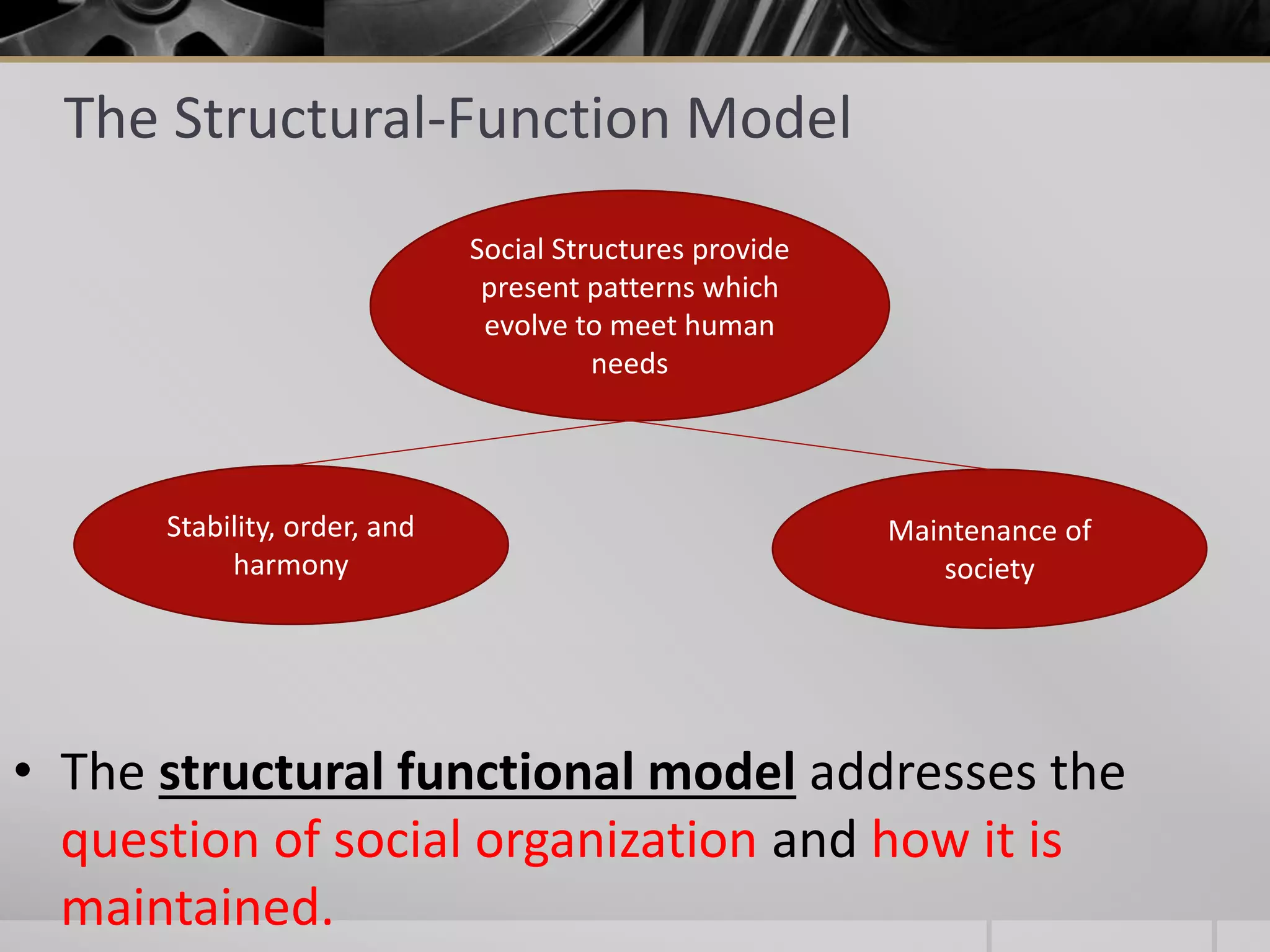
The functionalist perspective focuses on understanding why societies take specific forms, emphasizing interdependence among societal parts, the roles of social structure and culture, and the importance of consensus and cooperation. Emile Durkheim, a founding figure in sociology, developed this perspective, which highlights the maintenance of social order and stability through structures that fulfill essential functions. Modern functionalist theories also stress the significance of education in promoting equality of opportunity in democratic societies.