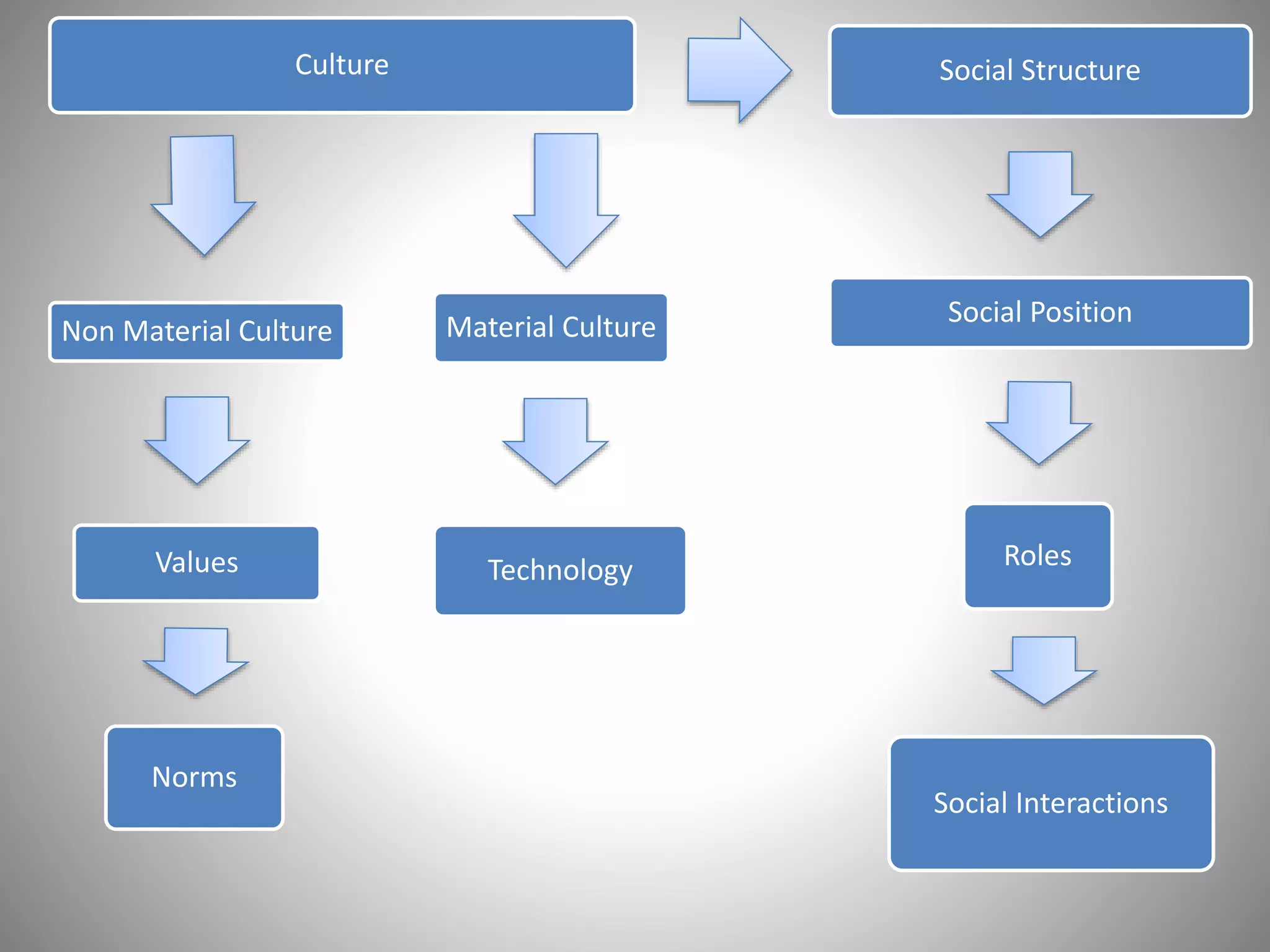
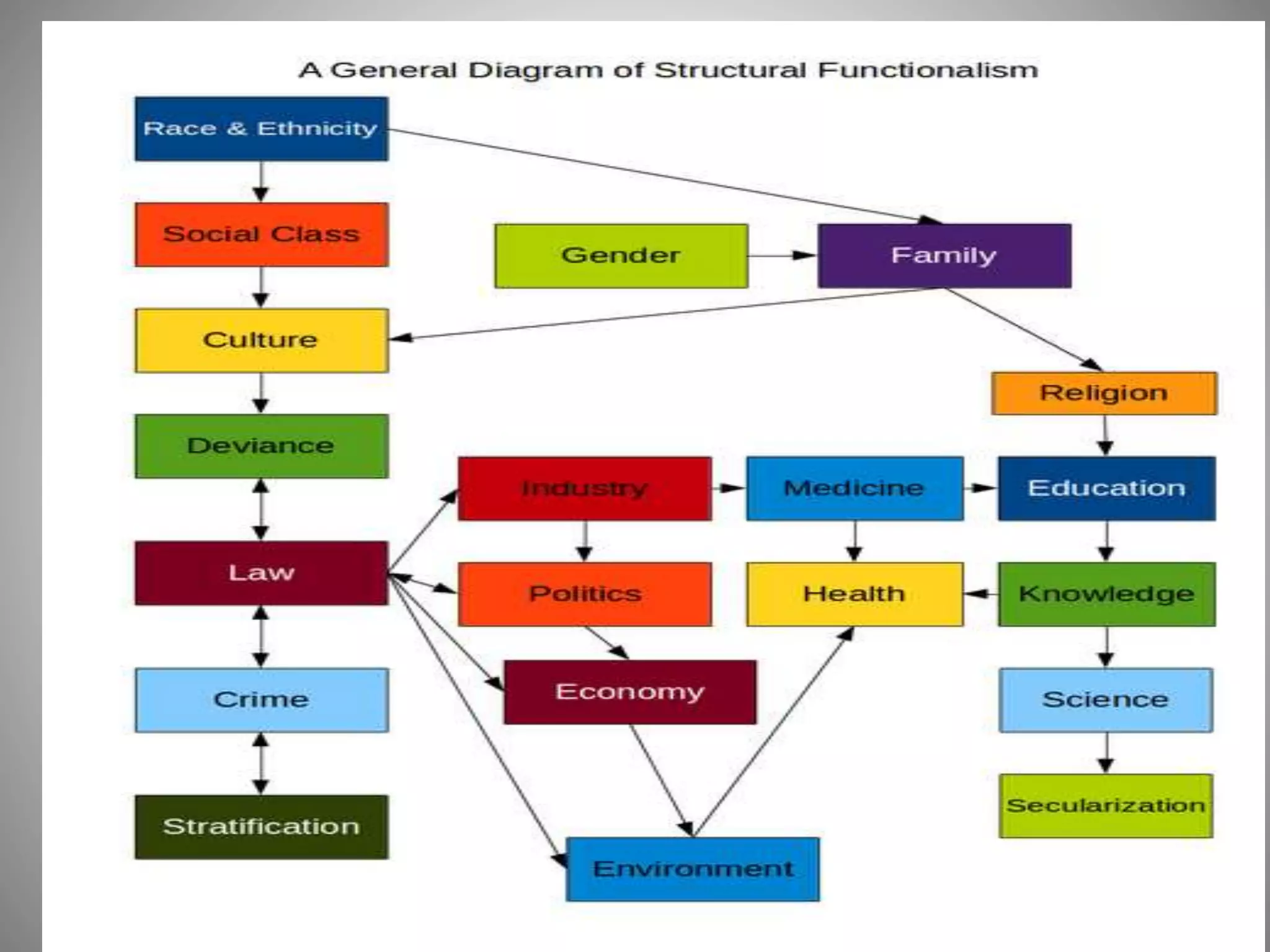
This document discusses the structural-functional approach in sociology. It explains that society can be viewed as a complex system with different parts that work together to promote stability. Social structures like families and communities give shape to people's lives. The structure of a society refers to the interrelationships between individuals and their roles. Functionalism sees society as a system where all parts contribute to maintaining society as a whole through social consensus and order. However, limitations include social patterns changing over time and place, and structures sometimes creating barriers between groups.