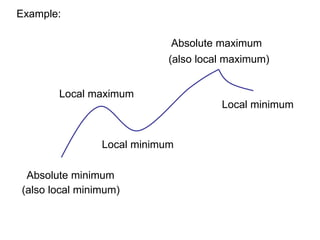
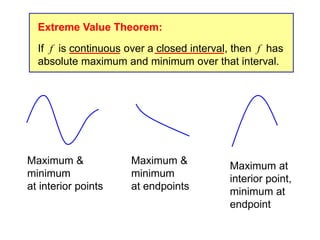
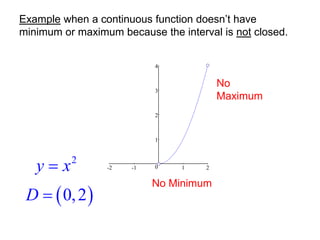
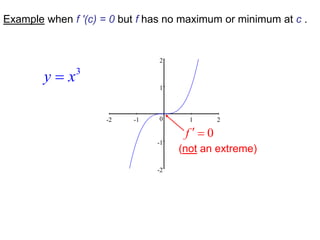
The document defines absolute and local maximum and minimum values of functions. An absolute (or global) maximum is the highest value a function can take over its entire domain, while an absolute minimum is the lowest value. A local maximum/minimum is the highest/lowest value a function takes in the neighborhood of a particular point. The Extreme Value Theorem states that continuous functions on closed intervals attain both absolute maximum and minimum values. Fermat's Theorem provides that local extrema occur where the derivative is 0 or undefined. To find absolute extrema, one evaluates the function at critical points and endpoints.






![The closed interval method for finding
absolute maximum or minimum
To find the absolute maximum and minimum values
of a continuous function f on a closed interval
[a,b]:
1. Find the values of f at the critical numbers of f in
(a,b) .
2. Find the values of f at the endpoints of the
interval.
3. The largest of the values from Steps 1 and 2 is
the absolute maximum value; the smallest of
these values is the absolute minimum value.
Examples on the board.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2301maxmin-220908044059-70496b3d/85/2301MaxMin-ppt-11-320.jpg)