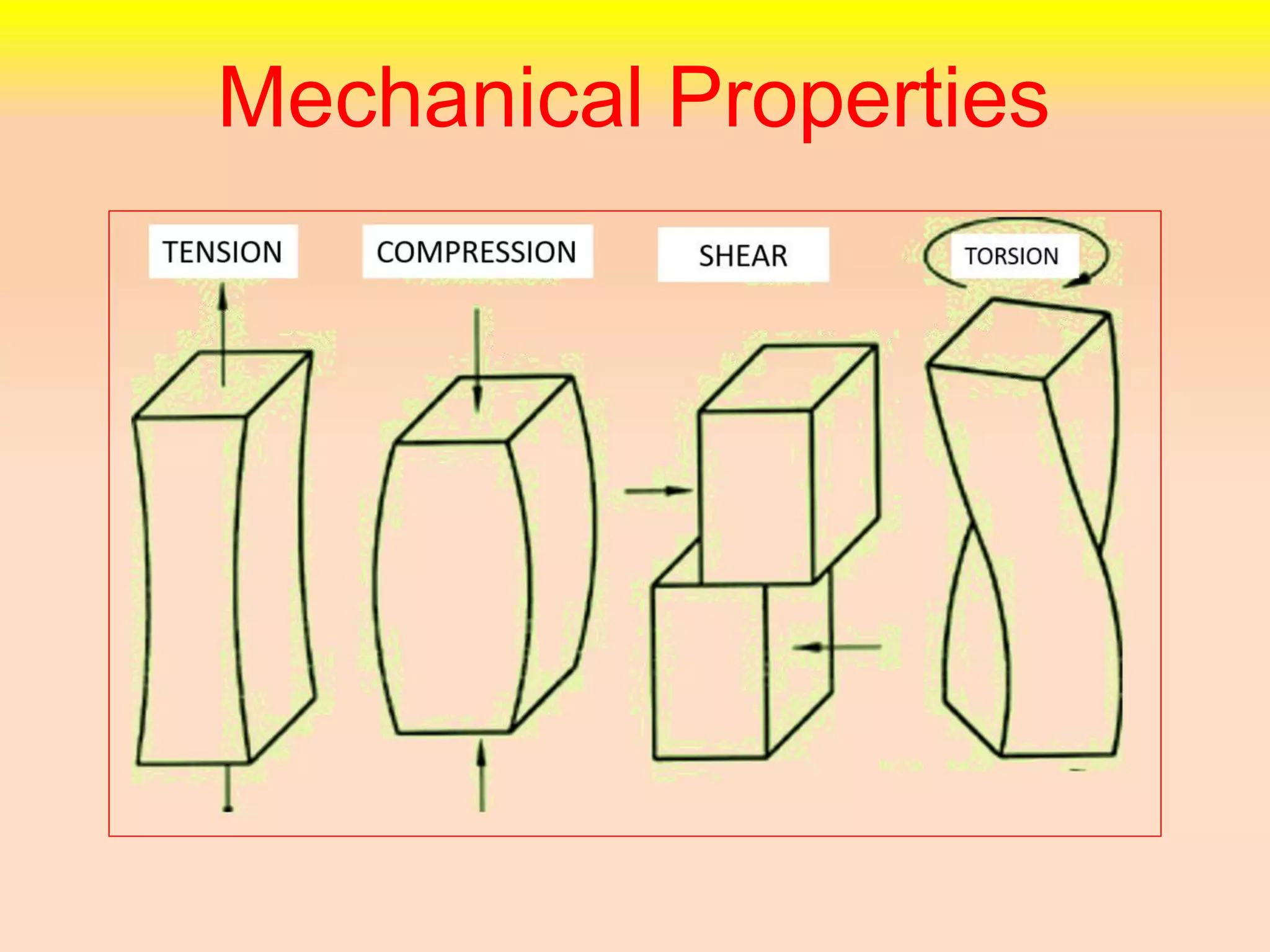
This document discusses various mechanical properties of materials:
1. Elasticity and plasticity refer to a material's ability to regain or not regain its original shape after a load is removed.
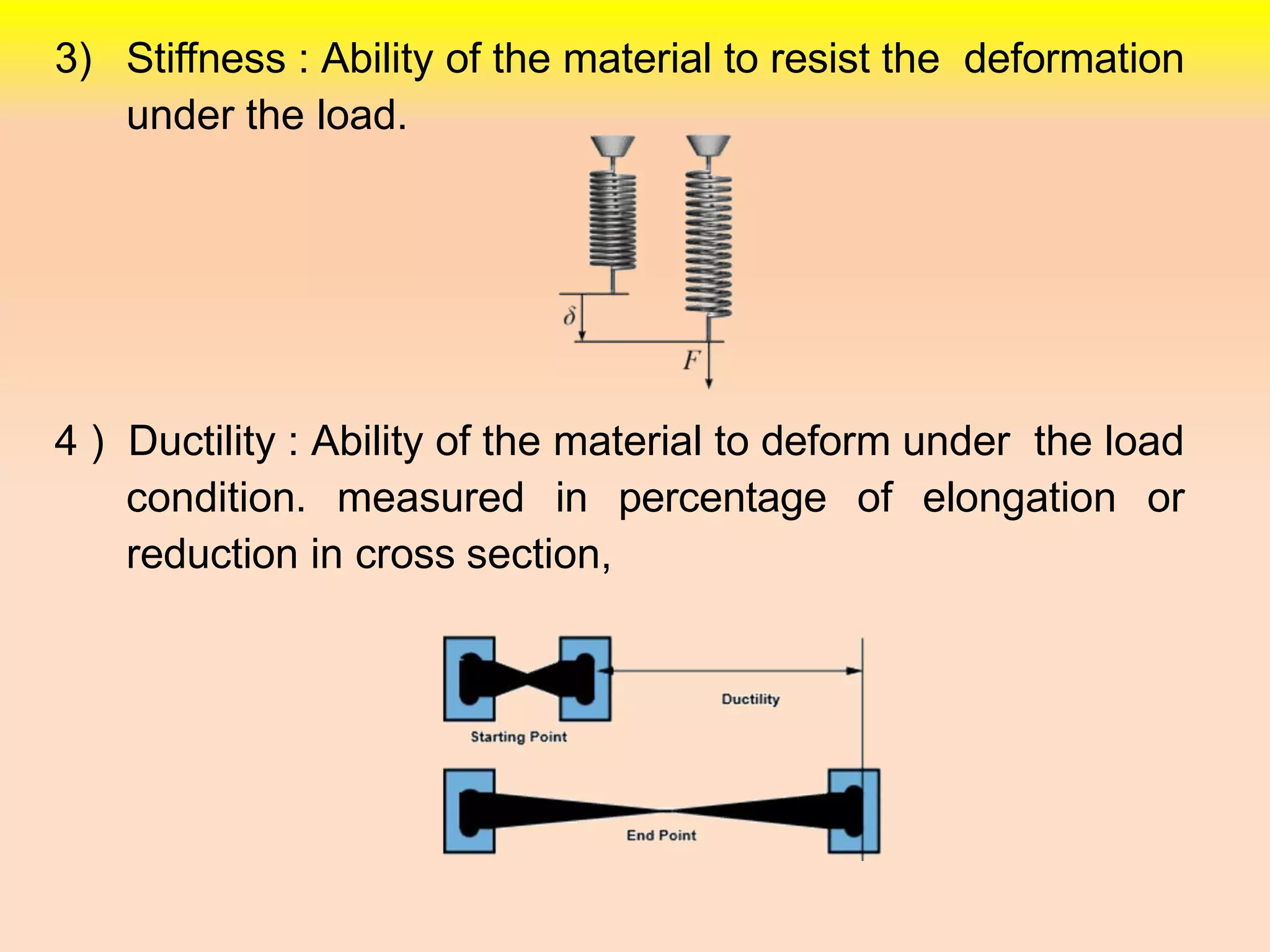
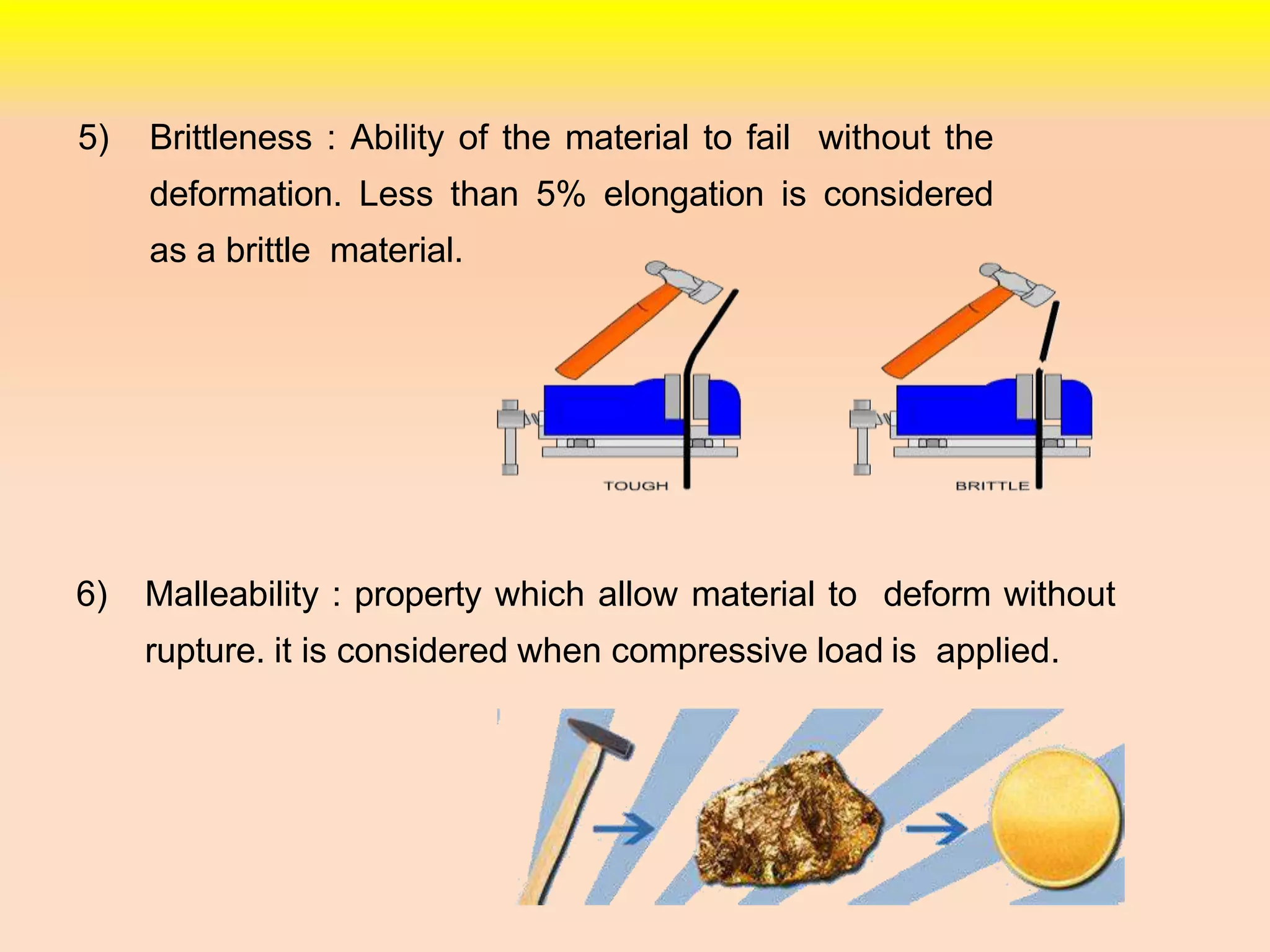
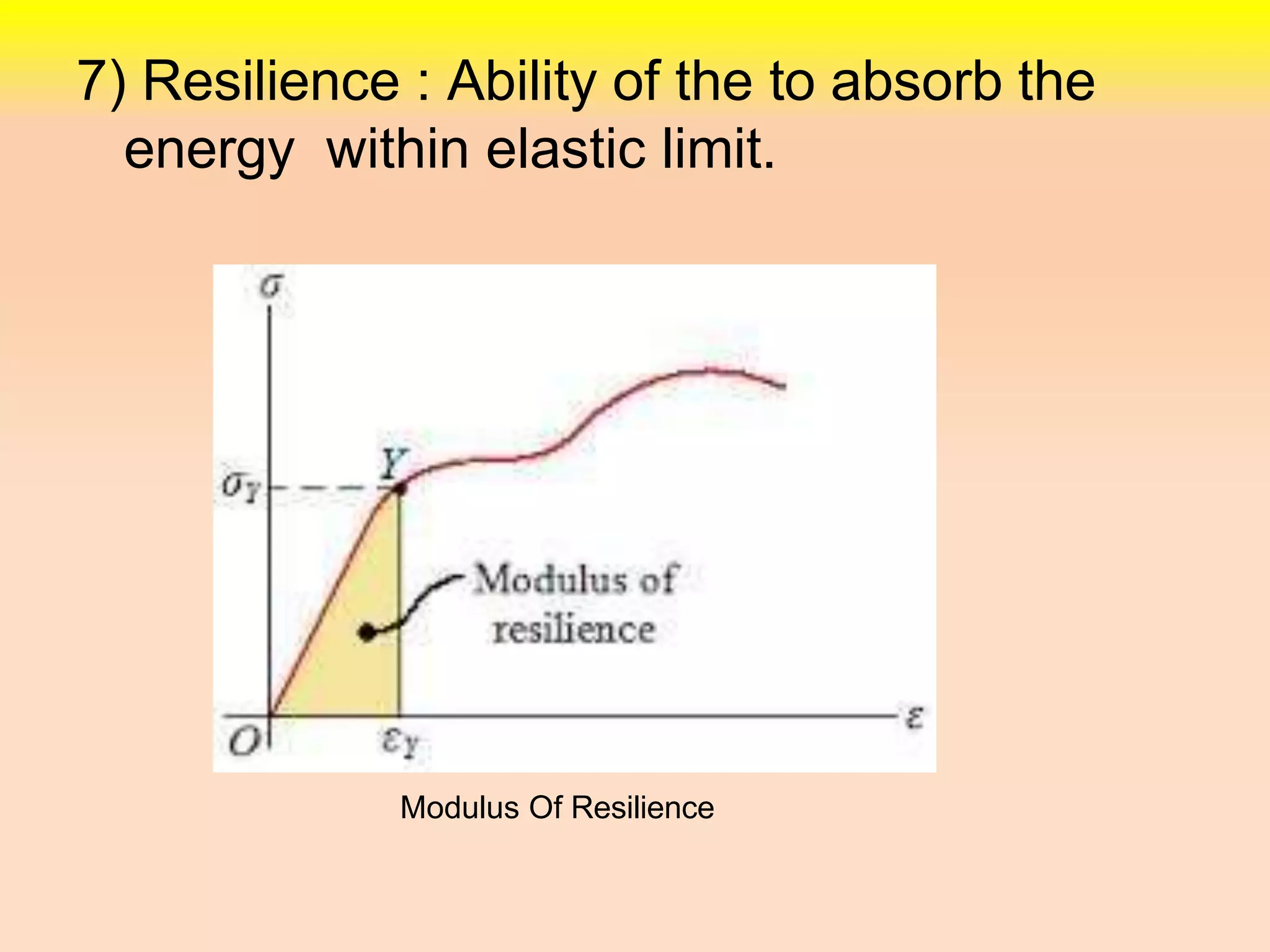
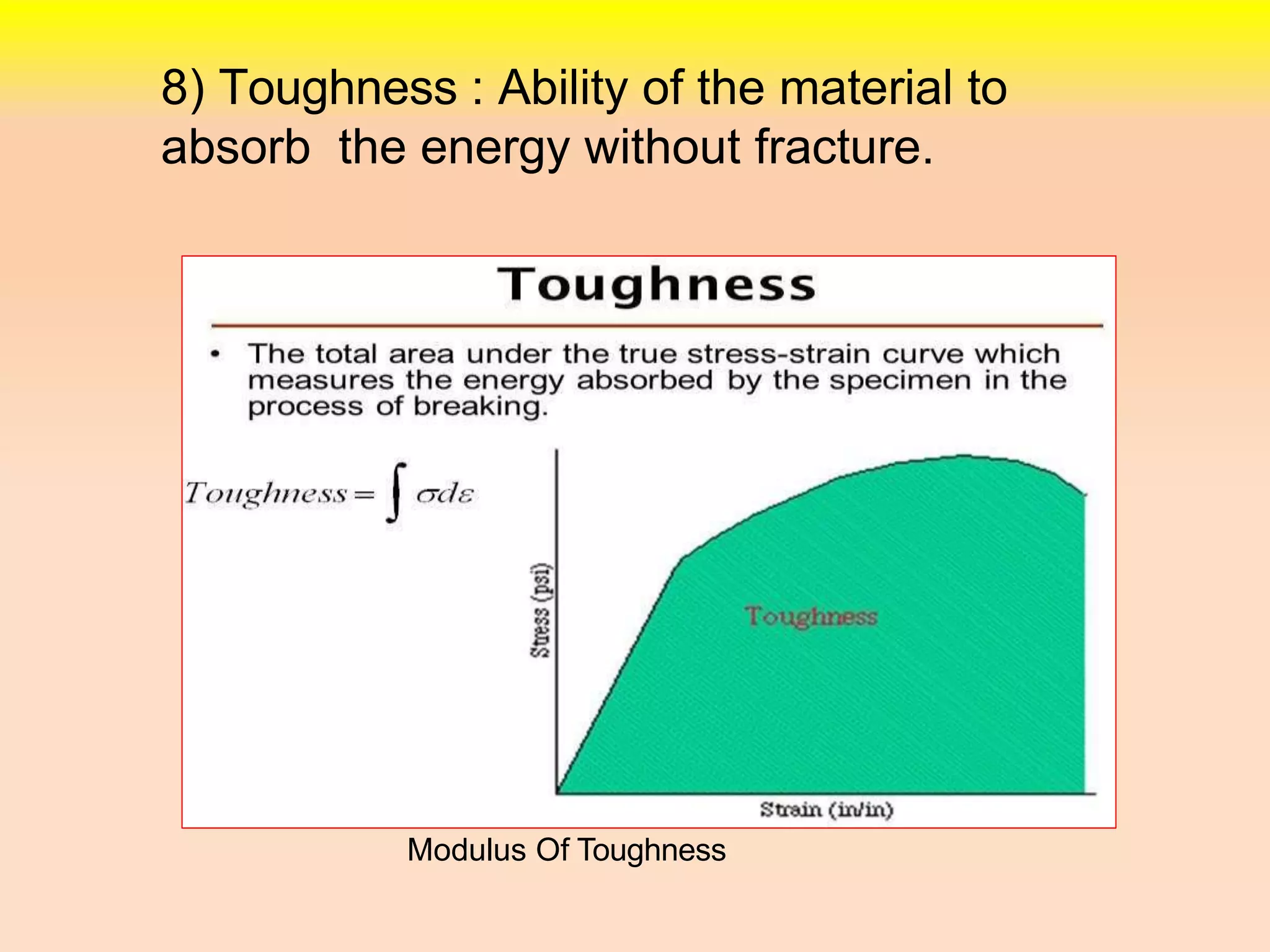
2. Other properties discussed include stiffness, ductility, brittleness, malleability, resilience, and toughness.
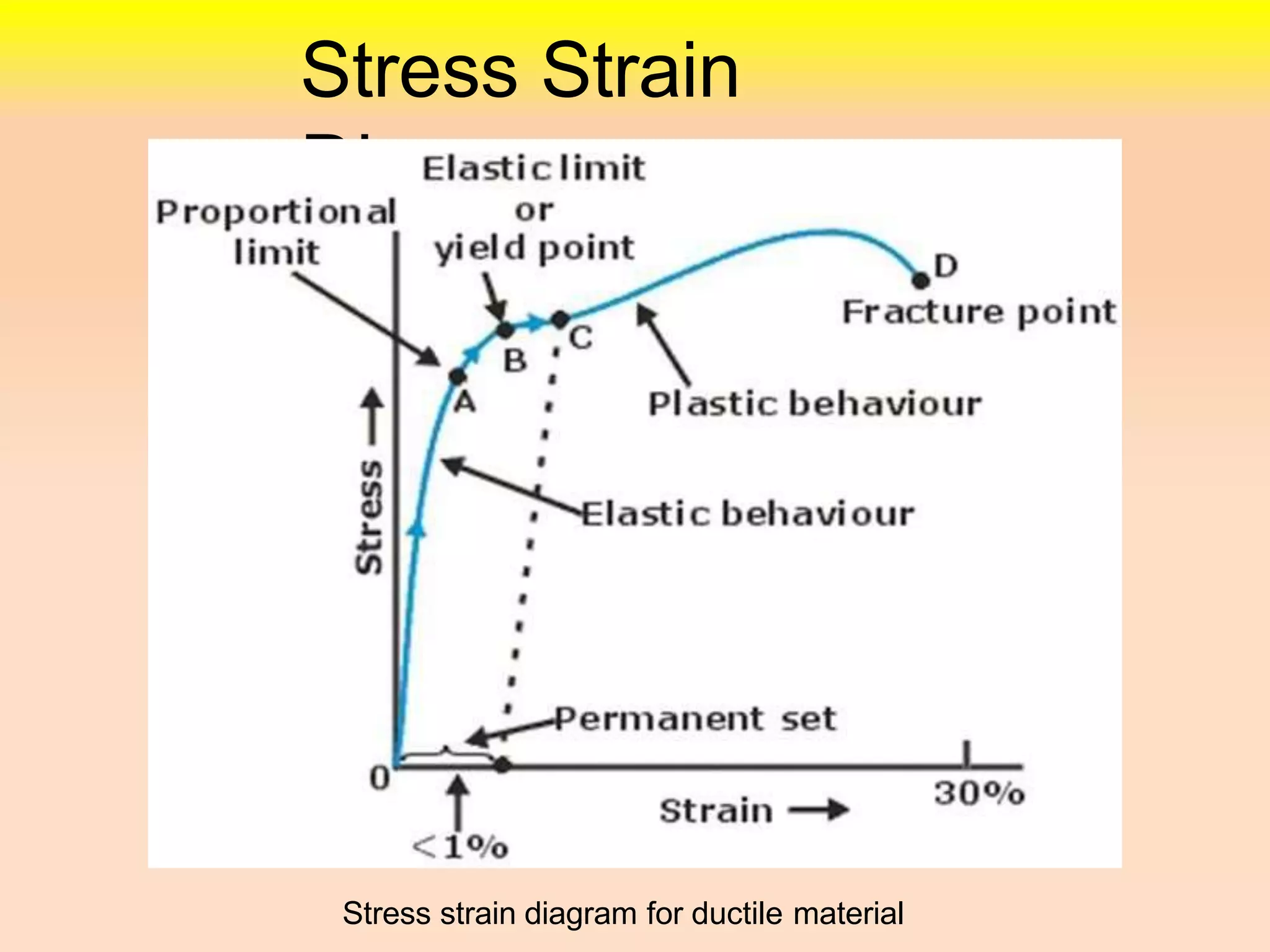
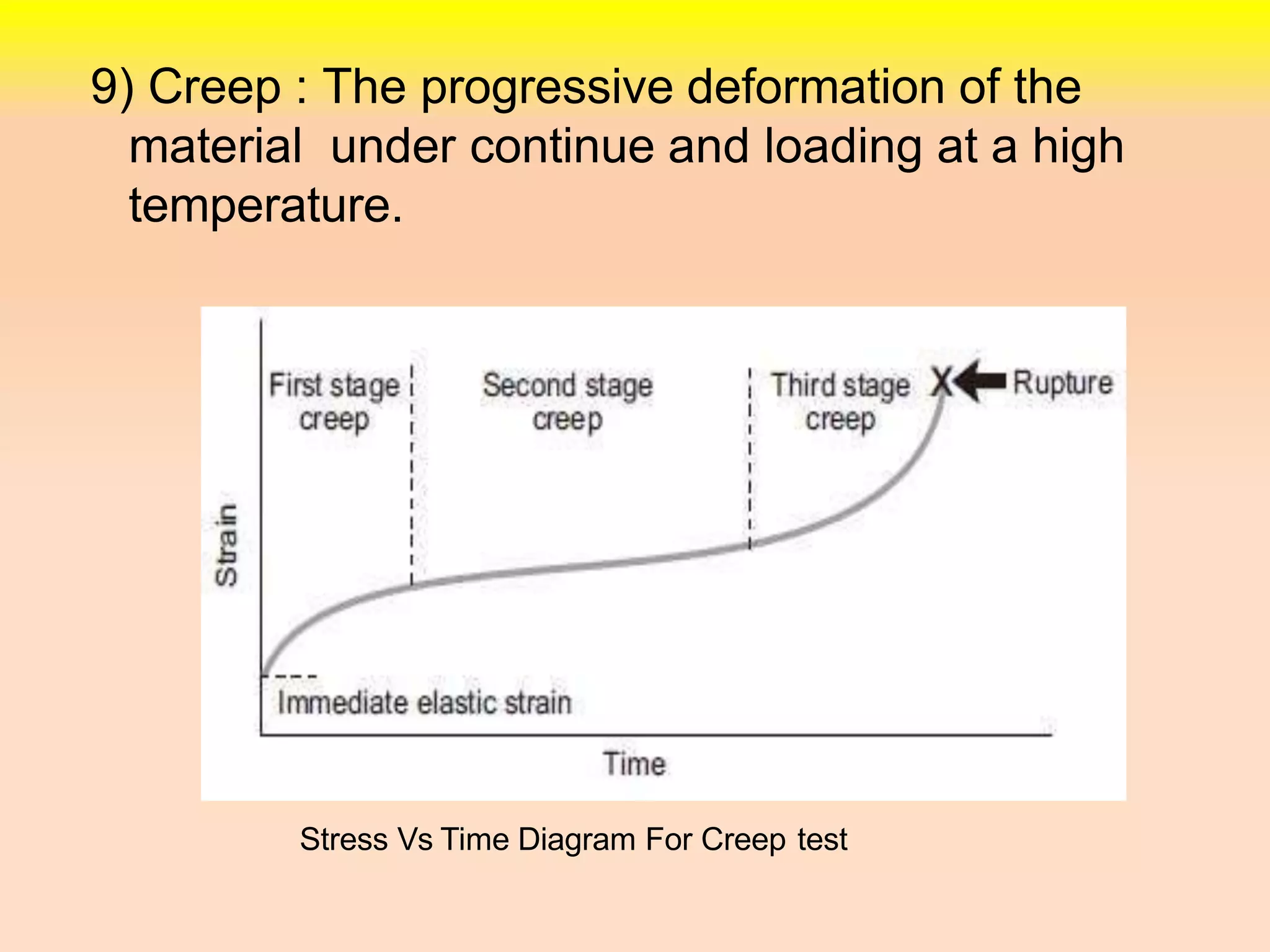
3. The stress-strain diagram is explained showing proportional limit, elastic limit, yield limit, ultimate point, and fracture point for ductile materials. Creep is also defined as deformation under continued loading at high temperatures.