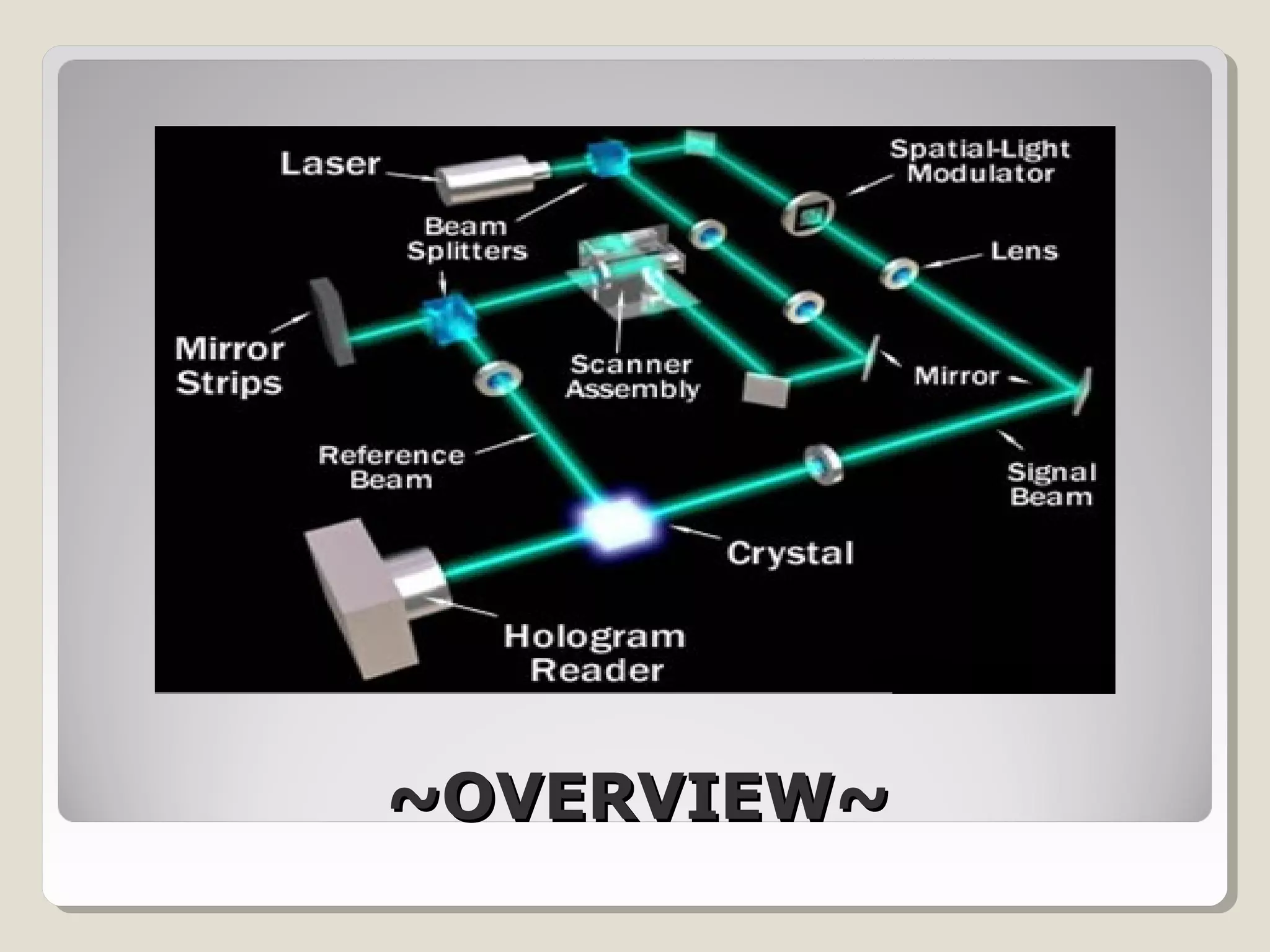
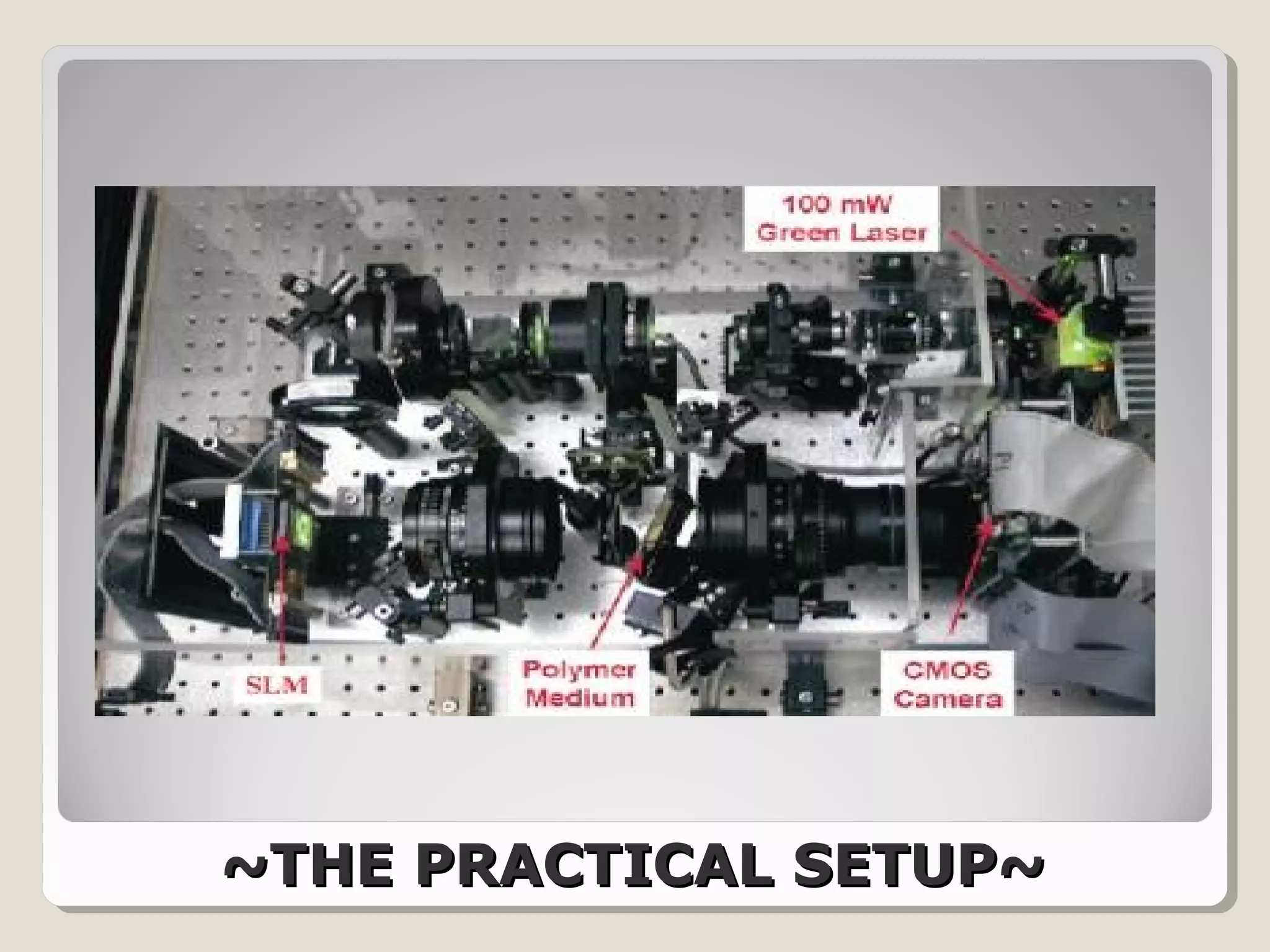
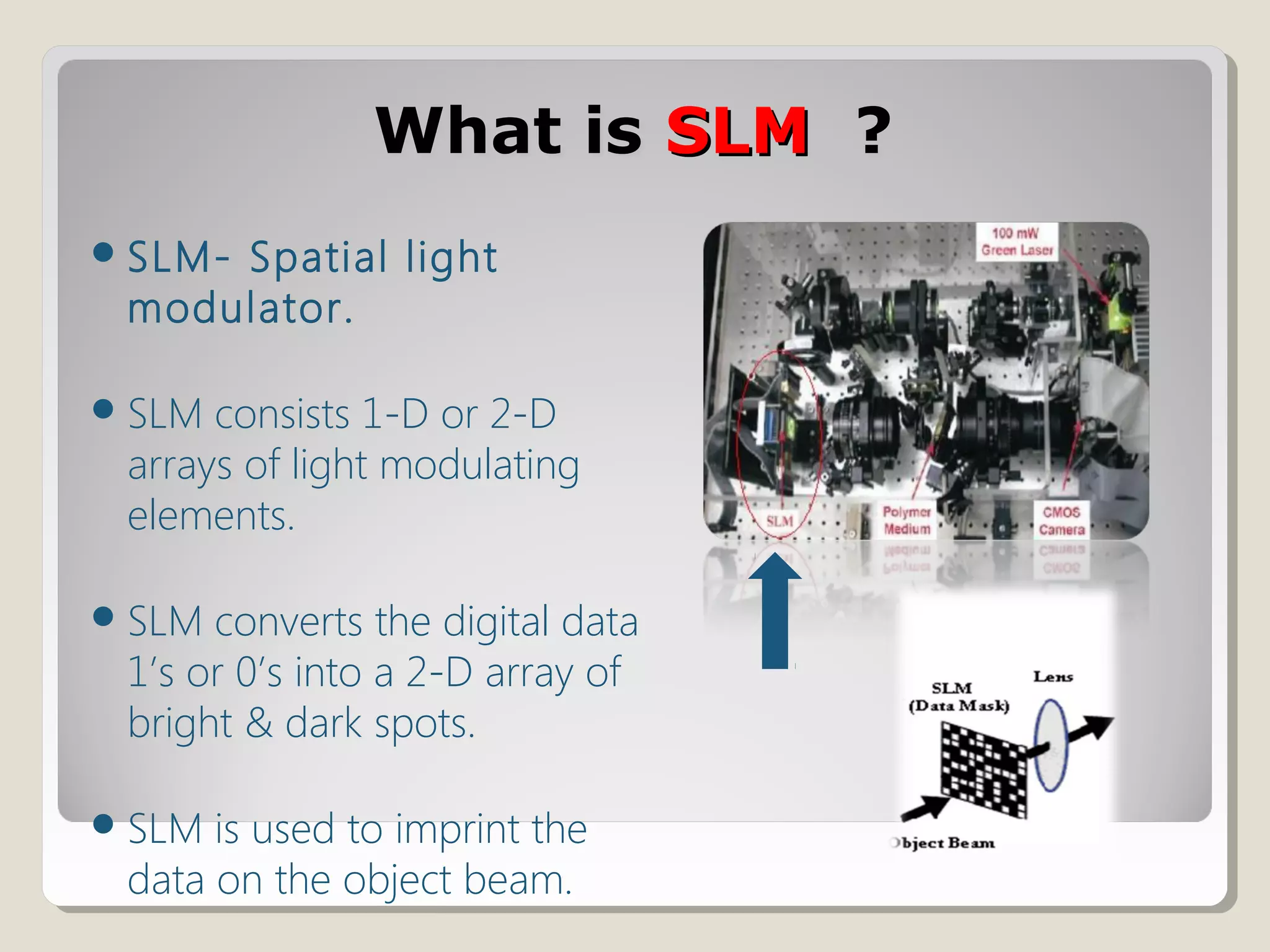
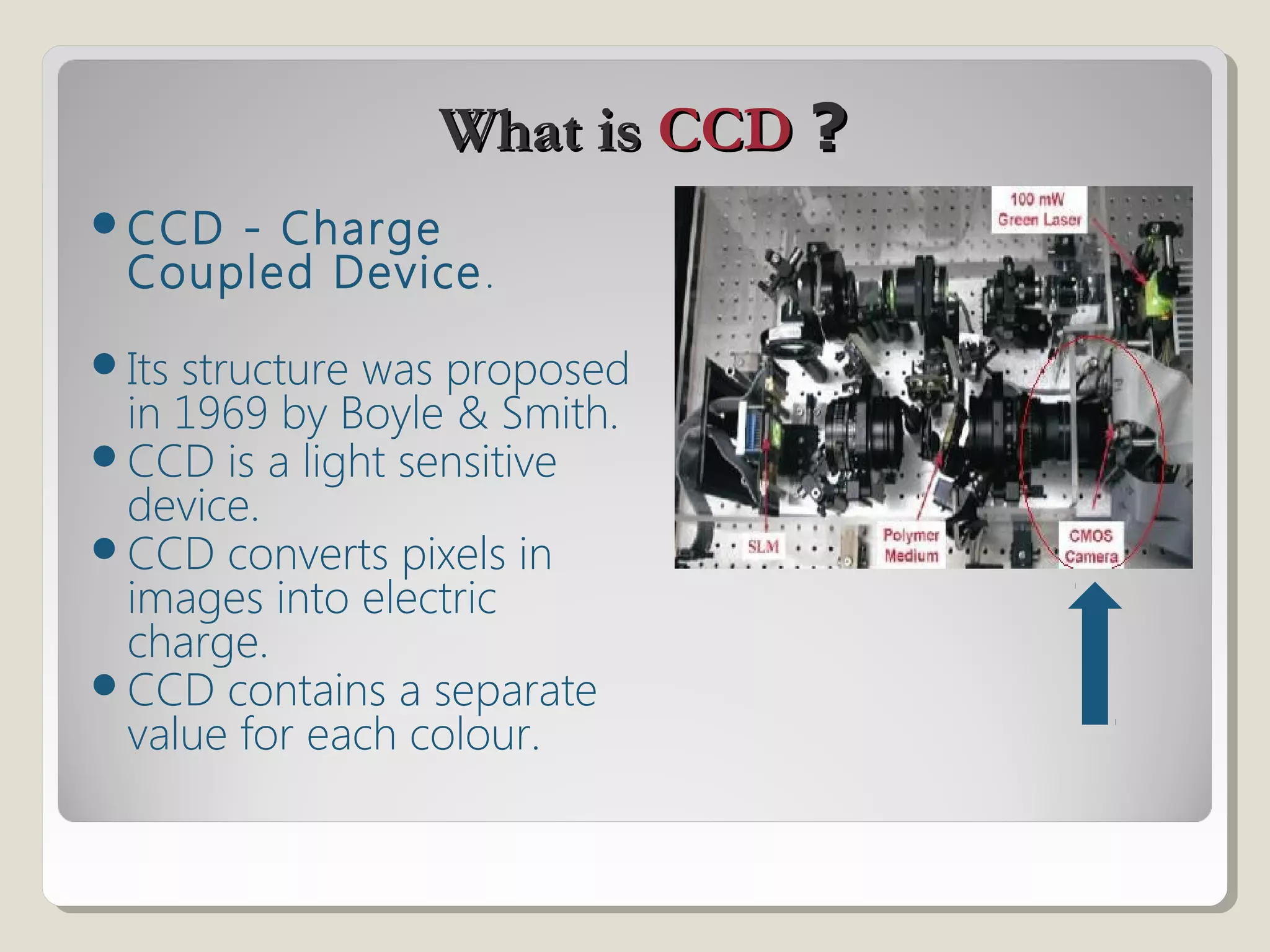
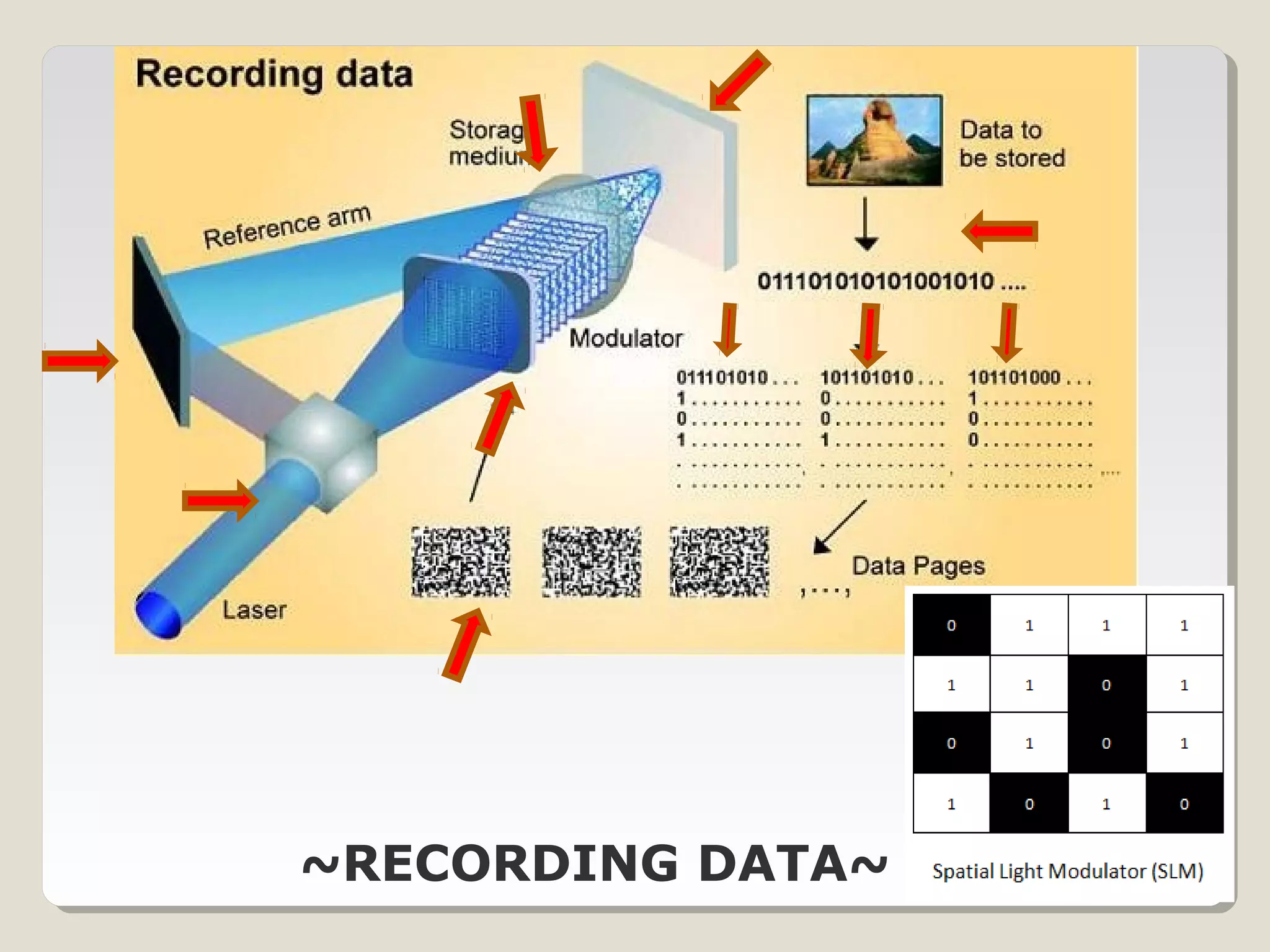
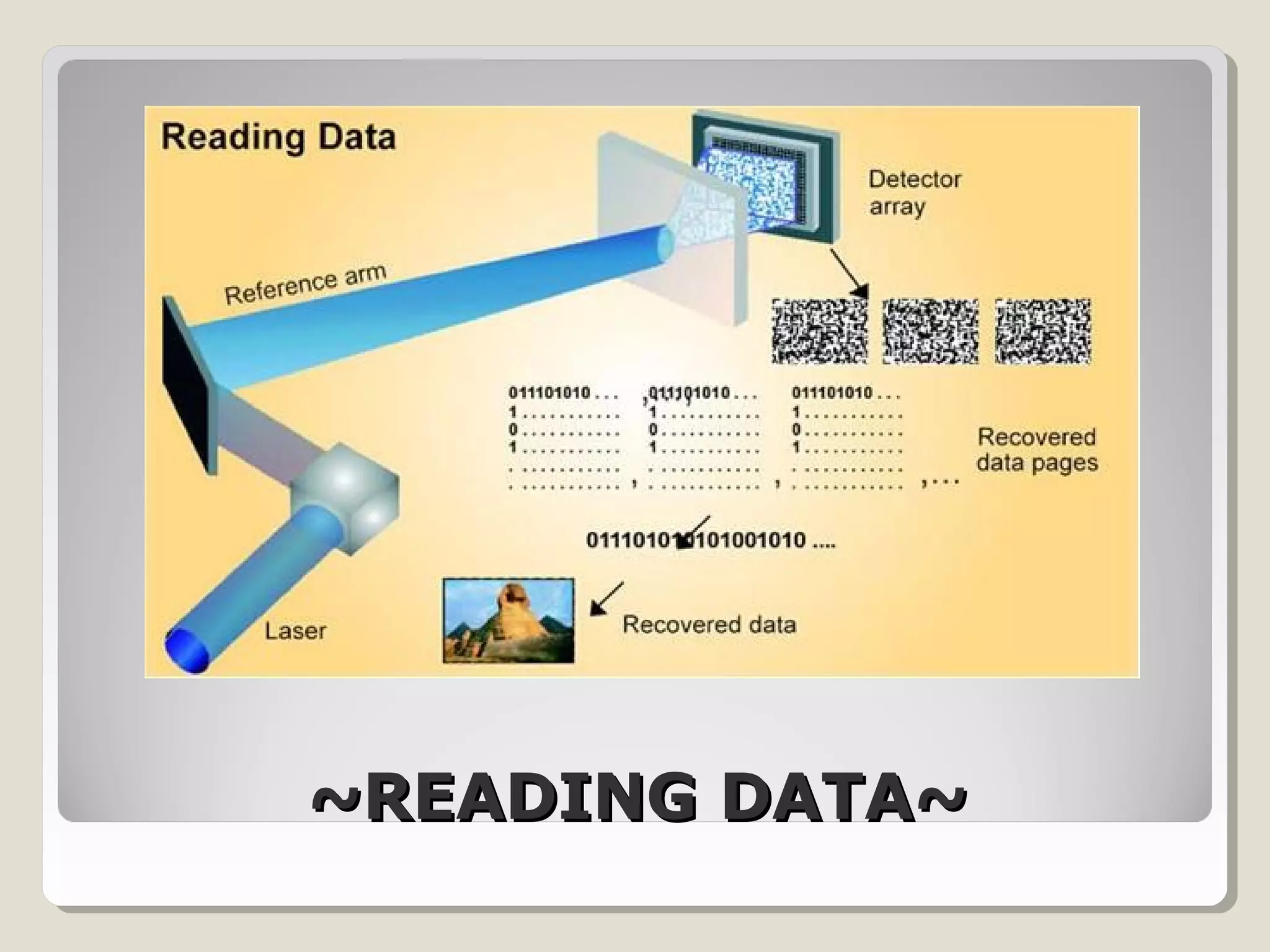
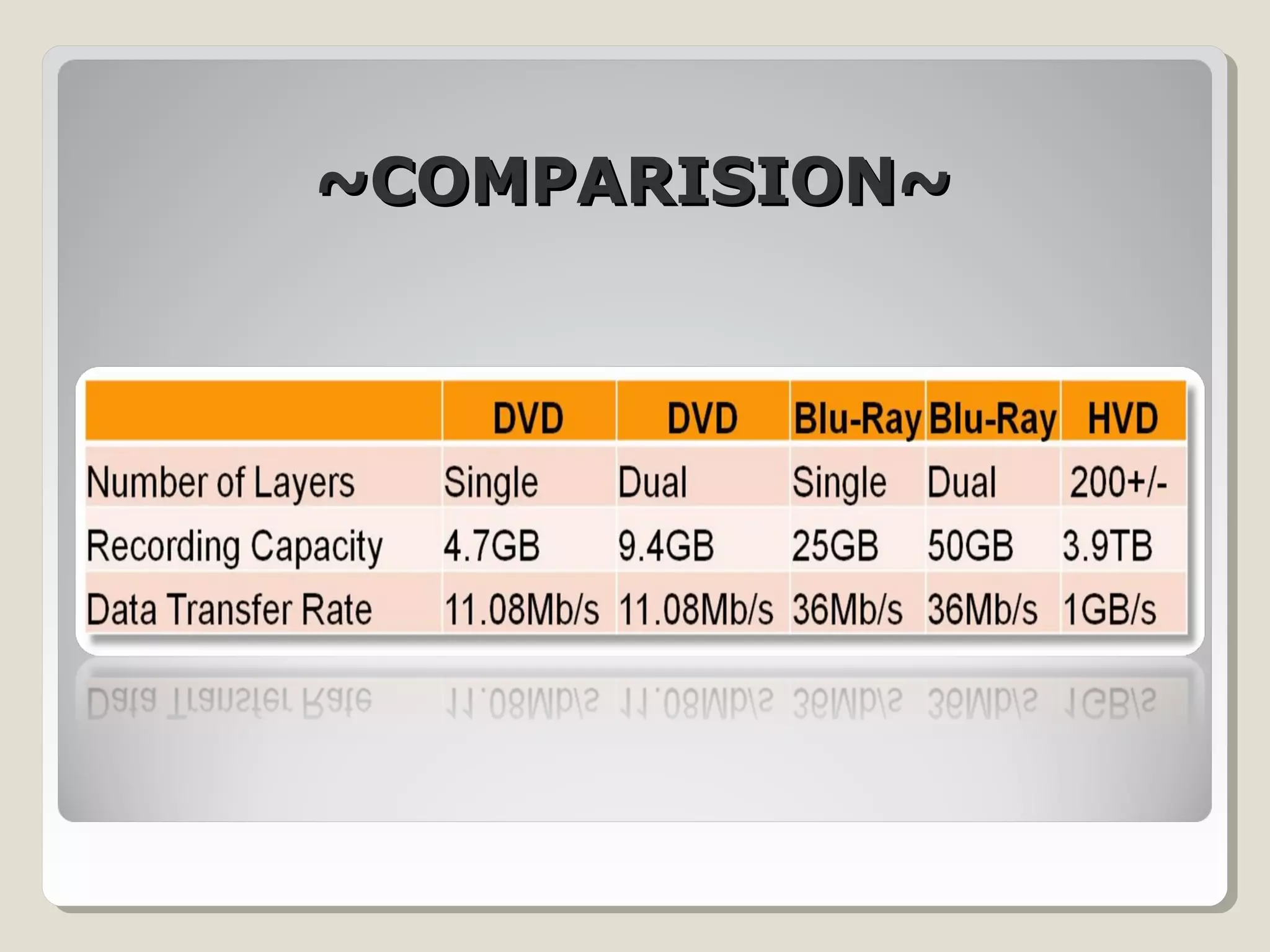
Holographic data storage uses lasers and optical materials to store massive amounts of data in three dimensions. Pieter van Heerden first proposed the idea in the 1960s, and a decade later scientists demonstrated storing 500 holograms in a lithium niobate crystal. Holographic data storage offers significant advantages over traditional storage methods by storing data in all three dimensions within a crystal, allowing millions of bits to be written or read in parallel with a single flash of light. Current research aims to develop holographic versatile disks with terabyte storage capacities and fast data transfer rates.