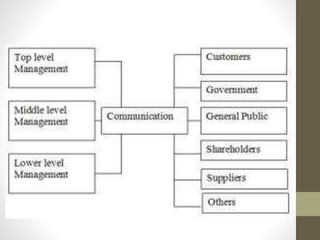
The document outlines the managerial function of directing, emphasizing its importance in guiding employees, maintaining discipline, and achieving organizational goals through supervision, communication, motivation, and leadership. It discusses the critical role of communication in organizations, detailing the various channels and types, including formal and informal communication, as well as upward, downward, horizontal, and diagonal flows of communication. It highlights the significance of supervision and motivation in leadership, noting that effective leaders can inspire and influence their teams to enhance performance and productivity.