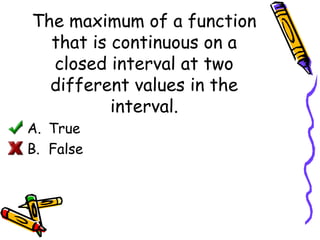
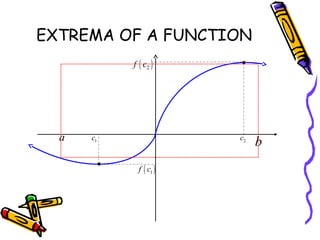
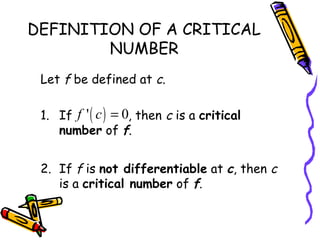
The document defines extrema as the extreme or maximum and minimum values of a function on an interval. An absolute extremum occurs at an endpoint of a closed interval, while a relative extremum occurs in the interior of an open interval. A function has extrema at points where the derivative is equal to 0 (critical points) or where the function is not differentiable. The Extreme Value Theorem states that a continuous function on a closed interval will have both an absolute maximum and minimum. To find the extrema of such a function, evaluate it at all critical points and endpoints. A function can have a maximum or minimum at multiple points within an interval.




![THE EXTREME VALUE
THEOREM
If f is continuous on a closed interval
[ a, b] , then f has both a minimum
and a maximum on the interval.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cps3-131031190738-phpapp02/85/3-1-extrema-on-an-interval-7-320.jpg)


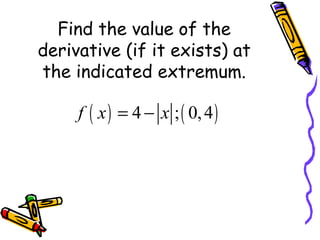
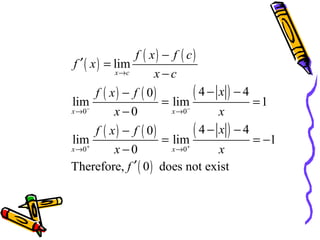



![GUIDELINES FOR FINDING
EXTREMA ON A CLOSED
INTERVAL
To find the extrema of a continuous function
f on a closed interval [ a, b ] , use the
following steps.
1. Find the critical numbers of in .
2. Evaluate f at each critical number in ( a, b ).
3. Evaluate f at each endpoint of [ a, b] .
4. The least of these outputs is the
minimum. The greatest is the maximum.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cps3-131031190738-phpapp02/85/3-1-extrema-on-an-interval-17-320.jpg)