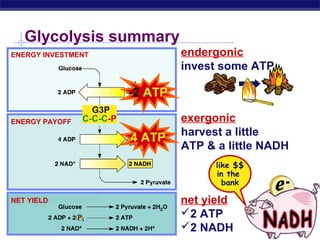
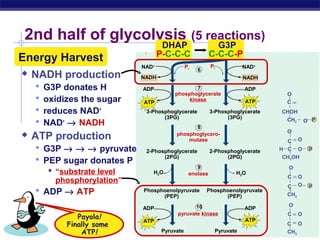
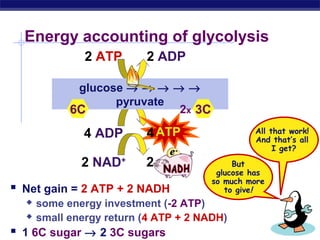
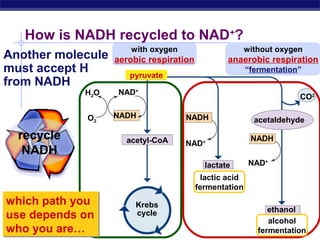
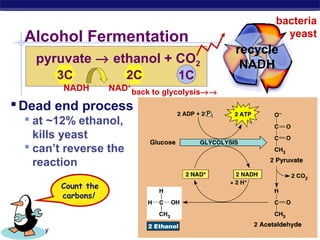
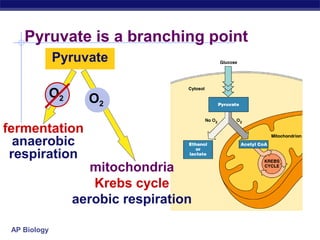
Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration where glucose is broken down to produce a small amount of ATP. It occurs in the cytosol of cells and was one of the earliest metabolic pathways to evolve. During glycolysis, glucose is converted into two pyruvate molecules via a series of 10 enzyme-catalyzed reactions. This stage generates a small energy return with a net production of two ATP molecules and two NADH molecules but consumes two ATP initially. Glycolysis alone is not sufficient to fully extract energy from glucose, so cells have developed additional stages of aerobic respiration using oxygen or fermentation without oxygen to further break down pyruvate and generate more ATP.