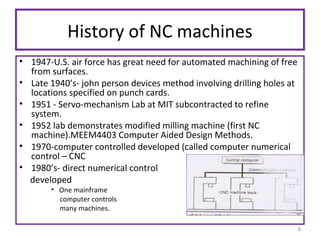
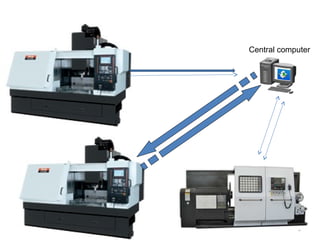
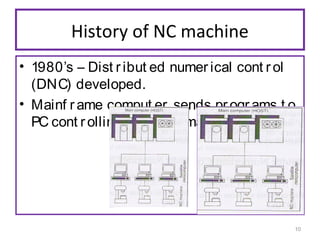
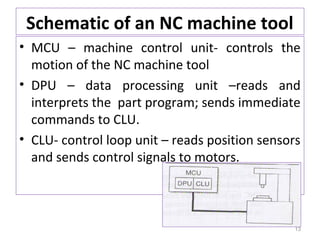
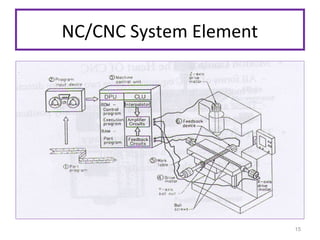
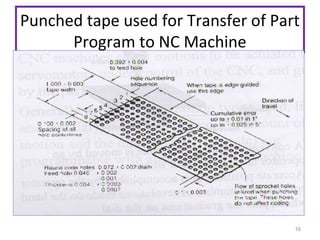
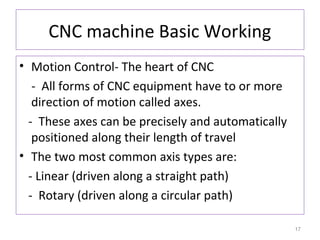
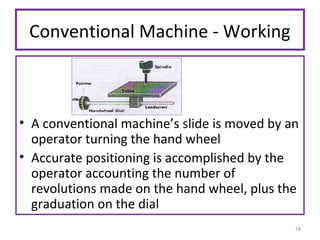
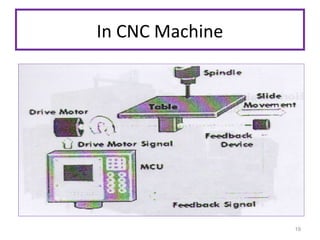
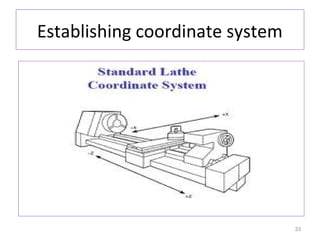
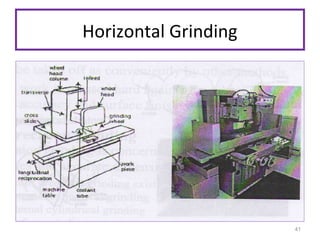
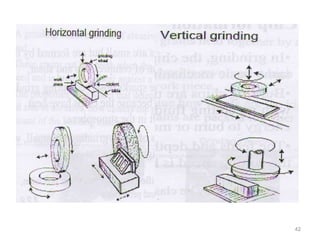
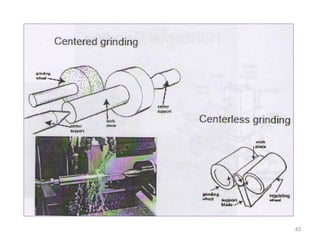
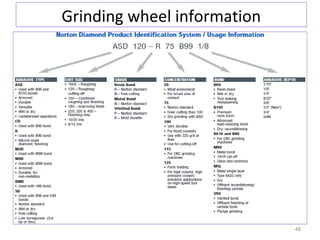
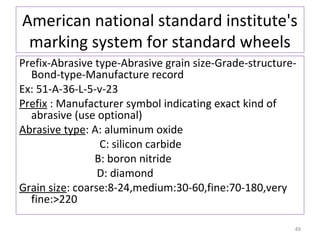
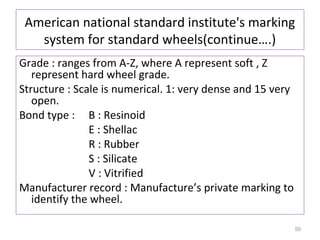
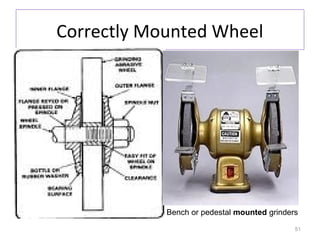
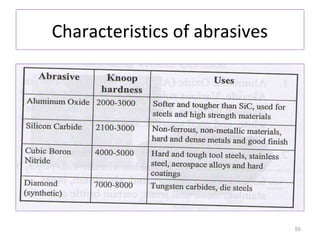
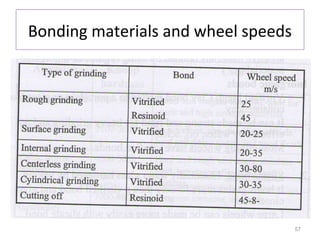
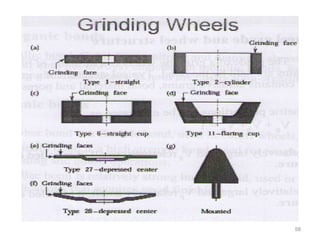
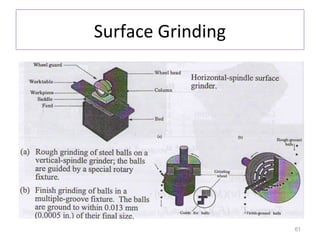
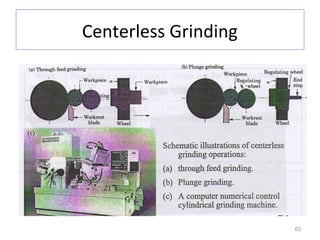
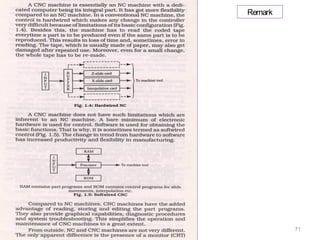
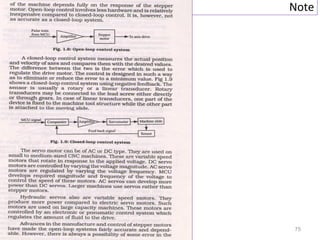
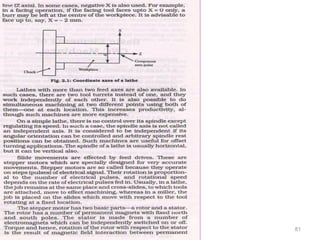
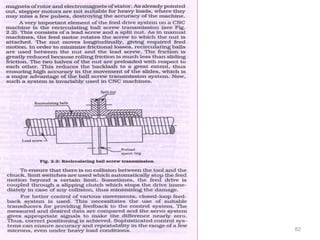
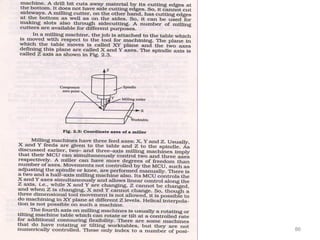
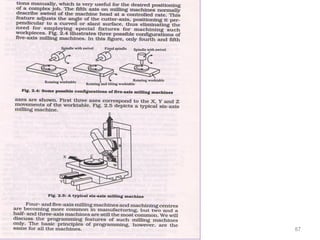
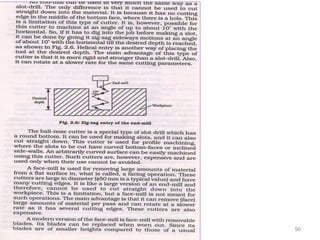
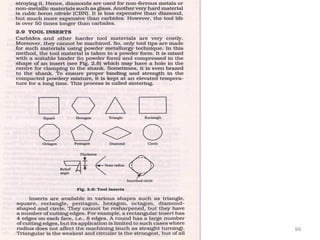
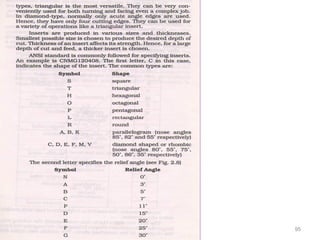
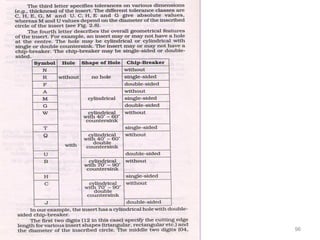
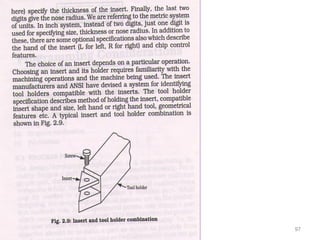
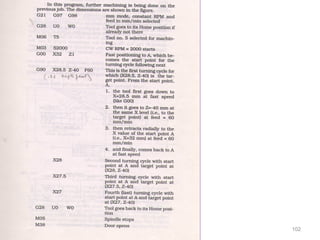
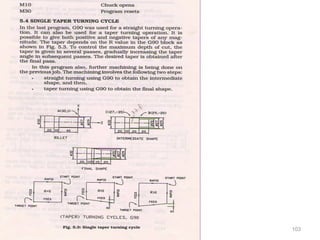
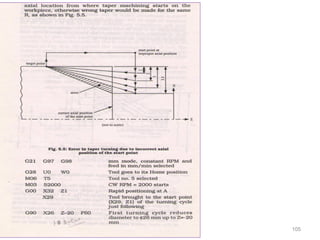
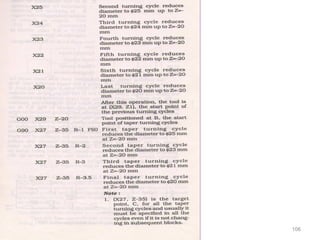
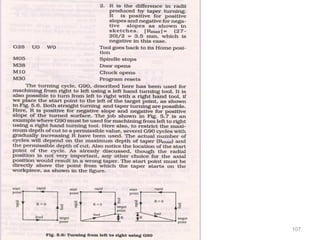
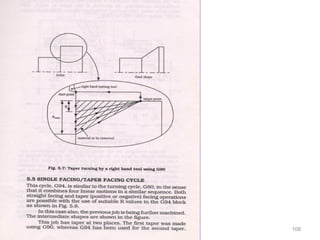
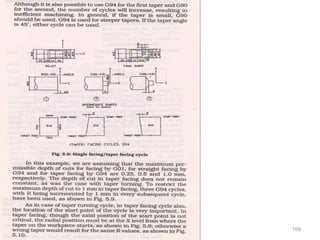
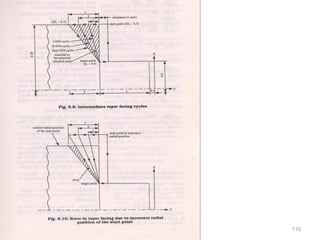
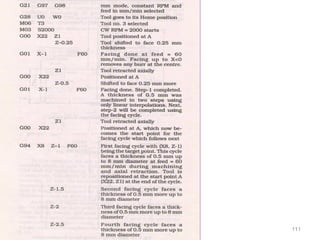
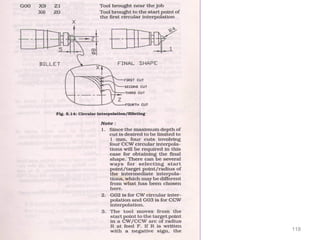
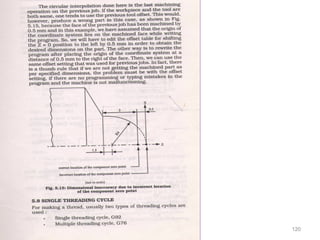
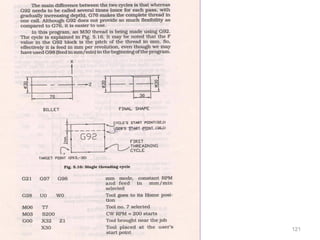
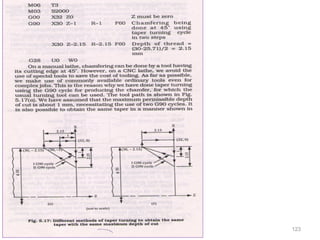
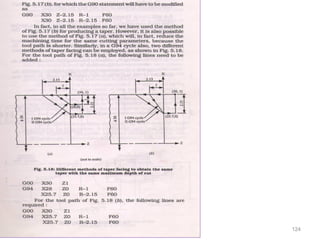
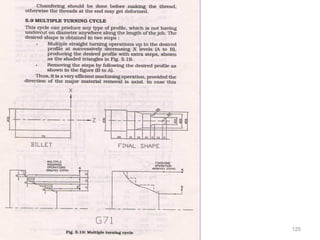
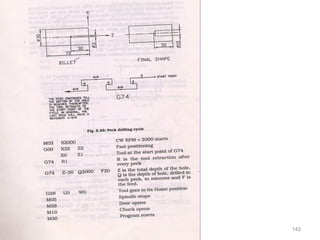
The document provides an overview of fundamentals of CNC technology. It discusses the history of NC and CNC machines, components of a CNC machine like its control system and drive motors, how CNC machines work by precisely controlling axes movements, applications in various industries, and advantages like flexibility and precision over conventional machine tools. The document also covers establishing coordinate systems, different CNC machine types including lathes, milling machines and machining centers, and grinding processes.