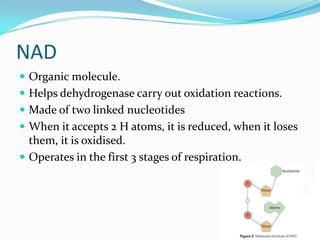
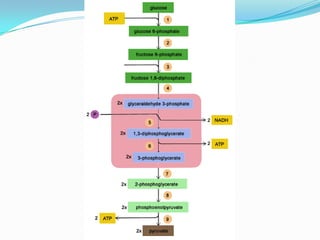
Respiration is the process by which cells use oxygen to break down glucose and other food molecules, and use the energy from these reactions to produce ATP, which cells use as energy currency. It occurs in three main stages - glycolysis, the Krebs cycle in the mitochondria, and oxidative phosphorylation. During these stages, electrons are transferred through electron carriers and coenzymes like NADH and FADH2, building up a proton gradient across the mitochondrial inner membrane. ATP is then produced as protons flow back through ATP synthase enzymes. The overall process converts glucose and oxygen into carbon dioxide, water, and ATP to power cellular work.