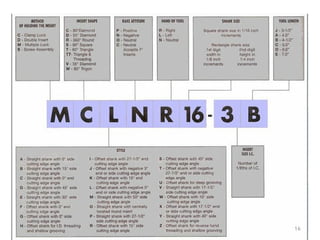
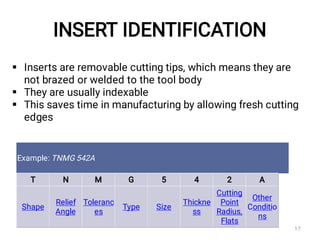
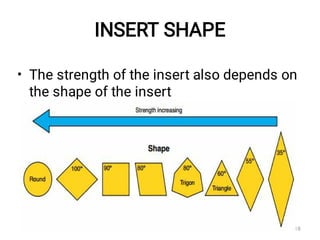
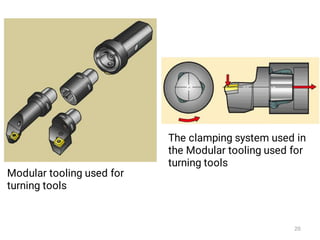
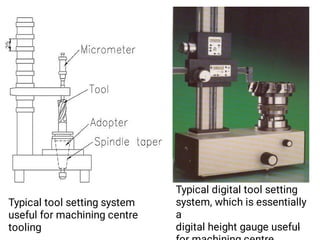
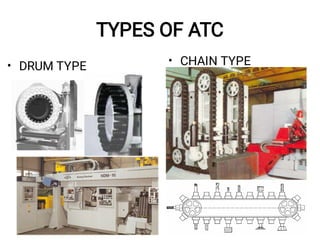
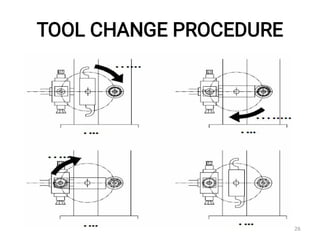
The document discusses CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining, introducing its components, operation, and tool types used in processes like milling, drilling, and turning. It highlights the advantages of CNC over traditional methods, including reduced operator involvement and improved precision. Additionally, it covers aspects such as tool materials, modular tooling systems, tool presetting, and trends in CNC cutting tools development.