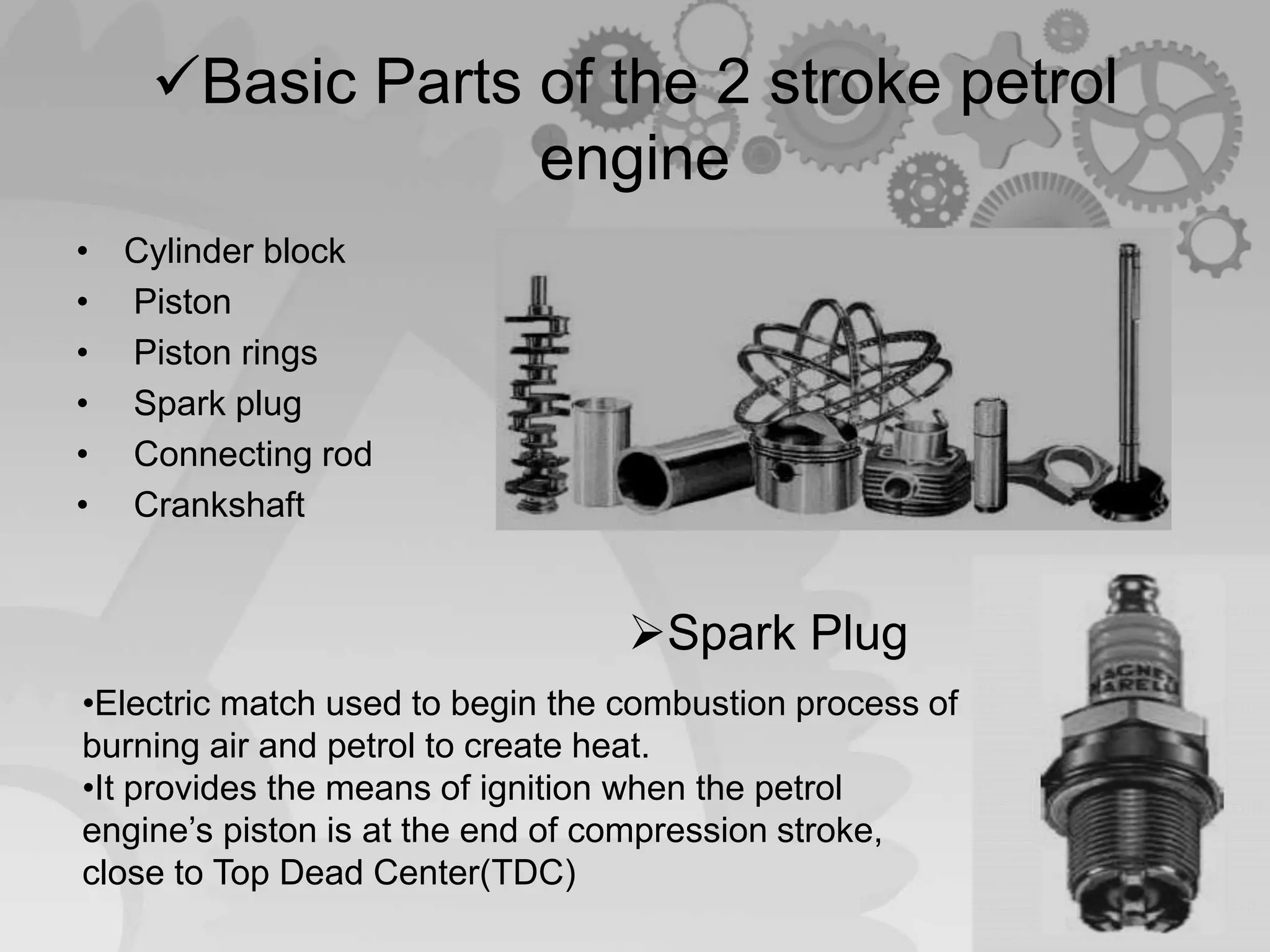
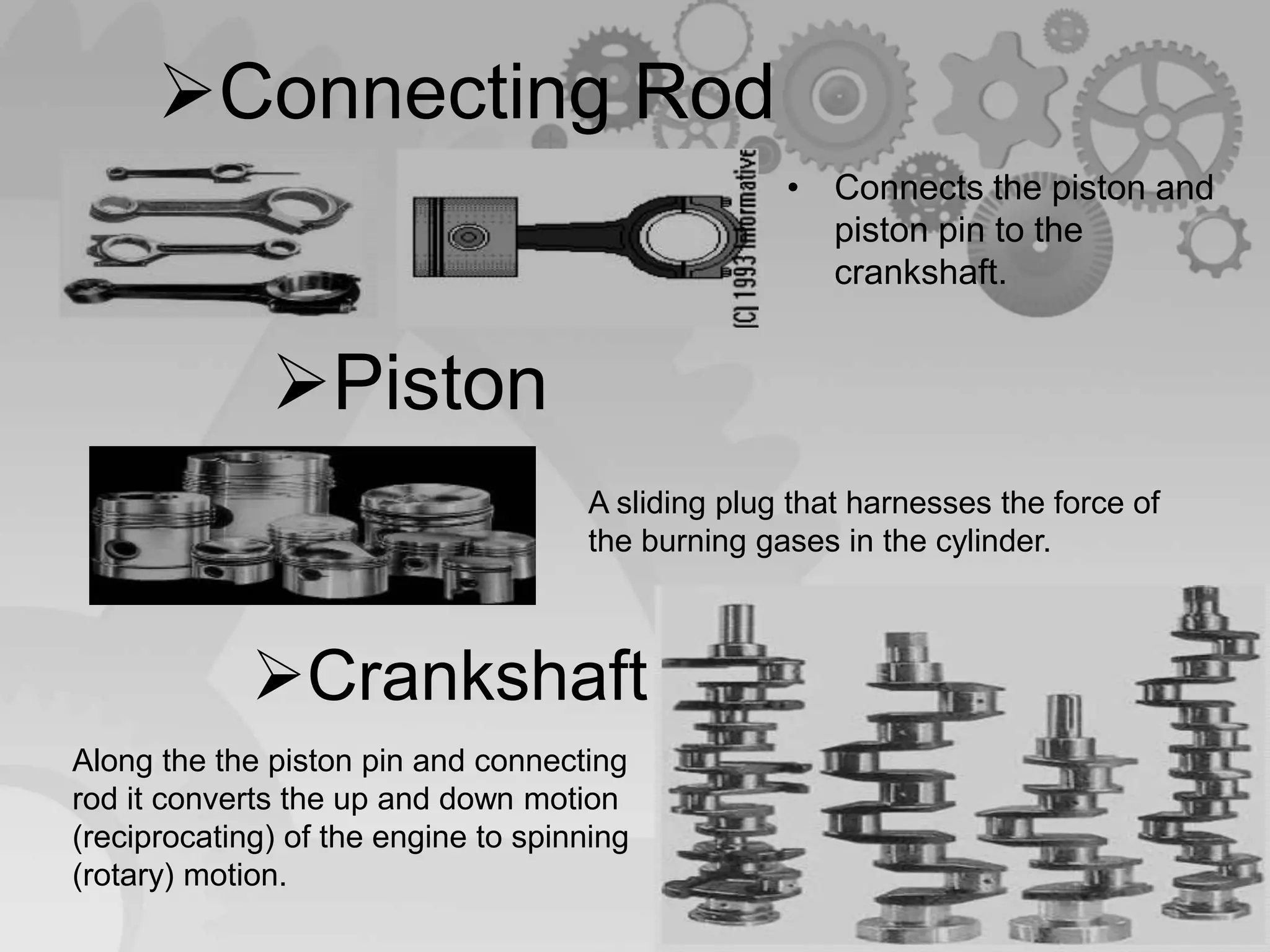
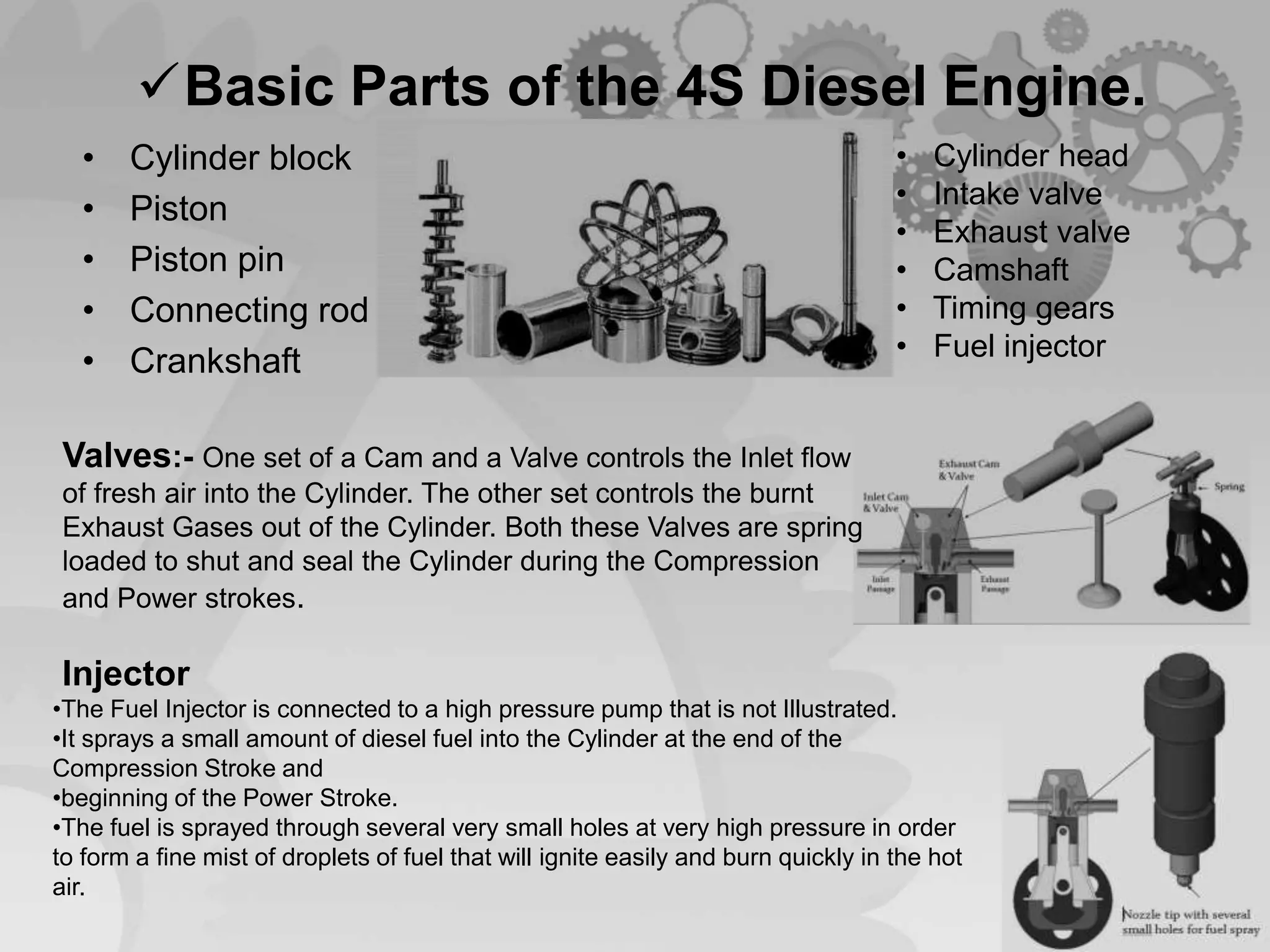
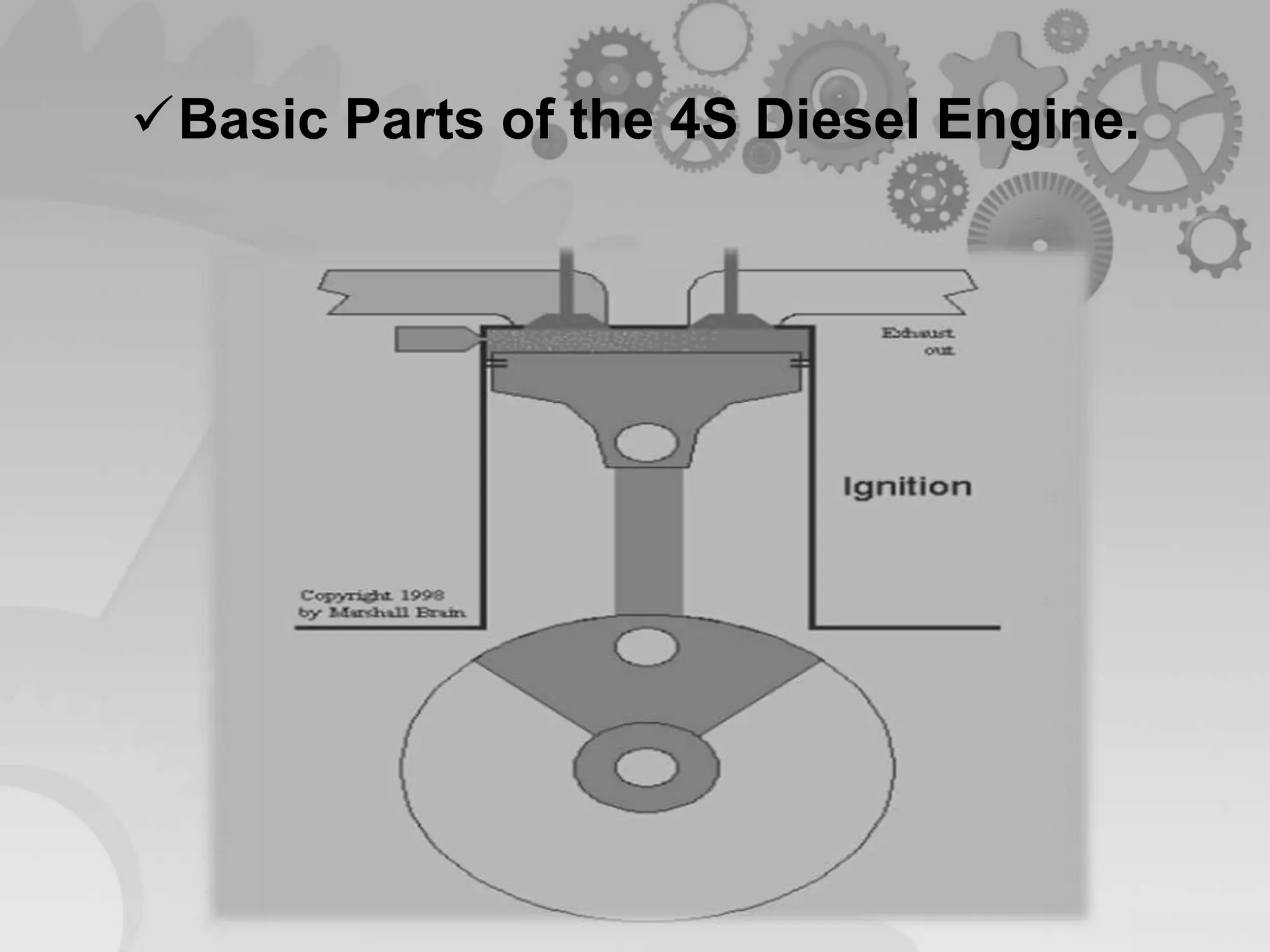
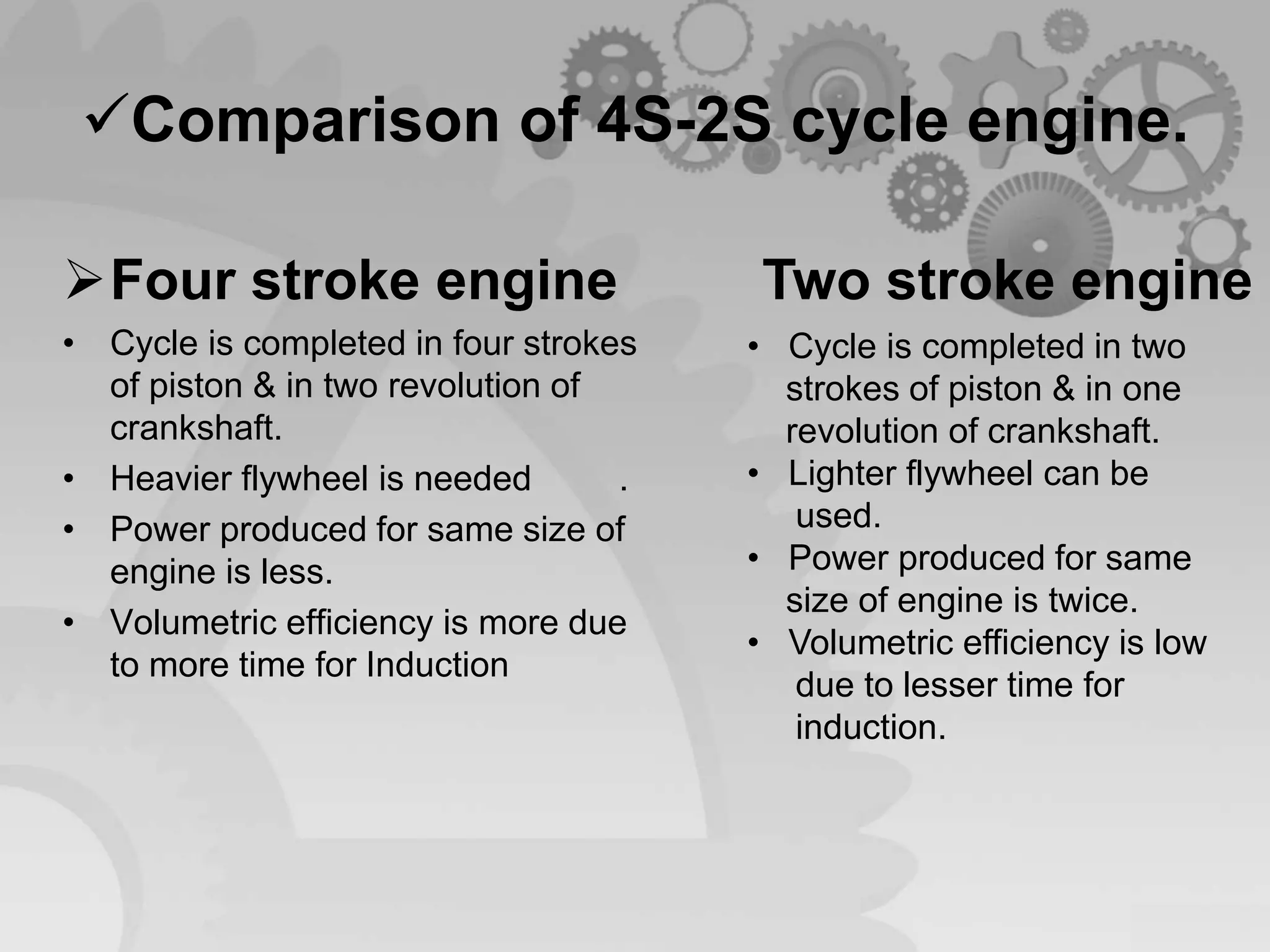
The document presents a comparison between two-stroke and four-stroke engines, discussing their definitions, working principles, and key components. It highlights the advantages and disadvantages of each engine type, emphasizing efficiency, power output, and design complexity. Additionally, it provides details on specific parts and their functions in both engine types.