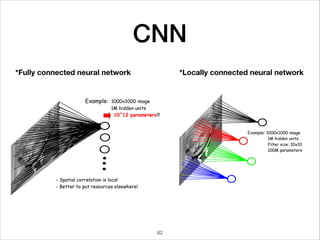
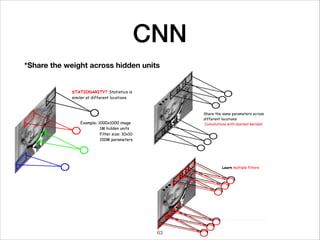
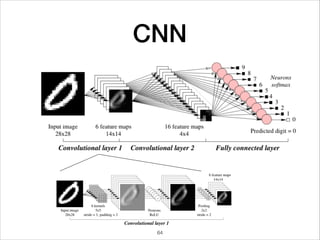
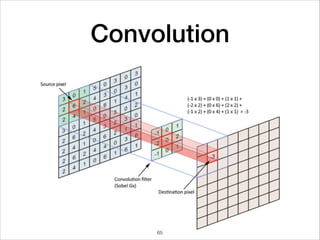
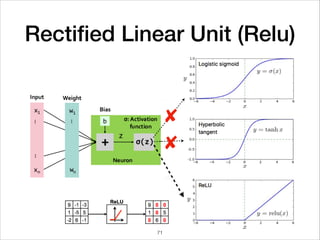
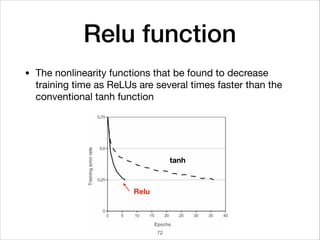
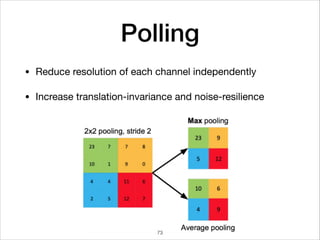
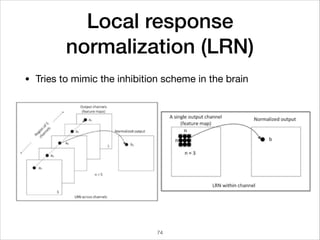
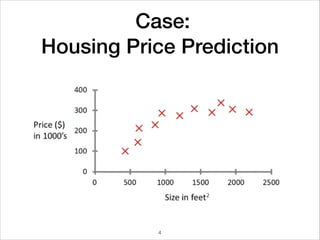
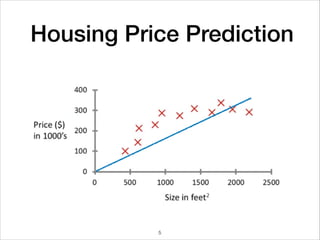
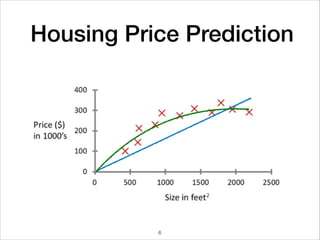
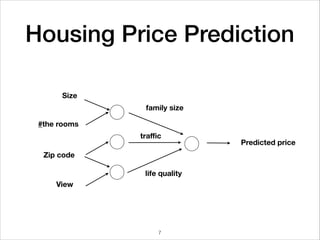
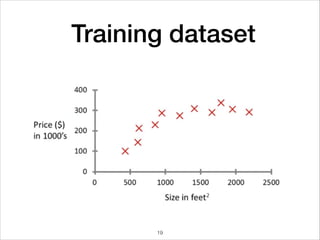
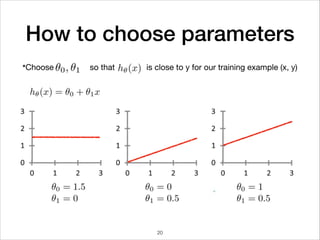
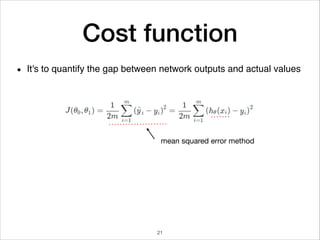
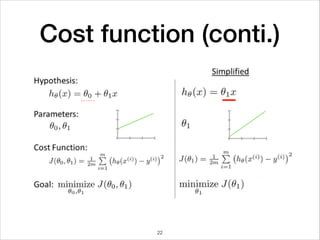
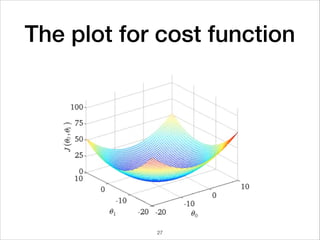
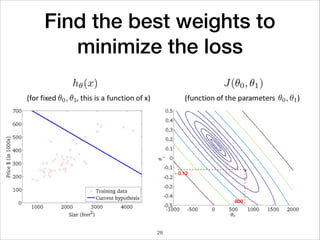
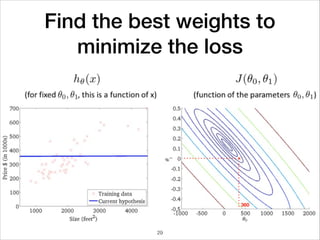
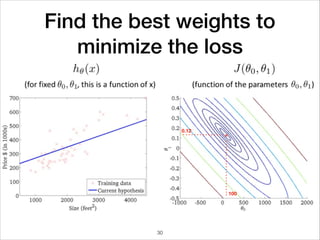
This document provides an overview of deep learning concepts including neural networks, regression and classification, convolutional neural networks, and applications of deep learning such as housing price prediction. It discusses techniques for training neural networks including feature extraction, cost functions, gradient descent, and regularization. The document also reviews deep learning frameworks and notable deep learning models like AlexNet that have achieved success in tasks such as image classification.





![Mini-Batch optimization
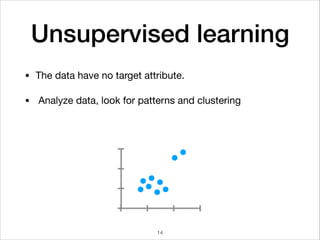
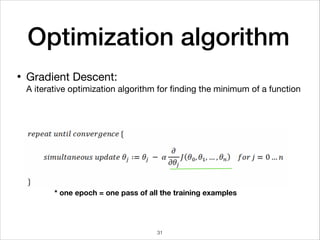
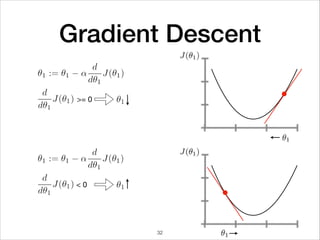
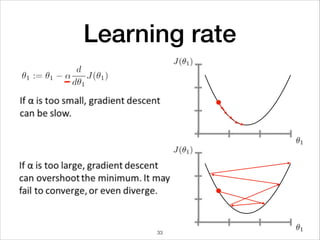
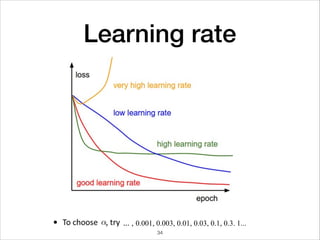
• Mini-batch optimization has the following advantages.
• Reduce the memory usage.
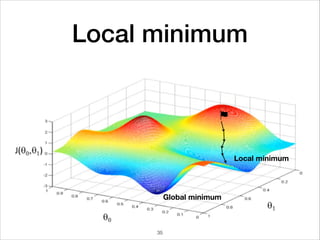
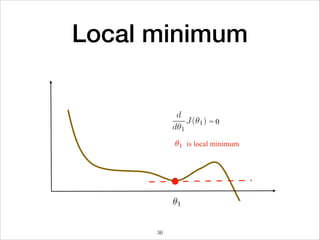
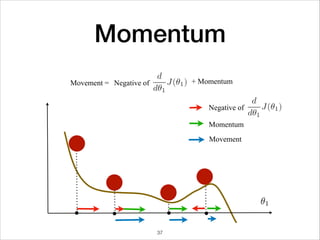
• Avoid being trapped in the local minima with the random m
*Batch size = the number of training examples in one pass
Iterations = number of passes, each pass using [batch size] of examples
38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deeplearning-170828064322/85/Deep-learning-38-320.jpg)